![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
GHRH, relased from the hypothalamus, stimulates the secretion of ______ from the pituitary
|
Growth Hormone
|
|
|
What directly inhibits the release of growth hormone?
|
Somatostatin
|
|
|
A deficiency in which hormone(s) can cause short stature?
(select all that apply) A. Dopamine B. Growth hormone C. Prolactin D. TSH E. Cortisol F. Thyroid hormone G. Somatostatin H. IGF-1 I. GHRH |
B. Growth hormone
D. TSH F. Thyroid hormone H. IGF-1 I. GHRH |
|
|
The major regulator of prolactin is _______ which is released from the ________ .
|
Dopamine
hypothalamus |
|
|
MOA: Dopamine inhibiting prolactin
|
Dopamine (aka prolactin-inhibiting
hormone) from the hypothalamus binds to D2 receptors on lactotroph cells of the anterior pituitary |
|
|
Differentiate between primary, secondary and tertiary growth hormone deficiency.
|
Defective hypothalamic release of GHRH
(tertiary disease) Pituitary insufficiency of GH (secondary disease) Failure of IGF-1 secretion in response to GH (primary disease) |
|
|
List the forms of growth hormone available for clinical use
|
Somatropin
Somatrem |
|
|
What are Somatropin and Somatrem?
|
Forms of recombinant GH
|
|
|
Why do we use Somatropin and Somatrem in pediatric patients?
|
It is best used BEFORE epiphyseal plates have closed
|
|
|
Clinical Use:
- Growth hormone deficiency in children Congenital or acquired form - Other conditions associated with short stature despite adequate GH production Turner’s syndrome End stage renal disease in children -Idiopathic, non-GH-deficient short stature - Anti-aging supplements - Athletes for a purported increase in muscle mass and athletic performance. Banned by the Olympic Committee. - AIDS-associated wasting - Malabsorption associated with **short bowel syndrome** |
Somatropin
Somatrem (recombinant GH) |
|
|
How can end stage renal disease
cause short stature? |
Decreased filtration of some IGF binding proteins
↓ Binds more IGF-1 in the serum (hence inactive) ↓ Less effect on bone growth |
|
|
How do Somatropin and Somatrem treat Malabsorption associated with short bowl syndrome?
|
GH stimulates growth and adaptaion of GI epithelial cells
|
|
|
What amino acid releases GH?
|
argenine
|
|
|
One of your pediatric patients is very short in stature so you decide to give a drug that will help stimulate growth. The patient has has success for months but now is seeing you with a displacement of the portion of the proximal femur distal to the growth plate.
Whats the drug? What happened? |
Somatropin and Somatrem
**Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis** (SCFE) - Growth hormone can cause rapid bone growth and expansion of the zone of hypertrophy in the growth plate - Epiphyseal growth plate is unusually widened and weakened - Growth plate is less able to handle shearing forces |
|
|
Side effects of rapid growth in children?
|
- Scoliosis
- Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) |
|
|
What type of endocrine disorders
might occur with GH therapy? |
**Hypothyroidism**
( pos. feedback: GH stimulates somatostatin → inhibits TSH) **Insulin Resistance** |
|
|
GH Common Adverse Effects in Adults?
|
Peripheral edema
Carpal tunnel syndrome Myalgias and arthralgias |
|
|
A 5-year-old girl is evaluated and determined to have short stature. A GH stimulation test revealed a normal basal level of GH, and an elevation in serum GH levels post-stimulation, but IGF-1 levels were very low in both cases.
What is the most likely cause? |
There is problem with the GH receptor!
(IGF-1 levels are low and are stimulated by GH binding to its receptor!!) |
|
|
Mecasermin is a complex of _____ and _________
|
Complex of:
Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-1 (rhIGF-1) Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (rhIGFBP-3) |
|
|
Clinical Use:
** Severe primary IGF-1 deficiency ** (typically a mutation on GH receptor) |
Mecasermin
|
|
|
Adverse Effect:
**Hypoglycemia** - Eat 20 min before or after taking the drug –to avoid hypoglycemia |
mecasermin
(Acts like insulin!!!!) |
|
|
A 36-year-old male presented with a 12-month history of arthralgia, hyperhidrosis, headaches, and sleep apnea. He states his shoe size has increased and that he ran into an old college friend who commented that his jaw has gotten larger. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed an enlarged pituitary fossa harboring a soft tissue mass extending into the suprasellar cistern. What would you expect to see on his labs?
|
↑ IGF-1 from pituitary adenoma!!
|
|
|
How can you stop the effects of excess growth hormone from a pituitary adenoma?
|
Surgery/Radiation
Block GH receptor Use Somatostatin to block GH release |
|
|
What inhibits the release of GH from the pituitary?
(select all that apply) A. Arginine B. GH C. CRH D. IGF-1 E. GHRH F. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia G. Somatostatin H. Ghrelin |
GH (feedback)
IGF-1 (feedback) Somatostatin |
|
|
Feedback Loop
|
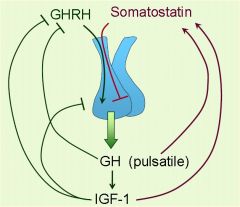
|
|
|
Name the drug class:
Octreotide Lanreotide Pegvisomant Bromocriptine Cabergoline |
GH Antagonists
|
|
|
Which 2 growth hormone antagonists are somatostatin analogs?
|
Octreotide
Lanreotide |
|
|
Which Somatostatin analog (GH antagonsit) has the longest half life and has a greater:
-inhibition of GH -inhibition of glucagon, insulin and gastrin release Than somatostatin in the body? |
Octreotide
|
|
|
MOA: Octreotide and Lanreotide in ancromegaly and gigantisim
|
Activates Somatostatin receptor
↓ ↓ Growth Hormone ↓ ↓ IGF-1 |
|
|
MOA: Octreotide and Lanreotide in Carcinoid syndrome Diarrhea from
pancreatic VIPoma |
Activates Somatostatin receptor of tumor
↓ ↓ Released Hormones ↓ ↓ Diarrhea, flushing, etc... |
|
|
Clinical Use:
Acromegaly (adults) or gigantism (children) Carcinoid syndrome Diarrhea from pancreatic VIPoma |
Octreotide
Lanreotide (GH antagonists) |
|
|
Adverse Effects:
Inhibit gallbladder contraction, Decrease bile secretion ↓ "Biliary Sludge" and Gallstones |
Octreotide
Lanreotide |
|
|
Adverse Effects:
Inhibit secretion of insulin and glucagon ↓ Hypoglycemia, Hyperglycemia |
Octreotide
Lanreotide |
|
|
Adverse Effects:
Inhibit secretion of thyrotropin ↓ Hypothyroidsm |
Octreotide
Lanreotide |
|
|
Adverse Effects:
Alter absorption of GI dietary fats ↓ Steatorrhea |
Octreotide
Lanreotide |
|
|
What type of drug is Pegvisomant?
|
GH receptor antagonist
|
|
|
How does Pegvisomant prevent acromegaly caused by pituitary adenoma (↑GH)?
|
Blocks GH receptors on liver and other tissues
↓ ↓IGF-1 ↓ ↓GROWTH |
|
|
Excessive amounts of ____ lead to acromegaly in adults
|
IGF-1
(released by excessive GH) |
|
|
This drug normalizes serum IGF-1
concentrations in persons with acromegaly. |
Pegvisomant
|
|
|
Name the dopamine agonists (2)
|
Bromocriptine
Cabergoline |
|
|
Name the drug class:
Bromocriptine Cabergoline |
Dopamine Agonists (D2)
|
|
|
A 32-year-old female presents to her gynecologist because
she has had no menses for the past 8 months. She reports a negative pregnancy test at home. She also has frequent headaches, a change in vision, and a milky discharge from the breast. She has no medical problems and is not taking any medications. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reveals a mass, 3 mm in diameter, in the anterior lobe of the pituitary. What does she most likely have? |
Hyperprolactinemia
|
|
|
Why does a prolactinoma cause
amenorrhea (women), infertility, loss of libido, and galactorrhea (men and women)? |
HIGH levels of prolactin inibit GnRH release!
|
|
|
Prolactin is released from _____
|
pituitary gland
|
|
|
If you had a pituitary adenoma that is secreting too much prolactin, how can you treat it pharmacologically?
|
Use a D2 AGONIST
Dopamine inhibits prolactin release! |
|
|
Which of the dopamine agonist has the longest half-life with the fewest side effects?
|
Cabergoline
|
|
|
What would cabergoline do for a
pre-menopausal female with a prolactinoma? |
↓ prolactin
shrink tumor restore ovulation |
|
|
A frequent side effect of dopamine is Postural Hypotension. Please explain
|
At low doses, dopamine causes VASODILATION
|
|
|
A less frequent side effect of dopamine is digital vasospasm. Please explain.
|
Dopamine activates α-1 receptors causing vasocontriction!!
|
|
|
How could a prolactinoma cause vision loss? What drug would you use to treat?
|
It can press on the Optic Nerves
Treat with: Bromocriptine Cabergoline (Dopamine Agonists that will shrink the tumor!!) |

