![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
WNK1/WNK4 |
Pseudohypoaldosteronism Type 2 (Gordon Syndrome) |
|
|
GLI3 vs GLIS3 |
GLI3: micropenis, hypospadias, hypothalamic hamartoma, postaxial polydactyly (extra pinky). GLIS3 (transcription factor): SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM (regulates genes including SLC2A1). congenital hypothyroidism |
|
|
SLC2A1 |
GLUT1 (glucose transporter type 1): autosomal dominant, developmental delay, seizures, microcephaly |
|
|
CDKNIC gene |
1. IMAGE syndrome (gain of function): IUGR, metaphysical dysplasia, adrenal hypoplasia, genital anomalies 2. Beckwith- Weidemann |
|
|
SLC2A2 |
GLUT2 (glucose transporter type II) Fanconi-Bickel: autosomal recessive, type of GSD, hepatorenal glycogen accumulation, proximal renal tubular dysfunction, hepatomegaly, glucosuria, hypophosphatemic rickets, poor growth |
|
|
WFS1 |
Wolfram syndrome (aka DIDMOAD): SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM. DIDMOAD- DI, DM, optic atrophy, deafness |
|
|
SLC34A3 |
Hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria |
|
|
GLUD1 |
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) Activating mutation = HIHA (hyperinsulinemia hyperammonemia syndrome) |
|
|
NROB1 gene |
Encodes DAX1 protein (chromosome Xp21) X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita (AHC) |
|
|
NR3C1 vs NR3C2 |
NR3C1: generalized GC resistance. Everything in pathway elevated (lo aldosterone, lo renin). Adv BA.
NR3C2: PHA type 1 (renal. +salt wasting in infancy but resolves over them. AD). |
|
|
AAAS gene |
Encodes ALADIN protein Triple A Syndrome (Allgrove): achalasia, alacrima, ACTH resistance adrenal insufficiency. Can get neuro deficits later in life. |
|
|
ABCC8 gene |
KATP Channel subunit receptors: SUR1, Kir6.2. When SUR1 receptor activated in the beta cell, channel is closed which causes insulin release. Mutations in ABCC8 gene causes mutations in SUR1 receptor. Neonatal DM vs Hyperinsulinism (diffuse). |
|
|
PRKAR1A |
Carney Complex: multiple neoplasia syndrome. Heart (myxomas), skin (pigmentation, freckles), and endocrine (adrenal tumor, gonads, GH/PRL hypersecretion, thyroid cancer) Can develop PPNAD: primary pigmented nodular adrenal cortical disease (hypercortisolism) |
|
|
ALPL |
Produces tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (loss of function can cause hypophosphatasia) |
|
|
ABCD1 gene |
Encodes protein ALDP (transporter involved in importing VLCFA into peroxisome). Chromosome Xq28. X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (Neuro dx and/or primary AI) |
|
|
KCNJ11 gene |
KATP Channel subunit receptors: SUR1, Kir6.2. When receptors activated in the beta cell, channel is closed which causes insulin release. Mutation in KCNJ11 gene causes mutation in Kir6.2 receptor. Neonatal DM vs Hyperinsulinism. |
|
|
DHCR7 gene |
Smith-Lemli-Optiz syndrome: caused by mutation in DHCR7, which encodes 7-dehydro cholesterol reductase leading to block in cholesterol synthesis pathway (distal to HMG). AR. 7-DHC is an immediate precursor to cholesterol and is a toxic metabolite that builds up. Intellectual disability and other malformations including agenesis corpus callosum, GU (ambiguous genitalia in 46XY) |
|
|
CYP27B1 |
CYP27B1 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called 1-alpha-hydroxylase. Causes vitamin D dependent rickets type 1a. AR. |
|
|
NR3C1 |
Mutation leads to glucocorticoid resistance. |
|
|
MC2R |
MC2R gene provides instructions for making a protein called adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) receptor = type of melanocortin receptor. Mutation causes familial glucocorticoid deficiency (hypoglycemia, infections, hyperpigmentation). |
|
|
AVPR2 |
AVPR2 gene provides instructions for making a protein known as the vasopressin V2 receptor. Mutation causes X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. |
|
|
PCSK1 |
PCSK1 gene encodes enzyme PC1/3= prohormone convertase. POMC (proopiomelanocortin) to ACTH, proinsulin, proglucagon. loss-of-function mutation= obesity, malabsorptive diarrhea, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, altered thyroid and adrenal function, and impaired regulation of plasma glucose levels |
|
|
KAT6B |
Genitopatellar syndrome: abnormal genitalia (undervirilized 46XY; overvirilized 46XX), absent patella, contractures, DD, thyroid problems, CHD, hydronephrosis |
|
|
CHD7 |
CHD7 gene encodes a chromatin-remodeling factor (chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 7). Mutations lead to CHARGE syndrome (Coloboma of the eye, Heart defects, Atresia of the nasal choanae, Retarded growth and development, Genital abnormalities, and Ear abnormalities/deafness/vestibular disorder). CHD7 mutations are also found in patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and Kallmann syndrome |
|
|
AIRE |
Autoimmune regulator. Mutation leads to APS1 (hypoparathryoidism, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, primary AI) |
|
|
AIRE |
Autoimmune regulator. Mutation leads to APS1 (hypoparathryoidism, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, primary AI). APS1 aka APECED. APS2 does not have specific genetic mutation association (AI, thyroid, T1D), though there is genetic susceptibility with HLA DR3-DQ2 and DR4-DQ8 |
|
|
CYP2R1 |
CYP2R1 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called 25-hydroxylase. Mutation can lead to vitamin d dependent rickets. require increased vitamin D supplementation or calcium. Vit D to 25OHD. 25 hydroxylase is in the liver. |
|
|
PTPN11 |
PTPN11 gene provides instructions for making a protein called SHP-2. Mutation cause the autosomal dominant condition Noonan syndrome. |
|
|
GNAS 1 |
Inactivating mutation: psuedohypoparathyroidism type 1a |
|
|
NSD1 gene |
Sotos Syndrome (cerebral gigantism) |
|
|
H19 gene |
H19 is part of a cluster of genes on the short (p) arm of chromosome 11 that undergoes genomic imprinting. Changes in IC1 can cause Beckwith Wiedemann, some forms of Russell Silver. Beckwith- Abnormal methylation of the IC1 region leads to loss of H19 activity and increased IGF2 activity in many tissues. Russell- abnormal methylation leads to increased H19 and decreased IGF2 |
|
|
PAX8 gene |
Mutation leads to TSH resistance. Autosomal dominant. |
|
|
COL1A1 (ch 17) and COL1A2 (ch 7) |
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
|
|
GNAS |
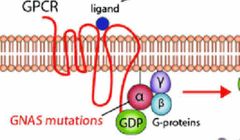
GNAS1- activating: McCune Albright. Inactivating: Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy. |
|
|
LIPA gene |
Wolman disease is caused by mutations in the lysosomal acid lipase (LIPA) gene and is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Wolman disease is characterized by infantile-onset malabsorption that results in malnutrition, storage of cholesterol esters and triglycerides in hepatic macrophages that results in hepatomegaly and liver disease, and adrenal gland calcification that results in adrenal cortical insufficiency. Unless successfully treated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), infants with classic Wolman disease do not survive beyond age one year. |
|
|
FGFR1 |
Inactivating Mutations in KAL1 and FGFR1 cause Kallmann syndrome (KS) KAL1: X linked Kallman FGFR1: autosomal dominant Kallman |
|
|
GNRHR, GPR54 gene |
mutations in the GNRHR and GPR54 genes cause idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with normal olfaction (nIHH) |
|
|
LRP5 |
Can be related to bone mass. Also occurs frequently in general population. |
|
|
TCIRG1 |
Associated with osteopetrosis |
|
|
SDHB |
Succinate dehydrogenase b mutation. Leads to paragangliomas/pheochromocytomas. Autosomal dominant with varianlenpenetranve. Metastatic disease in half of ppl with mutation. |
|
|
FOXP3 |
SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM. IPEX syndrome (immunodysregulation polyendocrinopathy X-linked). A mutation in the gene encoding the transcription factor forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) impairs the ability of regulatory T cells to discern self from nonself antigens, resulting in a clinical phenotype of enteropathy (diarrhea), eczema, type 1 diabetes, and hypothyroidism. IPEX syndrome is extremely rare with prevalence of 1:1,000,000 and frequently presents in early infancy. |
|
|
WSF1, HNF1B, FOXP3, EIF2AK3, GATA4, GATA6, GLIS3 |
SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM |
|
|
HNF1B |
SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM, renal cysts, GU (MODY 5) |
|
|
EIF2AK3 |
Walcott-Rallisom syndrome: SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM, epiphyseal dysplasia, osteopenia |
|
|
GATA4 |
SYNDROMIC NEONATAL AND CHILDHOOD DM, pancreatic hypoplasia, cardiac defects, cognitive defects |
|
|
GATA6 |
SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM, pancreatic agenesis, congenital heart defects |
|
|
IER3IP1, MNX1, NEUROD1, NEUROG3, NKX2-2, PTF1A, RFX6, SLC19A2, ZFP57 |
Other causes of SYNDROMIC NEONATAL DM IER3IP1: microcephaly, epileptic encephalopathy MNX1: neurological features NEUROD1: cerebella’s hypoplasia, sensorineural hearing loss, visual impairment NEUROG3: malabsorptive diarrhea NKX2-2: neurological features PTF1A: pancreatic and cerebellar aplasia RFX6: Mitchell-Riley Syndrome- pancreatic and gall bladder hypoplasia SLC19A2: deafness and thiamine- responsive megaloblastic anemia ZFP57: intrauterine growth restriction, neurologic features, hypomethylation |
|
|
6q24 defects- over expression of paternally imprinted allele of PLAGL1 or HYMAI |
Transient neonatal diabetes (50% resolves by 1-2yo). SGA, macroglossia, umbilical hernia. |
|
|
Mild mutations in KCNJ11 or ABCC8 |
Transient neonatal diabetes |
|
|
PDX-1 |
Neonatal dm + MODY |
|
|
HNF4A |
MODY 1. Trt: most likely to be able to stay on sulfonylurea for a while but will eventually require insulin |
|
|
GCK |
MODY 2. Insulin not released until BG 125-135 (not phosphorylation until this level). Trt: diet/none |
|
|
PDX-1, IPF-1 |
MODY 4. Absent pancreas. |
|
|
HNFB, TCF2 |
MODY 5. Can be part of Syndrome with renal cysts. |
|
|
Chromosome location of MEN1 gene |
11q13 |
|
|
CYP21A2 |
varying degrees of deficiency of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme. 5% to 10% of patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia have haploinsufficiency of TNXB, which can result in the Ehlers-Danlos phenotype. |
|
|
COL5A1 |
Ehlers-Danlos |
|
|
DHCR7 |
Mutation in gene leads to Smith Lemli Optiz Syndrome. Autosomal recessive. Elevated 7-dehydrocholesterol (enzyme deficiency between 7DHC and cholesterol). microcephaly, a cleft palate, cataracts, syndactyly of his second and third toes bilaterally, and undervirilized external male genitalia. Low maternal estriol levels (bc low fetal cholesterol leads to low fetal androgens. Fetal and maternal precursors are therefore necessary to sustain the increase in placental estrogen production throughout pregnancy bc placenta has deficiency of 17 alpha and 17 lyase and fetal adrenal has deficiency of 3 beta). |
|
|
splice-intron 3 mutations in the GH1 gene |
growth hormone deficiency (GHD) type 2. Elevated 17.5 kDa isoform of growth hormone. |
|
|
GH deficiency types |
In classic IGHD (type 1A), mutations or deletions (6.7-45 kb) in the GH1 gene lead to absent or significantly decreased GH production which causes profound early onset GHD. In IGHD type II, a mutation may occur in exon 5 (Arg183His) or a 5′-splice donor site of intron 3 resulting in skipping of exon 3. These mutations cause increased production of the 17.5 kDa isoform of growth hormone; this exerts a dominant-negative effect on the secretion of the normal 22 kDa isoform leading to manifestations of GHD. IGHD type III is transmitted in a X-linked manner and often associated with agammaglobulinemia. In IGHD type IV (or GHD type 1b), mutations or rearrangement in different exons of the GH1 gene are thought to result in a less effective GH and moderate GHD. Also, mutations in splice junction of exon 1 and intron 1 of GH-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) gene can result in autosomal recessive familial IGHD with a type IV (or type 1b) pattern. |
|
|
PRKAR1A gene |
Mutation causes Carney complex: primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease (PPNAD), cardiac myxomas, and skin lentigines. A paradoxical increase in cortisol is seen after the Liddle test in individuals with bilateral adrenocortical hyperplasia due to PPNAD. |
|
|
DAX1, WNT4 |
On X chromosome. Promote ovarian development. |
|
|
Precocious puberty |
Maternally imprinted: MKRN3, DLK1 |
|
|
Absent puberty: hypogonadotropic hypogonadism |
KISS1, GPR54 (kisspeptin receptor), GnRH receptor, LEP, LEPR, TAC3, TAC3 receptor |
|
|
Kallmann syndrome |
KAL1, FGFR1, PROK1, PROK2, CHD7, FGF8 |
|
|
LHCGR |
Testotoxicosis (familial male limited gonadotropin independent precocious puberty) |
|
|
STK11 |
Peutz- jegher. Mucosal pigmentation, sex cord stromal tumor (increased estrogen production) |
|
|
PRKARIA |
Carley complex: hyperpigmentation, adrenal hyperplasia (Cushing) |
|
|
CDC73 |
Familial isolated hyperparathyroidism (type 2: hyperparathyroidism jaw tumor syndrome) |
|
|
Russell silver |
Methylation defect ch 11p15.5. Maternal uniparental disomy ch 7 |
|
|
Prader willi |
Methylation defect ch 15q11 (loss paternal imprinting). Maternal uniparental disomy ch 15. |
|
|
Beckwith Wiedemann |
Mutation/deletion imprinted gene on ch 11p15.5 (particularly gene CDKN1C) |
|
|
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus |
AVP, AVP2, AQP2 |
|
|
HHRH- hereditary hypophosphatemic tickets with hypercalciuria |
SLCA34A3 |
|
|
Juvenile osteoporosis |
WNT, LRP5, PLS3 |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
COL1A1, COL1A2 |
|
|
FMR1 |
Fragile x |
|
|
TBX19 |
Congenital isolated central ACTH deficiency |
|
|
Congenital hypopituitarism |
PROP1, LHX3, FGF8, LHX4, ARNT2, GLI2, PCSK1, POMC. |
|
|
NPR2 inactivating mutation |
AR. Acromesomelic dysplasia Maroteaux type. Short stature, shortening of distal and mid segments of the extremities, prominent forehead, wide/depressed nasal bridge, prominent lips, normal IQ=homozygous. |
|
|
FGFR3 activating |
Achondroplasia. Shortened proximal (not distal like NPR2). AD or de novo (so less likely if concern for consanguinity like NPR2). Trident hands at birth. |
|
|
COMP mutation |
Pseudoachondroplasia- short stature, limb laxity, lower limb deformities |

