![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
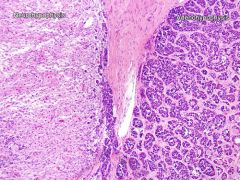
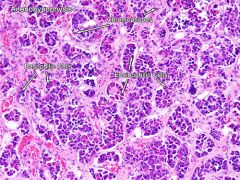
Normal pituitary features
|
- Clusters of different colored cells
- Eosinophilic/acidophilic cells = GH and prolactin - Basophilic cells = ACTH, MSH, TSH, FSH and LH - ADH and oxytocin = made in hypothalamus, released at neurohypophysis |
|
|
Normal pituitary
|
|
|
Normal adenohypophysis
|
|
|
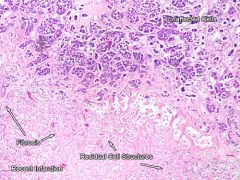
Pituitary infarct
|
|
|
Pituitary infarct
|
Most common in adenohypophysis due to low pressure venous blood supply.
- Coagulative necrosis |
|
|
Sheehan Syndrome
|
Pituitary enlarged during pregnancy already
- Lots of hormones being produced - Enlargement occludes adenohypophysis blood supply - Becomes ischemic... - Blood loss from delivery, shock -> infarction, necrosis |
|
|
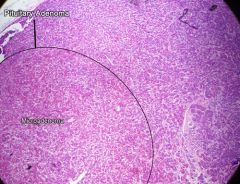
pituitary adenoma
|
|
|
Pituitary adenoma features
|
Predominant basophilic or eosinophilic regions
- Most common cause of pituitary hyperfunction - Monoclonal = only one cell type - Classified by hormone produced - could be silent... - Prolactinoma most common |
|
|
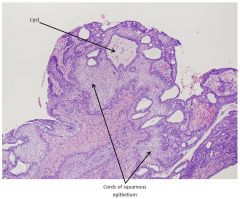
craniopharyngioma
|
|
|
Craniopharyngioma features
|
NOT pituitary tumor - from remnant of Rathke's pouch
- Adamantinomatous = hard - calcification and cysts - Papillary = softer, not much calc. or cysts Malignancy is rare - Growth retardation, vision issues, diabetes insipidus (from ADH losses) |
|
|
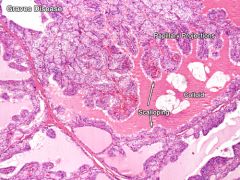
Grave's disease, thyroid
|
|
|
Grave's disease thyroid features
|
Auto-immune problem
- Antibodies activate the TSH receptor - hyper-thyroidism - Follicular cells become columnar from crowding - Scalloping of colloid follicles - Papillary projections into colloid |
|
|
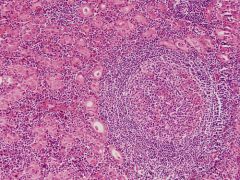
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
Hashimoto features
|
Auto-immune destruction of thyroid
- Mononuclear cell infiltrate - Very small/absent follicles - Hurthle cells - large, eosinophilic, surround follicles Child - cretinism - impaired skeletal growth, CNS dev - profound retardation, short, protruding tongue, hernia Adult - myxedema - Fatigue, mental slowness, cold intolerance, overweight |
|
|
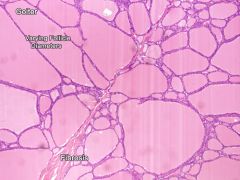
Goiter
|
|
|
Goiter features
|
Large, variable-size follicles
- NO scalloping! - Start as non-toxic (single nodule), progress to potentially toxic, multi-nodular |
|
|
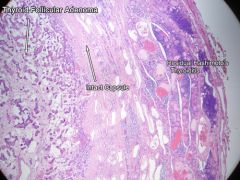
thyroid adenoma
|
|
|
Thyroid adenoma features
|
Solitary, spherical, encapsulated!
Some residual tissue remains outside - Interior is loosely cellular, some small follicles with colloid |
|
|
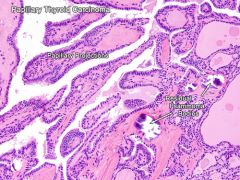
Papillary thyroid carcinoma
|
|
|
Papillary thyroid carcinoma features
|
Most common thyroid cancer - follicular epithelium
- Often mets to cervical lymph nodes, vascular invasion rare - Calcification, psamomma bodies - Little orphan Annie eye nuclei - Prognosis pretty good |
|
|
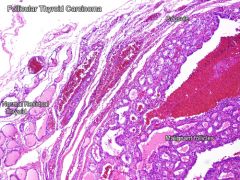
follicular thyroid carcinoma
|
|
|
Follicular thyroid carcinoma features
|
2nd most common thyroid cancer - follicular epithelium
- Often invades vasculature, only rarely LN mets - Compare to thyroid adenoma - Difference is penetration of capsule! - Very aggressive, high mortality |
|
|
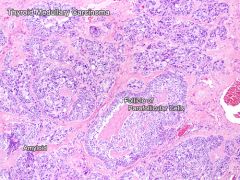
thyroid medullary carcinoma
|
|
|
Thyroid medullary carcinoma features
|
Neuroendocrine tumor - from parafollicular cells (C-cells)
- Secrete calcitonin - KEY for diagnosis - Nests of cancer cells surrounded by amyloid deposits - Salt n' pepper nuclei |
|
|
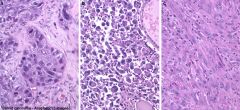
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
|
|
|
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma features
|
Undifferentiated follicular cell tumor
- Rare, but mortality ~100% - Mix of small cells, giant cells, very pleomorphic - Can have spindle cells too |
|
|
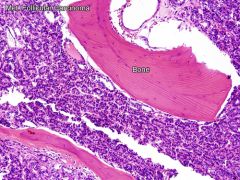
Thyroid follicular mets to bone
|
|
|
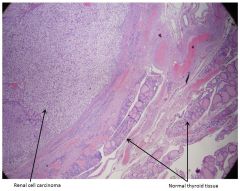
renal cell carcinoma mets to thyroid
|
|
|
Renal cell carcinoma mets to thyroid features
|
Solid sheet of round, polygonal cells with abundant clear cytoplasm
|
|
|
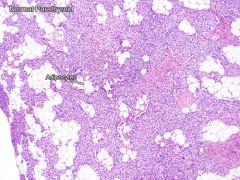
Normal parathyroid
|
|
|
Normal parathyroid features
|
Chief cells, oxyphil cells, abundant adipocytes
- Chief cells = release PTH, sensitive to blood Ca++ - Smaller and darker - Oxyphil cells - larger, paler, function unknown |
|
|
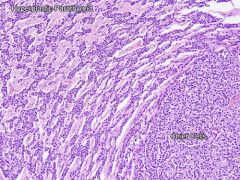
Hyperplastic parathyroid
|
|
|
Hyperplastic parathyroid features
|
- Very little/no fat left
- All four glands usually involved - Typically chief cell hyperplasia |
|
|
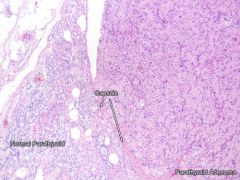
parathyroid adenoma
|
|
|
Parathyroid adenoma features
|
- Only ONE enlarged PT gland (not all four - hyperplasia)
- others often atrophic from feedback - Usually chief cell affected - Hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcemia |
|
|
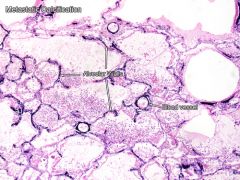
Hyperparathyroidism - metastatic calcification
|

