![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the layers of the adrenal cortex and what do they produce |
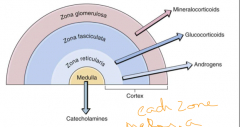
Cortex: Zona glomerulosa (mineralocorticoids (aldesterone)) Zona Fasciculata (glucocorticoids) Zona Reticularis (androgens)
Not cortex: Medulla (Epi)
Each zone makes a particular steroid |
|
|
What is the main glucocorticoid? |
Cortisol |
|
|
What is the mainmineralocorticoids? |
Aldosterone |
|
|
What is the origin of adrenocortical hormones? |
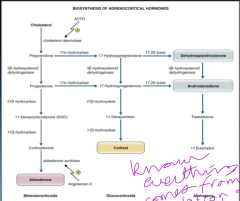
You have a precursor of cholesterol that is acted on by ACTH and it involves the cytochrome P-450 enzyme system
Don't worry about memorizing this just look at it so you know whats happening with the ACTH |
|
|
What could hypothetically happen with cross reactivity and steriods? |
The steriods are so similar in structure they could cross react with each other's receptors. The AFFINITY will not be as strong s |
|
|
Where is cortisol secreted? |
Occurs in Zona Fasciculata
|
|
|
What hormones regulate cortisol secretion? |
CRH (hypothalamus), ACTH (pituitary gland) |
|
|
What is a common variation in the secretion of corisol across species? |
WHEN the coritisol is secreted
Dog: episodic pulses throughout day Diurnal variation: human Cat most likely nocturnal |
|
|
What are the feedback mechanisms on cortisol secretion by HPA axis? |

|
|
|
What is going to happen if you rapidly stop giving steroids after a long term treatment? |
You are going to wish you were dead. The steroids will have negatively fed back on the pitutary and the hypothalamus that there will have been no stimulation to the adrenal gland and no cortisol |
|
|
What are the factors that stimulate ACTH secretion? |
Stress (hypoglycemia, infections/fever)
Low cortisol levels
|
|
|
What are the factors that are going to inhibit ACTH secretion |
High cortisol levels (from either you or stress)
Somatostatin
In the horse dopamine has a chronic tonic dampening affect on ACTH. Located in the pars intermedia. Mild dampening is normal. When you loose that dampening you are in trouble and get cushings |
|
|
What is the benefit of cortisol and proteinb inding? |
longer half life |
|
|
How do glucocorticoids work/what is their mechanism |
The steroid zips through the plasma membrane and binds to a receptor on the nucleus. This receptor sticks its fingers in and messes with the DNA and protein synthasis |
|
|
What are the general affects of cortisol? |

|
|
|
What are the effects of cotirsol on energy metabolism? |
It is catabolic (tearing things apart). It wants to get the BG UP. Its going to prevent hypoglycemia at any cost via direct and permissive (amplifying friends)
Increases gluconeogenesis Build up of glycogen for epi and glucagon to act on
LAST THREE SLIDES I AM BAD |

