![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hyper- or hypo- thyroidism?
- Irritability • Anxiety • Heat intolerance • Insomnia • Eye tearing • Dyspnea • Heart palpitations • Increased appetite, but weight loss • Diarrhea • Increased defecation • Sweating • Hair loss • Amenorrhea • Muscle fatigue • Tremors |
Hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
hyper- or hypo- thyroidism?
• Memory loss • Depression • Cold intolerance • Hoarseness • Periorbital edema • Peripheral edema • Chest pain • Decreased appetite, but weight gain • Constipation • Dry skin • Coarse hair • Menorrhagia • Muscle fatigue |
Hypothyroidism
|
|
|
What is the active form of thyroid hormone?
|
T3
|
|
|
TSH is released from the _______________
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
What cleaves T4 to active T3?
|
D1 & D2
(type 1 & 2 deiodonase) |
|
|
So, T4 is preferentially released from the thryroid gland. Explain the steps that occur for it to produce a thyroid hormone response
|
T4 converted to T3 via D2
↓ T3 enters cell via TH Receptor ↓ T3 interacts with retinoid X receptor (RXR) ↓ Binds to thyroid-hormone responsive gene ↓ Changes in critical proteins, thus, inducing a response |
|
|
D1 converts T4 --> T3 in what tissues?
|
Liver
Kidney Thyroid |
|
|
D2 converts T4 --> T3 in what tissues?
|
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle Hypothalamus Pituitary |
|
|
What hormone produces these effects?
• normal growth and metabolism • overall oxygen utilization • basal metabolic rate • carbohydrate metabolism • protein metabolism • lipid metabolism • thermogenesis |
Thyroid hormone
|
|
|
What form of Ca++ is biologically active?
|
Ionized Ca++
|
|
|
Name the hormone:
Binding of Ca++ to its receptor: - inhibits cAMP - stimulates PLC **unique situation in which an increase in [Ca] does NOT lead to exocytosis** |
PTH
|
|
|
PTH is secreted in response to (2)
|
Absolute [Ca]
Rate of fall of [Ca] (When [Ca] is getting low, PTH is released) |
|
|
PTH release:
increases/decreases bone resorption increases/decreases loss of calcium in urine increases/decreases absorption of calcium in intestines |
increases bone resorption
decreases loss of calcium in urine increases absorption of calcium in intestine |
|
|
How does low-dose PTH increase bone formation?
|
↑ β-catenin which is needed for bone formation
|
|
|
KNOW THIS TABLE
|
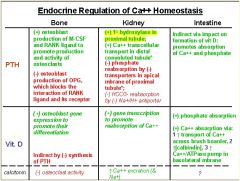
|
|
|
This hormone has an indirect effect on the formation of Vit. D:
Promotes absorption of Ca++ and phosphate in intestines |
PTH
|
|
|
How does PTH affect both osteoclasts and osteoblasts to ultimately increase bone resorption?
|
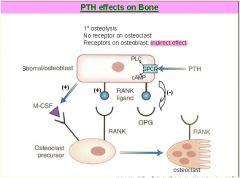
(+) osteoblast
production of M-CSF and RANK ligand to promote production and activity of osteoclasts (-) osteoblast production of OPG, which blocks the interaction of RANK ligand and its receptor |
|
|
How does PTH increase intestinal absorption of Ca++ and Phosphorus?
|
↑ 1α hydroxylase activity In PT cells
↓ ↑ synthesis of 1,25 (OH)2-Vit. D |
|
|
This hormone increases the reabsorption of Ca++ in the distal tubule and increases Ca++ ATPase and Ca+/Na+ exchanger activity on the basolateral membrane
(Net result is increased serum Ca++) |
PTH
|
|
|
Ca2+ in the lacunae is in equilibrium with plasma Ca2+ but, under the action of
_______, Ca2+ is taken up by the osteocytes, transported to the surface osteoblasts which pump the Ca2+ into the extracellular fluid, thus raising plasma Ca2+ concentrations. |
PTH
|
|
|
What is the primary mediator of hypercalcemia associated with malignacy?
|
Parathyroid Hormone Related Protein
(PTHrP) **Binds to same receptor as PTH – elicits the same response as PTH** |
|
|
This hormone:
↓ bone resoprtion; ↓ plasma Ca++ |
Calcitonin
|
|
|
This hormone:
↑ intestinal Ca++ absorption; ↑ bone resorption; ↑ plasma Ca++; (-) PTH |
Vit. D
|
|
|
Growth hormone, IGF-1, Insulin, Sex steroids (estrogens/androgens) all _____ bone formation
|
increase bone formation
|
|
|
Thyroid hormones, cytokines (IL-1) and Gluccocorticoids all _____ bone resorption
|
increase bone resorption
|
|
|
High Yield!!
|
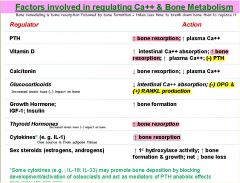
|
|
|
Reduced estrogen has what effect on osteoblasts?
|
Basically, it inhibits their formation by ↓preosteoblasts
It also ↑osteoclasts |
|
|
This is probably important
|
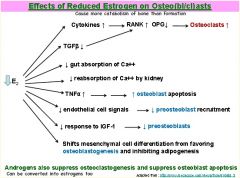
|

