![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the life cycle of a nematode?
|
It has three stages: egg, four-larval, adult.
|
|
|
What are nematodes?
|
Small worm-like organisms with a tough skin (cuticle). Also called roundworms.
|
|
|
Where can nematodes be found?
|
In almost any tissue of the body - skin, kidneys, lungs,urinary bladder, nervous system, blood.
|
|
|
What are cestodes?
|
Flat, ribbon-like worms with no digestive tract. They have heads (scolex) and bodies made of segments (proglottids)
|
|
|
What is the life cycle of a cestode and how many hosts does it have?
|
There are two hosts in the life cycle: the intermediate host where the larval tapeworm lives; the definitive host, where the adult lives.
|
|
|
Where do find tapeworms in the host?
|
In the host's intestines.
|
|
|
What are trematodes?
|
Flat, leaf-shaped worms with a mouth and intestine but no anus. Also called flukes.
|
|
|
What is the life cycle of the trematode?
|
Egg, several larval stages (some are endoparasites of snails and crayfish) and adult.
|
|
|
What are protozoans?
|
Single-celled animals.
|
|
|
What is the life cycle of a protozoan?
|
Each type has a different life cycle. They have no adult or egg stages. The ameboid, or asexula stage is sometimes called a trophozoite and the infectious stage a cyst.
|
|
|
What solution might you use in indentifying to identify protozoans when doing a fecal float?
|
Zinc sulfate.
|
|
|
What do you use to aid in the visualization of protozoans?
|
Lugol's iodine.
|
|
|
What are the important roundworms in cattle, sheep, and goats?
|
Ostertagia, Haemonchus, Trichostrongylus.
|
|
|
Where do Ostertagia, Haemonchus, and Trichostrongylus live in the host?
|
In the abomasum.
|
|
|
What are arrested larvae?
|
To survive harsh conditions, fourth-stage larvae arrest in late springs and resume development in the autumn. This ensures that adults do not lay eggs when free-living larvae could not survive.
|
|
|
How is Ostertagia treated?
|
Prophylactic dose of anthelmintics, timed to prevent heavy buildup of larvae in the pasture (late spring-midsummer kills adult worms before they lay eggs). Rotate pasture.
|
|
|
Describe infection in cattle, sheep, goats by intestinal strongyles.
|
Adult worms lay eggs in gut. L1 and L2 are free-living. Host eats L3. Adults live in small intestine. Do not cause much problem.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose and treat for strongyles?
|
Find eggs in feces. Use anthelmintics. Rotate pastures.
|
|
|
Describe infection by lungworms.
|
Lungworms lay eggs that hatch in host's lungs. L1 is coughed up and then swallowed, passing out in the feces. L2 lives on the ground; host ingest L3. Slugs/snails can be intermediate hosts to L1/L2.
|
|
|
What is diagnosis and treatment for lungworm?
|
Find eggs in feces. Use anthelmintics. Rotate pastures.
|
|
|
What tapeworms affect ruminants?
|
Moniezia, Taenia, Echinococcus.
|
|
|
Describe infection with Moniezia or ruminant tapeworm?
|
Adult lives in small intestine of host. Ruminant is definitive host. Mites are the intermediate host, eat eggs and then are consumed by ruminant.
|
|
|
What is the definitive host for taenia and echinococcus?
|
The dog.
|
|
|
Where do taenid larvae live in ruminants?
|
in the muscle.
|
|
|
Where do hydatid (echinococcus) larvae live in ruminants?
|
In the liver or lungs.
|
|
|
How do you treat taenia and echinococcus?
|
Treat dogs with prophylactic anthelmintics. Prevent consumption of raw meat. Restrict dogs from pastures.
|
|
|
What species are infected by liver flukes?
|
Ruminants, horses, and humans.
|
|
|
What is the life cycle of a liver fluke?
|
The eggs hatch in water, L1 infects a snail. Larvae leave snail and climb out of water on green plant and becomes a cyst. Plant is consumed by host. Cysts hatch in small intestine and burrow through to the liver.
|
|
|
How are liver flukes treated?
|
Eggs are found in the feces. Administer anthelmintics. Fence off ponds and wet areas.
|
|
|
Do deer liver flukes cause problems for cattle and sheep?
|
Cattle have little problems but sheep can die from one liver fluke.
|
|
|
How do you treat and prevent liver flukes?
|
Some anthelmintics kill the adult fluke in deer and cattle. Restrict access to wet areas and keep deer out of pastures.
|
|
|
What is coccidia and what is its scientific name?
|
Protozoans called Eimeria.
|
|
|
Is coccidia species specific?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
Where does coccidia live in its host?
|
Intestine.
|
|
|
How is coccidia transmitted?
|
Oocysts pass out with the feces. It is eaten by a new host and invades the intestinal wall.
|
|
|
How do you prevent coccidiosis?
|
Treat with appropriate drugs; prophylactic doses are given to ruminants being stressed (feedlots, shipping).
|
|
|
How do you diagnose coccidia?
|
Via a fecal test. However, symptoms may occur before cysts are shed, do diagnosis is often done on the age of the host and the diarrhea.
|
|
|
Does cryptosporidium infect humans as well as ruminants and horses?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
Is there effective treatment for cryptosporidium?
|
No good treatment exists. Rehydration and correction of acidosis is helpful.
|
|
|
What is tritrichomonas foetus?
|
A protozoan that lives in a cow's vagina and bull's penis. Leads to abortion and infertility.
|
|
|
How do you treat tritrichomonas foetus?
|
Drugs may not always be effective. Vaccinate animals before breeding. Artificial insemination avoid transmission of this disease.
|
|
|
What are the major parasites of swine?
|
Nematodes.
|
|
|
What are the most common parasites of pet pigs?
|
Ascarid or roundworm; whipworm, and nodular worm
|
|
|
How do you treat ascaris?
|
Administer anthelmintics.
|
|
|
What important disease does trichinella cause and describe its life cycle.
|
Trichinella causes trichinosis. Adults live in the small intestine. Female worms give birth to L1, which penetrate skeletal muscle, living there for years. Larva enter a new host when host consumes infected meat.
|
|
|
How is trichinella spread through pig herds?
|
Pigs are infected when they eat L1. L1 may come from infected garbage and other pigs. Pigs in overcrowded conditions may eat pigs that have died or bite and eat other pigs' tails.
|
|
|
How do you control trichinella?
|
Disease difficult to diagose although anthelmintics are effective. Control rats and cook garbage before pigs eat it.
|
|
|
What is nodular worm in pigs and what is its life cycle?
|
Oesophagostomum. Nematode living in large intestine. Pig eats food off ground. Larva burrow into intestine, lay eggs in nodules, then develop into adults
|
|
|
How do you diagnose and treat nodular worm?
|
Look for eggs in feces and administer anthelmintics.
|
|
|
What is whipworm in pigs?
|
A nematode (Trichuris suis) that lives in the large intestine. It feeds on blood from the intestinal wall. Eggs pass out in the feces?
|
|
|
Are whipworm eggs easy to recognize?
|
Yes, they are brown and lemon-shaped.
|
|
|
Do you need to treat for whipworm, and, if so, how?
|
Yes, the eggs can survive on the ground for years. Regular treatment with anthelmintics may be required.
|
|
|
Is coccidia a problem for pigs?
|
It is a problem for newborns as it can cause severe diarrhea.
|
|
|
What is the life cycle of coccidia in pigs?
|
Similar to that in ruminants. Host eats infective oocyst, it hatches in the intestine and invades the cells of the intestinal wall.
|
|
|
What are the nematodes that infect horses?
|
Ascarid, Strongyles, pinworms, threadworms.
|
|
|
Parascaris infects horses. What is its common name?
|
Ascarid.
|
|
|
What danger does Parascaris present to horses?
|
It usually does not bother the adult horses -affects the foals.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose and treat Parascaris?
|
Fecal exam. Treat with anthelmintics.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Parascaris infection?
|
May cause coughing. Usually unthriftiness in foals.
|
|
|
What is strongylus and how does it affect horses?
|
Strongylus is a group of nematodes that causes unthriftiness. Some can cause blood clots to form in the mesenteric artery leading to colic, bloating, and even death.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose and treat strongyles?
|
Fecal exam. Give prophylactic drugs every 4-6 weeks. Dichlorvos and ivermectin.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of pinworms in horses?
|
The eggs stick and cause itching around the anus. The horse may rub its tail, breaking tail hair and damaging skin.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose pinworms in horses?
|
Observing horse's scratching behavior, find eggs around anus. Fecal exam.
|
|
|
How do you treat pinworms?
|
Use anthelmintics. Ivermectin and Dichlorvos also kill strongyles and ascarids, in addition to pinworms.
|
|
|
What problems do threadworms (Strongyloides) present to horses?
|
Mainly infects foals. Passes through mother's milk. Use ivermection or dichloros just before foaling. Remove feces from stall of infected foals to reduce free-living stages.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose and treat tapeworms in horses?
|
Fecal exam will reveal eggs or proglottids. Treat with anthelmintics.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of tapeworms in horses?
|
Unthriftiness, colic, and diarrhea.
|
|
|
Does Eimeria (coccidia) infect horses?
|
Yes, it mainly causes diarrhea in young horses.
|
|
|
How do you dignoses coccidia in horses?
|
Fecal exam - find oocytes in feces.
|
|
|
What steps must you take in doing a fecal exam for coccidia?
|
The oocyst does not float in ordinary salt solution - use sugar, zinc sulfate, or centrifuge technique or direct fecal smear.
|
|
|
Does giardia cause problems in horses?
|
No.
|
|
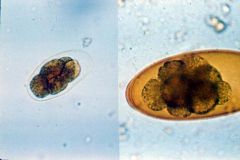
|
Strongyle egg on left. Nematodirus on right (sheep and cattle). Large egg - identified by size
|
|
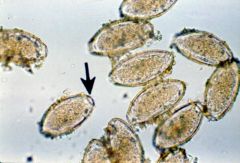
|
Horse ascarid on left; pig ascarid on right.
|
|
|
pinworm egg - horse
|
|
|
Strongloides egg (threadworm) cattle, sheep, pigs, horses
|
|
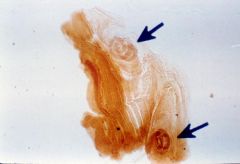
|
Trichinella larva in the diaphragm of a pig.
|
|
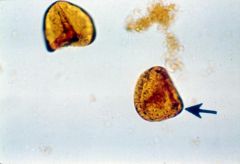
|
Tapeworm eggs -horses (anaplocephela), sheep, cattle (moniezia)
|
|
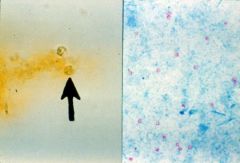
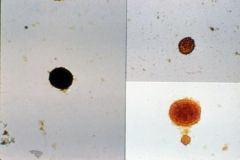
|
Cryptosporidium oocytes unstained and stained.
|
|
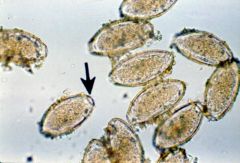
|
The pinworm (oxyuris) of horses lays its eggs on the skin around the anus. Eggs may be obtained for
examination from the perianal skin or the feces. |
|
|
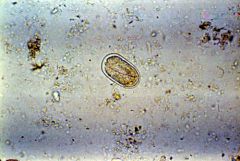
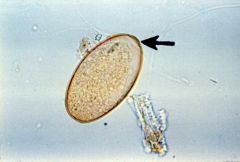
The trematode (flatworm) Fasciola hepaticalives in the liver and bile ducts of cattle and sheep.
Occasionally, it may be found in dogs. The egg is large (about 140 µm long) and spindle shaped, and has a lid at one end (arrow). The thin shell is smooth, and the contents of the egg fill most or all of the shell. (40×objective, unstained) |

