![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
203 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
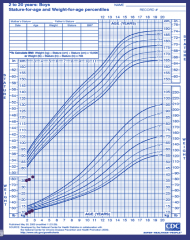
|
Growth hormone deficiency - severely restricted growth after postnatal period (after 6 mo of life) |
|
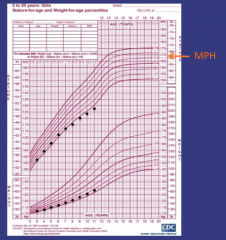
What's going on here? |
Turner's syndrome - lower height & weight percentiles, who falls off the growth curve in mid-childhood even as weight gain continues around pre-puberty |
|
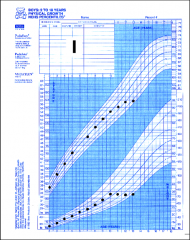
What's going on here? |
Systemic disorder (celiac Dx, anemia, IBS, etc.) affecting growth; note that weight is affected earlier and more dramatically than height |
|
|
What's going on here? |
"Late bloomer" - non-patholgoic variant in growth patterns |
|
|
Given that estrogen increases the synthesis of thyroid binding globulin, how will oral contraceptive pills affect: 1. Free T4 2. Bound T4 3. Total T4 4. TSH 5. TRH |
Increased in thyroid binding globulin --> increase in bound T4 --> decreased free T4 and production of more T4 to compensate --> increase in total T4.
1. Free T4: no apparent change 2. Bound T4: increased 3. Total T4: increased 4. TSH: No change 5. TRH: No change |
|
|
How will a mutation in the gene for thyroid binding globulin affect...
1. TRH 2. TSH 3. Free T4 4. Bound T4 5. Total T4 |
1. TRH: unchanged 2. TSH: unchanged 3. Free T4: negative feedback --> unchanged 4. Bound T4: Less 5. Total T4: Less |
|
|
How will congenital hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid gland development) affect...
1. TRH 2. TSH 3. Free T4 4. Bound T4 5. Total T4 |
1. TRH: unchanged 2. TSH: high 3. Free T4: low 4. Bound T4: low 5. Total T4: low |
|
|
Hi will grave's disease (autoimmune antibody binds to TSH receptors on thyroid gland) affect...
1. TRH 2. TSH 3. Free T4 4. Bound T4 5. Total T4 |
1. TRH: unchanged 2. TSH: low 3. Free T4: high 4. Bound T4: high 5. Total T4: high |
|
|
Hi will a TSH-secreting pituitary tumor affect...
1. TRH 2. TSH 3. Free T4 4. Bound T4 5. Total T4 |
1. TRH: no change 2. TSH: high 3. Free T4: high 4. Bound T4: high 5. Total T4: high |
|
|
Hi will thyroid-hormone resistance (mutation in receptor) affect...
1. TRH 2. TSH 3. Free T4 4. Bound T4 5. Total T4 |
1. TRH: no change 2. TSH: high 3. Free T4: high 4. Bound T4: high 5. Total T4: high |
|
|
How will central hypothyroidism (i.e. a brain tumor) affect...
1. TRH 2. TSH 3. Free T4 4. Bound T4 5. Total T4 |
1. TRH: no change 2. TSH: low 3. Free T4: low 4. Bound T4: low 5. Total T4: low |
|
|
If you have a low total T4, and low/normal TSH how do you figure out whether this is due to low thyroid binding globulin or central hypothyroidism? |
Measure free T4: it will be low in central hypothyroidism and normal in thyroid binidng globulin deficiency |
|
|
Ratio of catecholamines produced by the adrenal medulla |
80% Epinephrine |
|
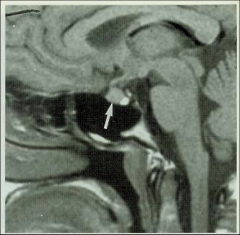
|
Bright spot in pituitary indicating functioning hypothalamus |
|
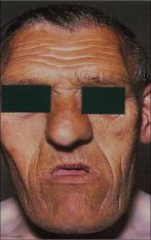
|
Coarse facies typical of acromegaly |
|
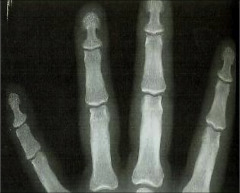
|
Distal tufting of phalanges typical of acromegalic hands |
|
|
The parathyroids are derived from... |
The third and fourth brachial pouches |
|
|
What is PTHrP? |
PTHrP is made in the placenta and binds PTH receptor type I. It is also secreted from some types of tumors. |
|
|
Serum PTH, calcium and phosphate in hypoparathyroidism? |
PTH: low Phosphate: high |
|
|
Serum PTH, calcium and phosphate in hyperparathyroidism? |
PTH: high Phosphate: low |
|
|
Serum PTH, calcium, 1,25-vitamin D and phosphate in vitamin D deficiency? |
Early: 1,25-Vitamin D: normal/elevated (remember, 1,25-Vitamin D is a reflection of PTH. Storage 25-Vitamin D levels are low).
Late ("classic"): 1-25 Vitamin D: normal/elevated (remember, 1,25-Vitamin D is a reflection of PTH. Storage 25-Vitamin D levels are low). |
|
|
What supplement do you need in your breast milk for your baby |
Vitamin D! |
|
|
Serum PTH, calcium, 1,25-vitamin D and phosphate in vitamin D deficiency? |
PTH: high Calcium: low Vitamin D: normal/elevated (unless VDDR type I, where 1,25-vitamin D is low) |
|
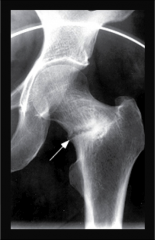
What's going on here? |
"Looser's zone": microfractures due to osteomalacia |
|
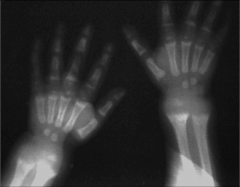
What's going on here? |
Rickets - note "fuzziness" of bone on xray. |
|
|
Patient presents with multiple Cushing's symptoms, including increased central obesity, hirsuitsm, water retention and hypokalemia. What etiology of Cushing's can you exclude? |
Exogenous glucocorticoids: don't bind aldosterone receptor and wouldn't cause hypokalemia or water retention. |
|
|
What are the two major effects of angiotensin II? |
1. Aldosterone secretion 2. Vasoconstriction |
|
|
When do you measure cortisol to assess for adrenal insufficiency? |
At highest point of cortisol release (around 6AM) |
|
|
When do you measure cortisol to assess for Cushing's syndrome? |
At the nadir (midnight) |
|
|
Clinical presentation of GnRH deficiency |
Asomnia (can't smell) and failure to initiate puberty |
|
|
Ddx for male breast development at onset of puberty? |
Very normal for breast bud to develop early in male puberty (50% of males) |
|
|
Male equivalent of menopause? |
Andropause - decline in testosterone with age (preservation of fertility). Normal aging; does NOT require supplementation. |
|
|
Patient presents w/symptoms of Cushing's. His labs are below:
1mg dexamethosone --> 10 ug/dL cortisol 8 mg dex --> suppression of cortisol from 14 --> 4 ug/dL ACTH 112
What do you suspect? |
High ACTH --> suggests ACTH secretion, not pituitary. High-dose partial dexamethasone suppression suggests that etiology.
Inferior petrossal sinus sampling indicated to localize and lateralize lesion |
|
|
Biggest risk: pituitary adenoma |
Hypofunctioning pituitary --> ACTH and cortisol deficiency --> adrenal crisis, shock, CV decompensation |
|
|
Principles of treating unstable adrenal insufficiency |
Treat (w/steroids) before you test! |
|
|
What can be said for multiple hormone-producing adrenal masses? |
Usually carcinomas |
|
|
Epidemiology of adrenal masses |
Adenoma more common adrenal mass in adults Carcinoma more common mass in children. |
|
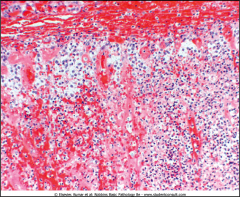
What is going on here? |
Adrenal hemorrhage |
|
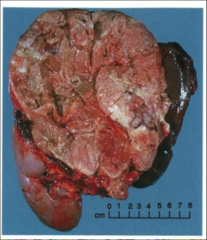
|
Adrenal carcinoma |
|
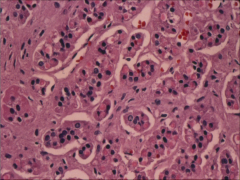
What is going on here? |
Aldosterone adrenal adenoma - note glomerulosa |
|
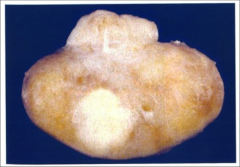
What is going on here? |
Anterior pituitary microadenoma |
|
What is going on here? |
Atrophic adrenal cortex - i.e. after suppression from deprivation of ACTH |
|
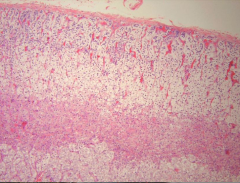
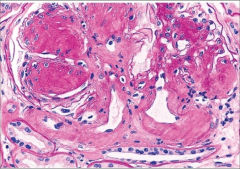
What is going on here? |
Autoimmune adrenalitis - note fibrotic adrenal gland w/lymphocytic infiltration |
|
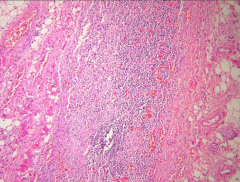
What is going on here? |
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
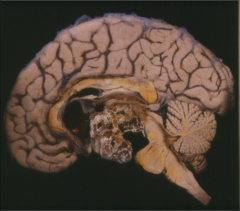
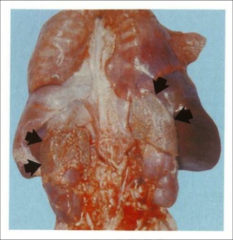
What is going on here? |
Craniopharyngioma |
|
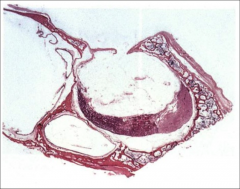
What is going on here? |
Empty sella syndrome - note compressed pituitary |
|
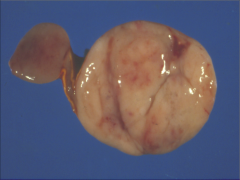
What is going on here? |
MEN2 - note multiple pheochromocytomas |
|
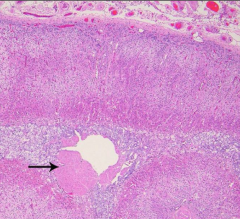
Name this organ and its components |
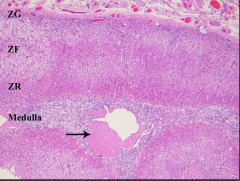
Adrenal gland |
|
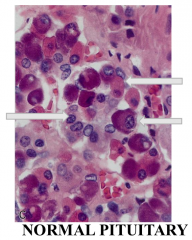
Name these cells of the pituitary |
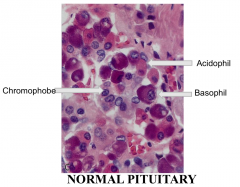
|
|
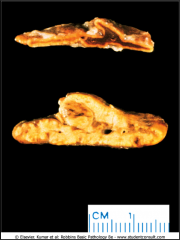
What is going on here? |
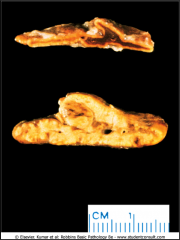
Normal adrenal gland (top) and adrenal hyperplasia (bottom) |
|
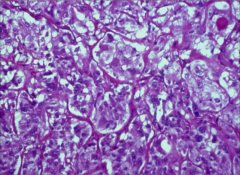
What is going on here? |
Pheochromocytoma - note "cell ball nest” pattern of growth |
|
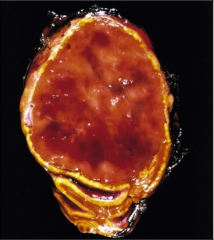
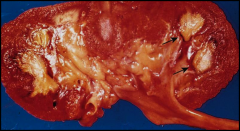
What is going on here? |
Pheochromocytoma: note flesh-colored and glossy mass w/a few areas of hemorrhage |
|
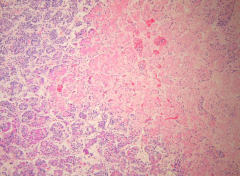
What is going on here? |
Pituitary infarct |
|
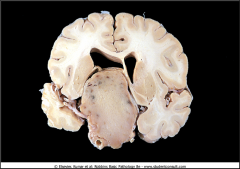
What is going on here? |
PItuitary macroadenoma |
|

What is going on here? |
Primary pigmented nodular adrenal disease |
|
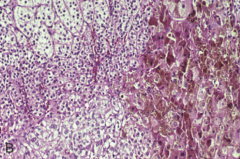
What is going on here? |
Primary pigmented nodular adrenal disease - note lipofuscin |
|
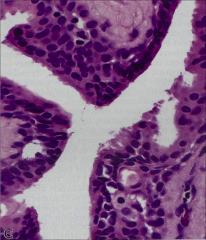
What is going on here? |
Rathke's pouch cyst |
|
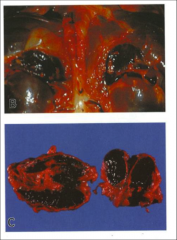
What is going on here? |
Waterhouse-Friederichson syndrome - note extensive pituitary hemorrhage |
|
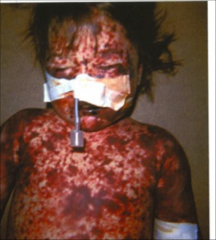
What is going on here? |
Waterhouse-Friederichson syndrome - note extensive purpura |
|
|
Thryoglobulin deficiency: total T4, free T4, TSH |
Total T4: low Free T4: normal TSH: normal |
|
|
When would free T4 be low and TSH be normal? |
Hypopituitarism + defect in thyroid binding globulin. Total T4 = low (not enough binding globulin) Free T4 = low; pituitary does not compensate for thyroid binding globulin deficiency. TSH = normal |
|
|
When would free T4 be low and TSH be high? |
Defect in TSH glycoylation - TSH is being produced well and is measured on our assays, but cannot act upon its receptors to upregulate thyroid hormone secretion |
|
|
Serum tests for cortisol |
Total cortisol (free cortisol is VERY difficult to measure) |
|
|
Group publishes study in the NEJM regarding ICU epidemic of adrenal insufficiency. Are you skeptical? |
Yes - they were likely measuring total cortisol, which would be low due to lack of cortisol binding globulin. HPA axis regulation of free cortisol would in fact be normal. Remember, there are no lab tests for free cortisol! |
|
|
Thyroid etiologies of obesity |
Trick question - hyperthyroidism is NOT a contributing factor to obesity |
|
|
Normal T3 with hyperthyroidism? |
Since physiologic stress suppresses TRH release from the hypothalamus, hyperthyroid patients will often have normal T3 when they are sick. |
|
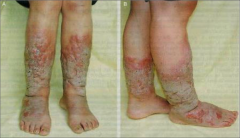
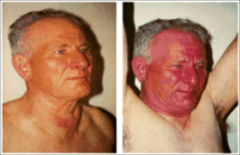
What is going on here? |
Pre-tibial myxedema or "dermopathy of Grave's disease." |
|
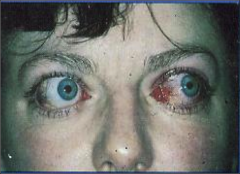
What is going on here? |
Grave's orbitopathy: note scleral injection and exopthalmos |
|
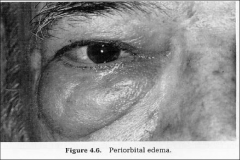
What is going on here? |
Grave's orbitopathy: note periorbital edema (could also be hypothyroidism... I guess) |
|
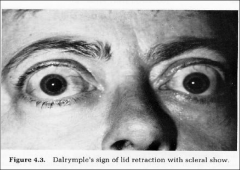
What is going on here? |
Lid retraction --> thyrotoxicosis (may or may not be Grave's) |
|
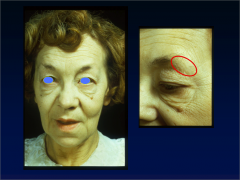
What is going on here? |
Laterally truncated eyebrows typical of hypothyroidism |
|
What is going on here? |
Periorbital edema secondary to hypothyroidism (could also be Grave's... I guess) |
|
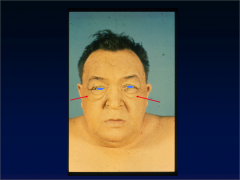
What is going on here? |
Pemberton sign: indicative of thoracic outlet syndrome, a compressive manifestation of thyroid mass. |
|
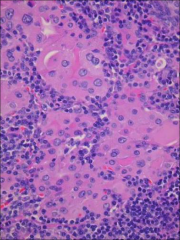
What's going on here? |
Lymphocytic (Hashimoto's) thyroiditis; note: - Lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates with germinal centers - Eosinophilic (Hurthle cell, filled w/mitochondria) change of the follicular epithelium - Follicular cell atrophy |
|
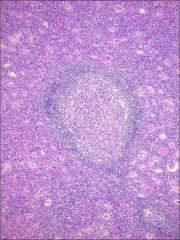
What's going on here? |
Lymphocytic (Hashimoto's) thyroiditis; note: - Lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates with germinal centers - Follicular cell atrophy |
|
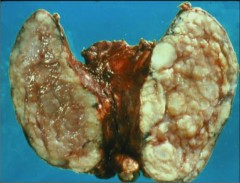
What's going on here? |
Lymphocytic (Hashimoto's) thyroiditis: note thyromegaly w/white and nodular parenchyma |
|
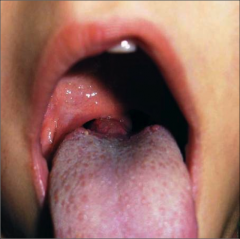
What's going on here? |
Lingual thyroid - failure of caudal migration of thyroid gland during embryogenesis |
|
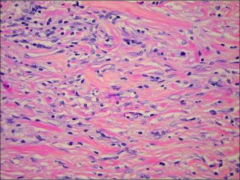
What's going on here? |
Riedel thyroiditis: note bands of collagenous tissue w/scattered lymphocytes, with no residual thyroid follicules |
|
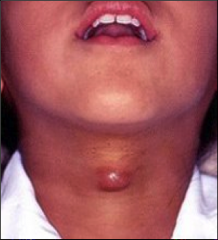
What's going on here? |
Thyroglossal duct cyst |
|
|
Occult papillary carcinoma |
<1 cm papillary carcinoma that is thought to be extremely prevalent in the population |
|
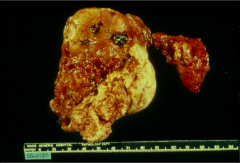
What's going on here? |
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma - note large size and areas of hemorrhage and atrophy |
|
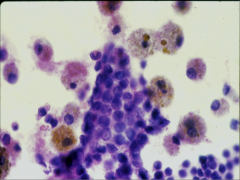
What's going on here? |
Benign FNA thyroid smear - note evenly-spaced follicular cells and iron-laden macrophages |
|
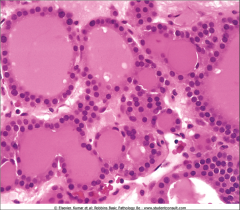
This mass was excised from the thyroid. What do you suspect? |
Follicular adenoma of the thyroid - closely resembles normal thyroid tissue on histopathology |
|
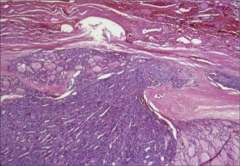
What's going on here? |
Follicular carcinoma of the thyroid with capsular invasion |
|
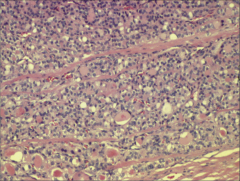
What's going on here? |
Follicular carcinoma of the thyroid with vascular invasion |
|
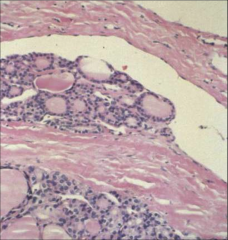
What's going on here? |
Follicular carcinoma of the thyroid with vascular invasion (follicle in mid-right of picture that projects into venous space). |
|
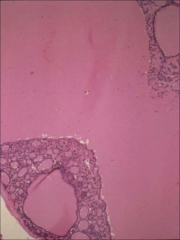
What's going on here? |
Nontoxic goiter (involution stage) - note filling of thyroid follicle with pink colloid material |
|
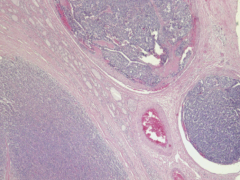
What's going on here? |
Widely invasive follicular carcinoma of the thyroid with vascular invasion |
|
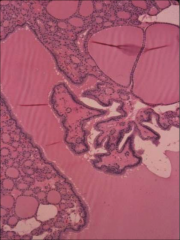
What's going on here? |
Nontoxic goiter - proliferative phase (note papillary formations) |
|
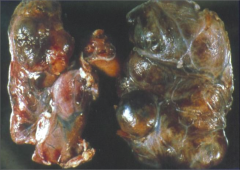
What's going on here? |
Nontoxic goiter - note diffuse, nodular enlargement |
|
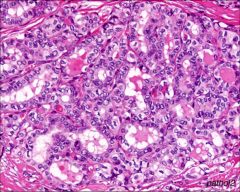
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - follicular variant. Note clear, papillary carcinoma-like nuclei without papillary architecture. |
|
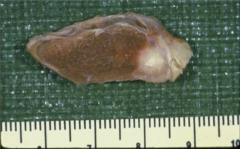
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - note white center surrounded by fibrous tissue |
|
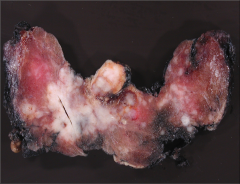
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - note multifocal, white centers surrounded by fibrous tissue |
|
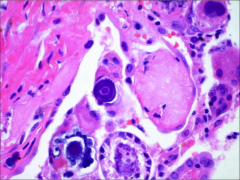
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - note psammoma bodies |
|
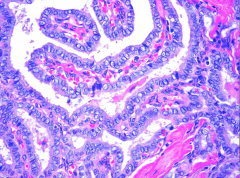
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - note papillary architecture w/clear, irregularly-shaped tumor cells with nuclear transperancy |
|
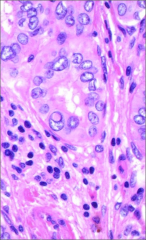
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - note papillary architecture w/clear, irregularly-shaped tumor cells with nuclear transperancy and nuclear "pseudo-inclusions". |
|
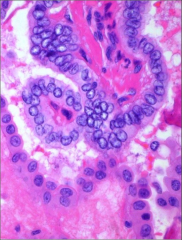
What's going on here? |
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid - note papillary architecture w/clear, irregularly-shaped tumor cells with nuclear transperancy |
|
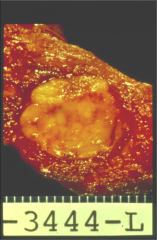
What's going on here? |
Medullary carcinoma - note soft, fleshy, unencapsulated mass |
|
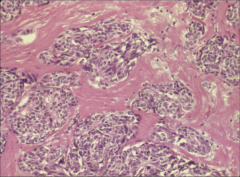
What's going on here? |
Medullary carcinoma - note spindly cells with eosinophilic stroma |
|
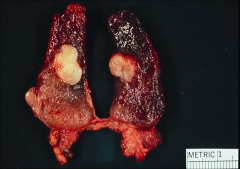
What's going on here? |
MEN2A medullary thyroid carcinoma: note bilateral thyroid masses in the upper 2/3 of the gland |
|
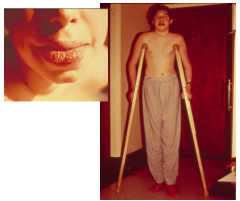
What's going on here? |
MEN2B - note marfanoid body habitus and mucocotaneous neuromas. |
|
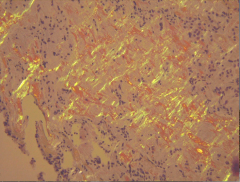
What's going on here? |
Medullary carcinoma - note amyloid congo-red-staining deposits |
|
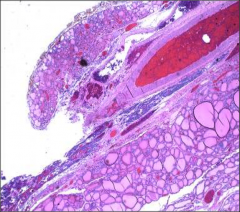
What's going on here? |
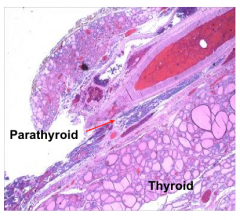
Normal thyroid and parathyroid |
|
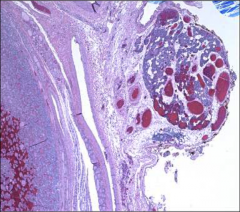
What's going on here? |
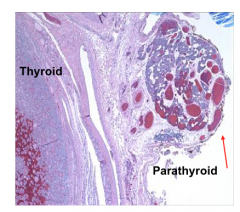
Normal thyroid and parathyroid |
|
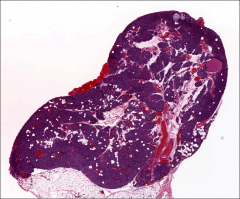
What's going on here? |
Adult parathyroid gland; note involution w/stromal fat |
|
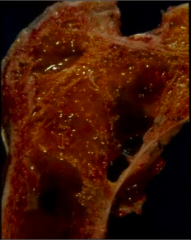
What's going on here? |
Bone in patient with primary hyperparathyroidism: note brown tumors, bone collapse and holes in bone |
|
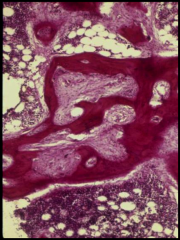
What's going on here? |
Dissecting osteitis of bone typical of primary hyperparathyroidism |
|
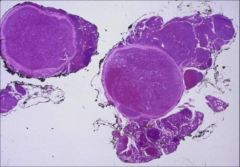
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid hyperplasia |
|
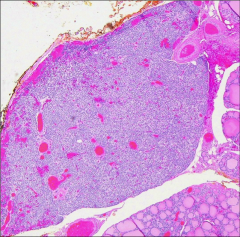
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid of a newborn; note absence of stromal fat |
|
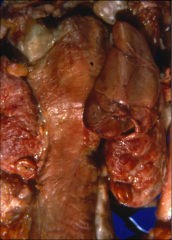
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid adenoma: note huge upper R parathyroid gland with 3 normal parathyroid glands |
|
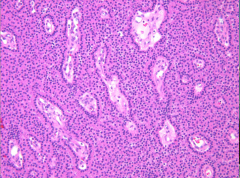
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid adenoma - note bland cells of the parathryoid without stromal fat invasion, lining up around the vasculature. |
|
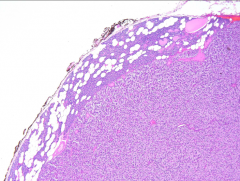
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid adenoma - note bland cells of the parathryoid without stromal fat invasion |
|
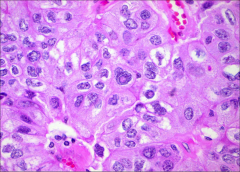
This was taken from the parathyroid gland. what can you deduce? |
Nuclear pleiomorphism and pseudoinclusions --> parathyroid carcinoma |
|
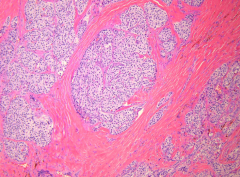
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid carcinoma - note prominent, dense, eosinophilic, fibrous bands |
|
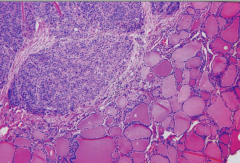
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid carcinoma - note thyroidal invasion |
|
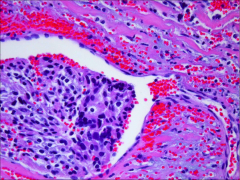
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid carcinoma - note vascular invasion |
|
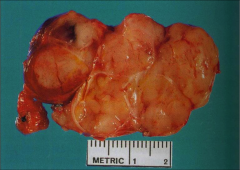
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid carcinoma - note large mass (often palpable) with nodular configuration and fibrous bands between tumor lobules |
|
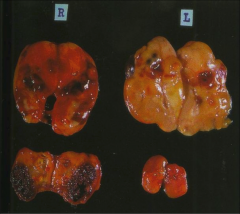
What's going on here? |
Parathyroid hyperplasia |
|
|
Which tissues utilize... Glucose? Fatty acids? |
Glucose: all tissues Ketones: all tissues except liver Fatty acids: all tissues except brain |
|
|
What does a kid with poorly controlled Type I DM look like? What is the blood sugar? |
Looks wasted: "catabolism run amok"
Serum glucose = high: - No insulin-induced glucose transport into adipocytes & muscle - No inhibition of catabolism --> gluconeogenesis in the liver |
|
|
A 32 year old, normal weight woman presents with a 2-month history of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss. A random serum glucose is 228 mg/dl. Her younger sister has celiac disease. Family history is negative for diabetes. The most likely diagnosis is: |
(A) Type 1 diabetes |
|
|
Which of the following is adequate to make a diagnosis of diabetes? |
(D) A hemoglobin A1c of 7.0% |
|
|
Which of the following is characteristic of T1DM but not T2DM? |
Twin concordance of approximately 50% |
|
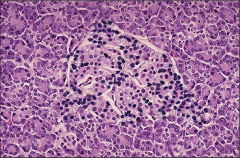
What's going on here? |
Insulinitis - lymphocytic infiltration of the pancreas typical of type I diabetes. |
|
|
Diabetic ketoacidosis is most frequently associated with which of the following? (B) Type 2 diabetes |
(A) Type 1 diabetes |
|
|
In DKA, which of the following is best correlated with the severity of the ketoacidosis? (A) The duration of symptoms (B) The degree of hyperglycemia (C) The degree of dehydration |
(D) The anion gap |
|
|
Which of the following would indicate that a patient likely has HSS rather than DKA? (B) Age 50 years, living independently (C) A serum glucose of 620 mg/dl |
(D) A normal serum bicarbonate |
|
|
Which is at a bigger risk for diabetic nephropathy: TIDM or TIIDM? |
Both at equal risk |
|
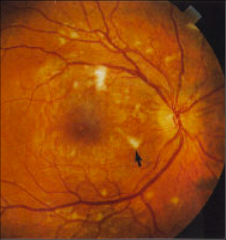
What's going on here? |
Cotton wool spots indicative of diabetic retinopathy |
|
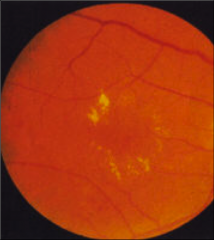
What's going on here? |
Exudates and edema indicative of advanced diabetic retinopathy |
|
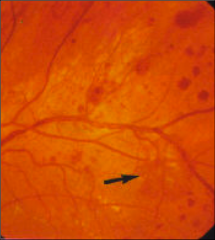
What's going on here? |
Hemorrhages indicative of advanced diabetic retinopathy |
|
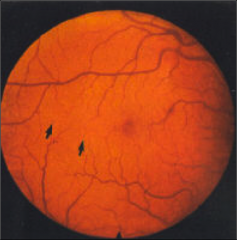
What's going on here? |
Microaneurysms indicative of advanced diabetic retinopathy |
|
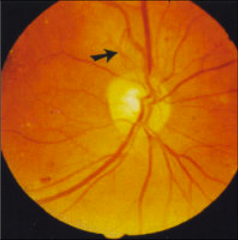
What's going on here? |
Neovascularization indicative of advanced diabetic retinopathy |
|
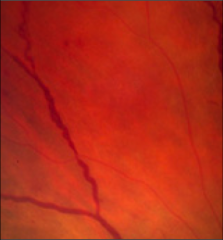
What's going on here? |
Venous bleeding indicative of advanced diabetic retinopathy |
|
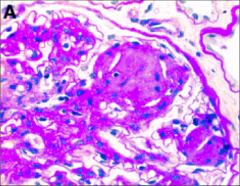
What's going on here? |
Diabetic neprhopathy with nodular glomerulosclerosis |
|
|
Target A1C |
<7 |
|
|
20 yo woman with h/o DM1 diagnosed age 14 yrs presents for a new patient appointment. What screening tests should you order? |
- Microalbumin - Dilated eye exam - Foot exam |
|
|
50 yo obese man with history of hyperlipidemia and hypertension presents for evaluation after he presented to the ED with 6 month history of polyuria/polydipsia and a random glucose of >200.
What is indicated at this visit? |
Early TIIDM --> management will prevent both microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Metformin for glycemic control, ACEis, statin
Also, screening tests: - Microalbumin - Dilated eye exam - Foot exam |
|
|
Role of glucagon in acute vs chronic fast |
Much more important in acute hypoglycemia than long-term hypoglycemia. |
|
|
What age group is at MOST risk for hypoglycemia |
Preterm infants - counterregulatory mechanisms may not be mature enough to transition from reliance on maternal glucose to independent synthesis. |
|
|
List the rare neuroendocrine tumors |
1. Carcinoid: serotonin-secreting w/diarrhea, flushing, wheezing, pain 2. Pancreatic endocrine: depends on homrone secreted 3. Gastrinoma: gastric acid hypersecretion 4. Insulinoma: hypoglycemic symptoms 5. Glucagonoma: dermatitis, DM, weight loss 6. Somatostatinoma: DM, gallbladder disease, diarrhea, steatorrhea 7. VIPoams: large volume diarrhea, hypokalemia, dehydration |
|
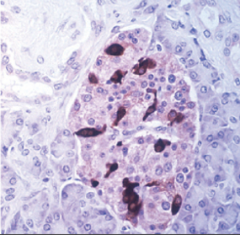
What's going on here? |
Pancreatic alpha-islet cells: note 15-20% of pancreatic islet topography w/peripheral distribution |
|
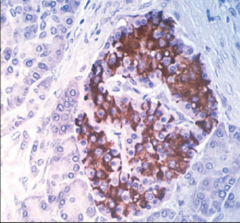
What's going on here? |
Pancreatic beta cells: note 75% of pancreatic islet topography w/central distribution |
|
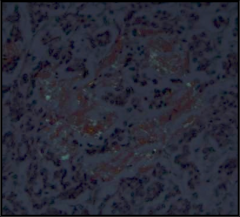
What's going on here? |
Amyloid w/apple-green birefringence: typical of type II DM |
|
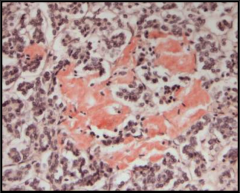
What's going on here? |
Amyloid deposits on congo-red stain: typical of type II DM |
|
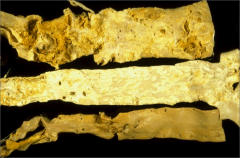
What's going on here and how does it relate to endocrinology? |
Aortic atherosclerosis secondary to hyperglycemia-related vascular changes |
|
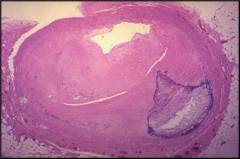
What's going on here and how does it relate to endocrinology? |
Coronary artery atheroscerosis secondary to hyperglycemia-related vascular changes |
|
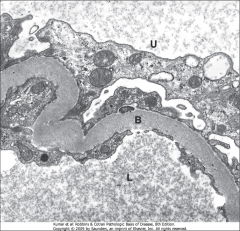
What's going on here? |
Basement membrane hypertrophy secondary to diabetes |
|
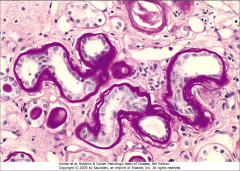
What's going on here? |
Hypertrophy of renal tubule basement membranes secondary to diabetes |
|
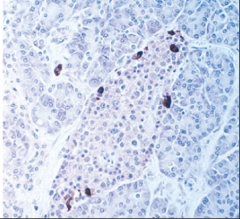
What's going on here? |
Pancreatic gamma-islet cells: note 5-10% of pancreatic islet topography w/peripheral distribution |
|
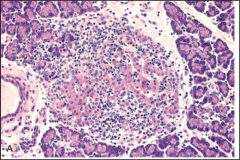
What's going on here? |
Insulinitis - infiltration of pancreatic islets with lymphocytes typical of type I diabetes mellitus. |
|
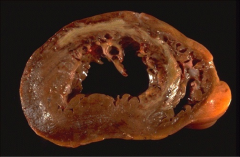
What's going on here and how does it relate to endocrinology? |
Myocardial infarct secondary to hyperglycemia-related vascular changes. Infarct 5-7 days old: note pale scar w/hyperemic border. |
|
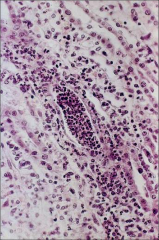
|
Acute pyelonephritis secondary to diabetic autonomic neuropathy, urinary stasis and ascending UTI |
|
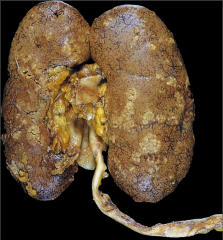
What's going on here and how does it relate to endocrinology? |
Acute pyelonephritis secondary to diabetic autonomic neuropathy, urinary stasis and ascending UTI |
|
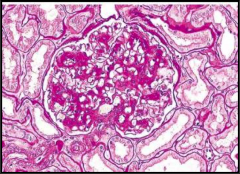
What's going on here? |
Diffuse glomerulonephropathy secondary to DM |
|
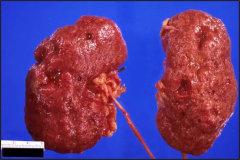
What's going on here? |
Renal scarring, atrophy and granularity secondary to DM |
|
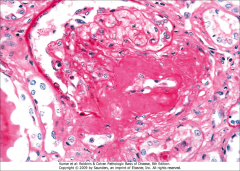
What's going on here? |
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis secondary to DM |
|
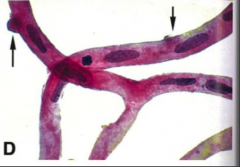
What's going on here? |
Loss of pericytes in the occular capillary secondary to DM |
|
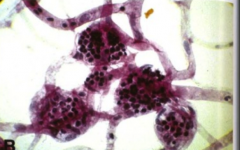
What's going on here? |
Occular microaneurysms secondary to DM |
|
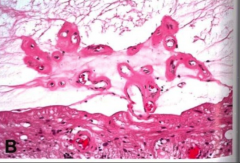
What's going on here? |
Neovascularization of occular vessels secondary to DM |
|
What's going on here? |
Nodular (KW) glomerulosclerosis: specific for DM-related renal disease |
|
What's going on here? |
Normal pericytes of the occular vessels (note how nuclei extend outside of the capillary lumen |
|
What's going on here? |
Papillary necrosis secondary to renal changes seen in DM |
|
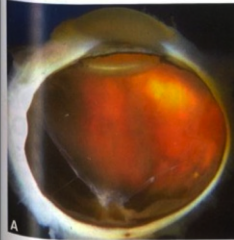
What's going on here? |
Retinal detachment secondary to DM |
|
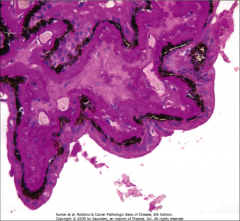
What's going on here? |
Thickened basement membrane in the cilliary bodies of the eye secondary to DM |
|
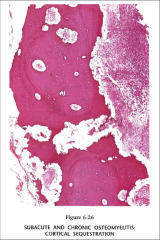
What's going on here? |
Necrosis of bone secondary to Charcot foot DM disease (note absence of nuclei in lacunae) |
|
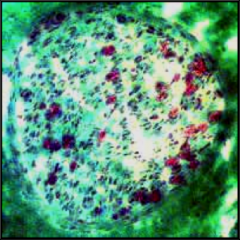
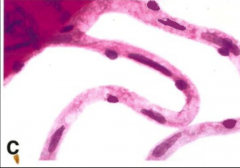
What's going on here? |
Nerve undergoing changes typical of diabetic neuropathy: demyelination and decrease of axon numbers |
|
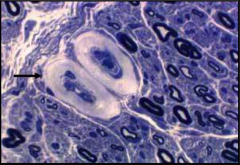
What's going on here? |
Nerve undergoing changes typical of diabetic neuropathy: thickening of vessel basement membranes |
|
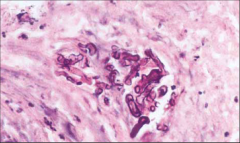
|
Mucormycosis - predilection for diabetic patients |
|
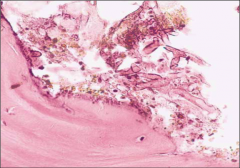
What's going on here? |
Mucormycosis - predilection for diabetic patients |
|
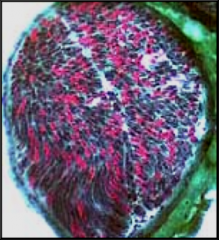
What's going on here? |
This is a normal nerve on histology. |
|
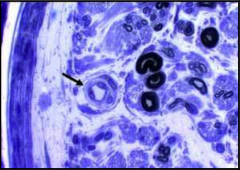
What's going on here? |
This is a normal nerve on histology. |
|
|
C.M. is a 27 year-old woman who had scheduled an office visit because of weight loss. She notes a decline in weight from 138 lbs to 119 lbs during the past 3 months despite a good appetite. She denies dieting, and her weight had been stable for several years at 135-140 lbs.On further questioning, Ms. M. also described recent insomnia despite feeling unusually fatigued at the end of the day. Her hands felt "shaky", which she attributed to her asthma medication. She described an itching, burning sensation in her eyes during the past month.On further questioning, Ms. M. also described recent insomnia despite feeling unusually fatigued at the end of the day. Her hands felt "shaky", which she attributed to her asthma medication. She described an itching, burning sensation in her eyes during the past month.
Based on this history, what are you worried about? Describe the pertinent clues. |
Hyperphagia, weight loss: Hyperthyroidism
Insomnia, fatigue: neurophsych hyperthyroidism symptoms
Tremor: neuro hyperthyroidism symptom
Burning sensation: Grave's orbitopathy
Likely hyperthyroidism, Grave's disease if eye burning/itching is orbitopathy |
|
|
C.M. is a 27 year-old woman presents to your office for evaluation. On physical examination, blood pressure was 130/68, heart rate 104 and regular. Her eyes seemed to be staring, and lid lag was noted. The thyroid was about 3 times normal size, diffusely enlarged, non-tender, and firm (almost rubbery) without identifiable nodules. The hands were warm and moist, and tremulous when held outstretched. Several depigmented circular areas, about 2-3 cm in diameter were present on the abdomen and both wrists.
Based on this exam, what are you worried about? Describe the pertinent clues. |
Goiter --> thyroid issue. Non-nodular makes toxic nodule less likely.
High bp/hr --> hyperthyroidism
Orbitopathy: lid retraction indicative of any hyperthyroidism, lid lag more specific for Grave's orbitopathy
Sweaty hands --> hyperthyroidism
Tremor --> hyperthyroidism
Vitiligo: often occurs in association with autoimmune thyroid disorders. Leads differential toward Grave's (this also happens in Hashimoto's but she would be hypothyroid). |
|
|
C.M. is a 27 year-old woman presents to your office for evaluation for weight loss. Interpret the following lab results
Free Thyroxine 4.2 (nl 0.8-2.7 ng/dL) Free T3 1,020 (nl 260-480 pg/dL) Glucose 84 (nl < 110 mg/dl)
I-123 uptake: 81% at 24 hrs. |
High T4 & T3 --> thyrotoxicosis
Low TSH --> not central (problem is independent of hypothalamus and pituitary, and is not ectopic TSH secretion)
Normal glucose --> r/o diabetes as etiology of weight loss
High I-123 uptake confirms hyperthyroidism; homogenous uptake rules out toxic nodule and makes Grave's disease much more likely. |
|
|
A 63 year-old postmenopausal women presents to the ER with a 2 day history of nausea and vomiting. She denied any fever or chills. DXA assessment found her to have a T-Score at the spine -1.5, hip -2.1 and forearm -2.8. ROS is essentially negative expect for heartburn, for which she takes Tums as needed, and low back pain, for which she takes acetaminophen as needed. Family history is significant for hip fracture in her mother. She does not smoke and drinks 1-2 glasses of wine per week.
Based on the history, what are you worried about? Describe the pertinent clues. |
DXA assessment > -2.5 --> osteoporosis (take the lowest number)
Family Hx fragility fracture in first-degree relative increases her risk for osteoporosis.
Nausea & vomiting --> infection vs. hypercalcemia (no fever or chills favors hypercalcemia)
Tums, alcohol --> aggravate hypercalcemia |
|
|
A 63 year-old postmenopausal women presents to the ER with a 2 day history of nausea and vomiting and the following labs:
Glucose 98 mg/dl Total Calcium 13.8 mg/dl (NL 8.5-10.5mg/dl) Albumin 3.2 g/dl (NL 3.5-5.0 g/dl) Ionized Calcium 6.6 mg/dl (NL 4.2-5.2 mg/dl) Phosphorus 2.8 mg/dl (NL 2.7-4.8 mg/dl) Magnesium 1.6 meq/l (NL 1.3-1.9 meq/l)
What are you worried about? Describe the pertinent clues. |
High total and ionized calcium with low albumin (no need to correct). Hypercalcemia is likely the primary defect.
High creatinine - has progressed to renal failure (perhaps from dehydration), which will further impair calcium excretion
Low normal phosphorous: indicates PTH etiology (over renal insufficiency as primary etiology, which would entail a high phosphorous)
|
|
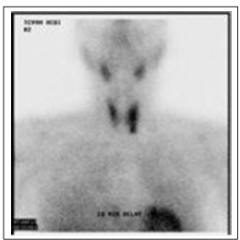
The patient was subsequently scheduled for surgery. A preoperative Technetium sestamibi scan is shown. What are you going to tell the surgeon? |
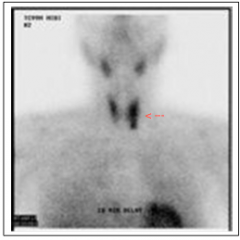
Top: salivary glands Bottom: heart Midneck: thryoid gland L > R
Hypersecreting parathyroid lesion likely located in L lower thyroid. |
|
|
Following resection of a hyperparathyroid mass,the patient complains of tingling around her mouth. Chvostek's sign was positive.
Total calcium 7.2 Albumin 3.6
What is going on? |
Chvostek's sign is hyperexcitability of the facial nerves; she is likely hypocalcemic.
Low total calcium --> hypocalcemic. |
|
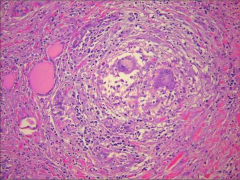
What's going on here? |
Subacute thyroditis: note granulomatous inflammation |
|
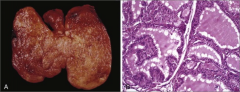
What's going on here? |
Grave's disease - note scalloping of colloid from accelerated colloid resorption |
|
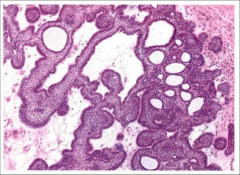
What's going on here? |
Cranioparyngioma: palisaded nuclei |
|
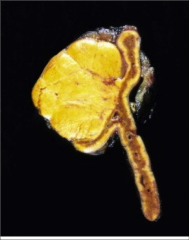
What's going on here? |
Cortisol-producing adenoma - note yellow color |
|
|
Sodium values and DKA? |
Hypernatremia in DKA due to osmotic diuresis and general water loss.
However, this is often masked ("pseudohyponatremia") due to the hyperglycemia. |
|
|
Glucose 568 Sodium 141 Potassium 5.4 Chloride 101 Bicarbonate 8 Creatinine 1.3 BUN 32 Hematocrit 48
pO2 106 pCO2 17 pH 7.09
What is going on? Justify it with each of the lab values. |
Glucose, ketones, acidosis --> DKA
Sodium: likely actual high but within normal range due to "pseudohyponatremia"
Potassium: acute hyperkalemia due to extracellular shift (insulin & hyperglycemia), hypokalemia due to fluid contraction and high aldosterone
Acidosis and low bicarb: high anion gap
High O2 and low CO2: compensatory respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
Classification of weight and indication for therapy |
Normal weight: 18 - 25 kg/m2a Overweight: 25 - 30 kg/m2 Extreme (morbid) obesitiy: >40 kg/m2
Everyone indicated for diet & exercise Medical therapy > 30 |
|
|
To lose a pound in a week you need to... |
1 lb = 3500 cal 500 cal deficit/day --> 1lb pound loss/week |
|
|
Long-term success rate of medical weight loss for morbid obesity |
5% :( |
|
|
Indications for weight loss surgery |
1. Failed non-surgical weight loss attempts 2. At least 100 pounds over ideal body weight 3. BMI > 40 OR BMI > 35 w/complications (DM, sleep apnea, HTN, sleep apnea) |
|
|
Surgical approach for bariatric surgery |
Wound infection rate and hernia rate is much higher in obese patients --> use laproscopic approach! Also allows for more activity & mobility. |
|
|
Contraindications for weight loss surgery |
1. Substance abuse 2. Severe cardiac/pulmonary conditions 3. Psychiatric disoders 4. Defined noncompliance |
|
|
Types of bariatric surgeries |
1. Adjustable gastric banding and sleeve gastrectomy (restriction) Biliopancreatic diversion +/- duodenal switch (malabsorption) 3. Roux-en-Y Gastric bypass (restriction + malabsorption) |
|
|
Ideal patient for restrictive bariatric surgery |
1. Young, few comorbidities 2. Less weight to loose (weight loss is shorter) 3. Not sweet eater 4. No hx esophageal dismotility |
|
|
Pros of restrictive bariatric surgery |
1. Reversible 2. No malabsorption --> no supplementation required 3. Less serious complications
|
|
|
Complications of restrictive bariatric surgery |
1. Slippage 2. Erosion 3. Vomiting, nausea, acid reflux |
|
|
Additional contraindications for Roux-en-Y weight loss surgery |
1. Preexisting malabsorptive conditions (Crohn's etc.) 2. Peptic ulcer disease 3. High risk for gastric cancer |
|
|
Roux-en-Y strategy |
1. Bypass stomach: food goes esophagus --> intestine 2. Connect stomach w/intestine to allow for gastric juices |
|
|
Supplementation for absorptive bariatric surgery |
Vitamins (w/extra B12), calcium, iron, protein etc. |
|
|
Dumping syndrome |
High fat and high sugar meals s/p Roux-en-Y --> osmotic diarrhea, hyperinsilunemia and hypoglycemia syndromes |
|
|
How does Roux-en-Y gastric bypass alleviate diabetes, theoretically? |
More nutrients arrive at a faster rate to duodenum --> more GLP-1 and PYY --> more insulin stimulation |
|
|
Pure absorptive gastric bypass indications |
BMI > 60 |
|
|
Duodenal switch |
Malabsorptive surgery addition to gastric sleeve |
|
|
Complications of bariatric surgery |
1. Intestinal leakage (fatal) 2. PE 3. Intestinal obstruction 4. Deficiencies (anemia, calcium deficiency) |

