![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Location of the thyroid gland |
In front and side of the trachea C5-7 T1 vertebrae |
|
|
|
Covering of the trachea |
Inner true capsule- condensing fibers of the stroma of the gland contain dense capillary plexus Outer false capsule- splitting of the pre-treacheal fascia |
|
|
|
Suspensory ligament of berry |
Thinkening of the false capsule Connect the medial surface of the lateral lobe to the Cricoid cartilage |
|
|
|
Attachment of the pre- treacheal facia |
Hyoid bone and oblique line of the thyroid cartilage |
|
|
|
External features of the thyroid |
Two lobes from the middle of the thyroid cartilage to the 4th or 5th 6th ttacheal ring isthmus joining them across the midline at the 2nd 3rd and 4th trachea rings |
|
|
|
Weight of the thyroid |
25 gram Weight increases in woman pregnancy and menstruation |
|
|
|
Medial surface of the thyroid gland |
Nerve external and recurrent laryngeal Muscle inferior constrictor cricothyroid Artery superior and inferior laryngeal Tube treaches and esophagus Cartilage thyroid and cricoid |
|
|
|
Anterior-lateral surface or superficial surface of the thyroid |
Skin and superficial fascia Steenocledomastoid with deep cervical fascia Sternothyroid Sternohyoid Superior belly of the omohyoid Pretreacheal fascia
|
|
|
|
Posterior lateral surface of the thyroid |
Carotid sheet and its content |
|
|
|
Apex of the thryoid gland |
Bounded by inferior constrictor (medically) and sternothyroid (laterally) Superior thyroid artery and external laryngeal nerve runs close to each other |
|
|
|
Base of thyroid gland |
4th or 5th t racheal ring Inferior thyroid artery and recurrent laryngeal nerve |
|
|
|
Anterior border of the thyroid |
Anterior descending branch of the superior thyroid artery |
|
|
|
Posterior border of the thyroid gland |
Inferior thyroid artery Anastomosis of the inferior thyroid and superior thyroid Parathyroid gland Thoracic duct on the left side |
|
|
|
Levator glandular thyroideae |
Extend from the istmus to the hyoid bone Nerve external laryngeal |
|
|
|
Anterior surface of the isthmus |
Sternohyoid and sternothyriod In deep cervical fascia and anterior jugular vein |
|
|
|
Posterior surface of the istmus |
2nd and 3rd treacheal ring |
|
|
|
Superior border of the isthmus |
Anastomosis of the surperior thyriod arteries |
|
|
|
Arterial supply to the thyroid |
Superior thyroid artery from the th first ECA divide in anterior and posterior branches Posterior branch anastomosis with the ascending branch of the inferior thyroid Inferior thyroid branch of the thyrocervical trunk of the 1st part of the subclavian give off 4-5 glandular branches one supply the parathyroid gland Middle cervical ganglion Anterior to the nerve |
|
|
|
Veins to the thyroid |
Superior thyroid vein- drain in the internal jugular vein ot common facial vein Middle thyroid vein- internal jugular vein Inferior thyroid vein- left brachiocephalic vein Sometimes a 4th vein drain in the internal jugular vein |
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage to thyroid |
Superior- jugulardigastric nodes Inferior- pre-tracheal nodes All deep cervical nodes |
|
|
|
Nerve to thyrode |
Parasympathetic- vagus/recurrent laryngeal Sympathetic- 3 cervical ganglion |
|
|
|
thyroidea ima artery |
Present in 3% of ppl From the brachiocephalic trunk or arch of the aorta or right common carotid |
|
|
|
Applied anatomy of the thyroid |
Ligate the superior thyroid artery close to the gland Ligate inferior thyroid artery away from the gland |
|
|
|
Parathyroid gland |
Posterior to the lobe of the thyroid writhing false capsule Superior parathyroid Inferior parathyroid Weighs 50mg |
|
|
|
Superior parathyroid gland |
Posteriormidial to the thyroid At C6 Dorsal to recurrent laryngeal nerve Endoderm 4th pharyngeal pouch |
|
|
|
Inferior parathyroid gland |
Below the inferior thyroid artery at the lower lobe of the thyroid Above the inferior thyroid artery behind and outside the false capsule Writhing the true capsule Endoderm 3rd pharyngeal pouch |
|
|
|
Blood supply to the parathyroid gland |
Inferior thyroid artery and anastomosis between the superior thyroid Veins and lymph same as thyroid |
|
|
|
Nerve supply to parathyroid gland |
Superior and middle cervical ganglion |
|
|
|
Pyramidal lobe |
A small portion of gland substance that projects upwards from the isthmus to th left of the midline and represent a development of glandular tissue from the caudal end of the thyroglossal duct |
|
|
|
Adenohypophysis |
Pars anterior Pars intermedius ; infront and side of nuerohypophysis Pars tuberalis surround the infundibulum |
|
|
|
Functions of the hypothalamus |
Ventro medial lobe- satisfactory parasympathric Dorso Lateral- hunger feeding sympathetic |
|
|
|
Development of the adenohypophysis |
Ectoderm of the stomatodeum 3rd week End of 2nd month it loosen its connection from stomatodeum |
|
|
|
Delopmeny of the nurohypophysis |
Nuero ectoderm from the diencephalon Infundibulum Oxytocin and ADH Unmulinated |
|
|
|
Outpoching of the neuropore |
Prosencephalon forebrain become telencephalon and diencephalon Mesencephalon midbrain Rhombencephalon hindbrain |
|
|
|
Diencephalon give rise to |
Subthalamus Epithalamus Thalamus Hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Formation of the pineal gland |
Epithalamusn epiphysis |
|
|
|
Hypophysis cerebri pituitary gland |
Located in the hypophyseal fossa In the floor of the third ventricle is the Salk of the pituitary gland the infundibulum 500mg Sits in the sella turcica |
|
|
|
Pineal gland |
Calcified with age Produce melatonin Increase in darkness decrease in light |
|
|
|
Infundibulum |
Connects hypophysis to hypothalamus Pars tuberalis surrounds it |
|
|
|
Pars anterior cells |
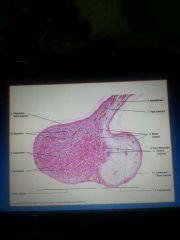
Chromophobe Chromophil- acidophils (alpha cells) Basophils (beta cells) |
|
|
|
Acidophils |
Smaller that basophils Numerous Contain somatotrophs (growth hormone) inhibition somatostatin Mammotrophs ( secrete prolactin) inhibition dopamine |
|
|
|
Basophils |
Thyrotroph - thyroid stimulating hormone Gonadotrophs - FSH LH Corticotrophs - |
|
|
|
Oxytocin |
Contracted the smooth muscles of the Uterus Participate in milk ejection reflex |
|
|
|
C cells parafollicular cells |
Release calcitonin Decrease calcium absorption Inhibiting reabsorption of bone |
|
|
|
C cells parafollicular cells |
Release calcitonin Decrease calcium absorption Inhibiting osteoclast reabsorption of bone |
|
|
|
Two type of parathyroid cells |
Chief cells - stimulate osteoclasyic bone reabsorption intestinal calcium uptake and calcium reabsorption in thr kidney Oxophilic cells - |
|
|
|
Venous drainage to the hypophysis |
Cavernous sinus which drain in the internal jugular vein contain nerve 6 |
|
|
|
Glabrous skin |
Sole and palm No hair follicles or sebaceous gland |
|
|
|
Origin of the skin |
Ectoderm - epidermis Mesoderm - dermis Neural crest -pigmented system |
|
|
|
Substances develope feom skin |
Breast Lacrimal glands Paratid gland |
|
|
|
Function of hypothalamus |
Cardiovascular system- posterior and lateral pre optic opposite effects Anger- lateral hypothalamus Sexual drive- anterior and posterior hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Venous drainage for the supra renal glands |
Right- IVC left-left renal vein |
|
|
|
Epithelium of the thyroid |
Choroidal epithelium follicular cells Simple cobiodal |
|
|
|
Foramen of Monroe |
Leads in the third ventricle |
|
|
|
Relation of the hypothalamus |
Superior thalamus Lateral internal capsule Medial 3rd ventricle coverwd by ependyma Posterior subthalamus Anterior lamina terminalis |
|
|
|
Artery to the hypothalamus |
Superior hypophysial artery of the ICA |
|
|
|
Major afferent of the hypothalamus |
Fornix- from hippocampus Stria terminalis- from amygdaloid Medial forebrain bundle- skeletal area Ventral amygdalofungal fibers- amygdala Periventricular fibers Pallido hypothalamic Autonomic ascending input |
|
|
|
Major efferents of the hypothalamus |
Mamillothalamic tract Mamillotegmental pathway Supraoptico/paraventricular/hypophyseal Fornix To subthalmic nuclie Projection to neocortex Paraventricular fibers Stria terminalis |
8 |
|
|
Tuber cinereum |
Between optic chiasma and mamilary body Laterally internal carotid grove |
|
|
|
Medial eminence |
No blood brain barrier Below the infundibulum |
|
|
|
Bone behind the pituitary |
Dorsum sellae |
|
|
|
Development of the supra renal gland |
Cortex- intermediate mesoderm 5th week Medulla- Neuro ectoderm |
|
|
|
Superarenal glands |
Lies anteriorsuperior to the upper part of the kidneys |
|
|
|
Right supra renal gland |
Pyramidal in shape Lies on the diaphragm Anterior- medial IVC Bare area of the liver Inferior- peritonium of the hepatorenal pouch
|
|
|
|
Left supra renal gland |
Crescentic shape Lies over the medial border of the left kidney above the hilium Upper part is covered by peritonium Lies on the left crus of the diaphragm Inferior- body of the pancreas and splenic vessels |
|
|
|
Blood supply to the supra renal gland |
Inferior phrenic artery- 2 or 3 branches superior supraadrenal artery Aortic artery- middle supraadrenal artery Renal artery- inferior supra renal artery |
|
|
|
Veins of the supra renal |
Left vein- connect with the inferior phrenic vein to drain in the left renal vein Right vein- IVC short 6mm |
|
|
|
Lymph drainage to the supr renal gland |
Para aortic nodes |
|
|
|
Nerves to the supra renal gland |
Preganglionic sympathetic via celiac plexus |
|
|
|
Content of the cavernous sinus |
Nerve 3- occulomotor " 4-trachular " 5-ophtalmic maxillary " 6- abducent |
|
|
|
Relation of the pineal |
Anterior- 3rd ventricle Posteroinferiorly- superior cerebellar cistern Superioly- vein of Galen internal cerebral vein stria modulates splenuium of corpus callosum Inferior- superior colliding of the midbrain |
|
|
|
Melatonin |
Blocks gonadotrophin |
|
|
|
Blood supply to the pineal gland |
Choroidal artery |
|
|
|
Pars nervosa |
Contain pituracytes Sinusoidal space Herring body |
|
|
|
Two types of hypophysis |
Andenohypophysis Nurohypophysis |
|
|
|
Neurohypophysis |
Smaller than adenohypophysis Pars nervosa posterior to the nurohypophysis Infundibular stem Median eminence |
|
|
|
Relations to the hypophysis |
Superior- Diaphragma sellae Infundidibular recess of the t hired ventricle Optic chiasma Anterior communicating artery Inferior- hypophysial fossa Lateral- cavernous sinuses and its contents
|
|
|
|
Artery to hypophysis |
Superior spit in the midial eminence supply the adenohypophysis infundibulum and ventral hypothalamus and inferior hypophysial nurohypophysis artery of the ICA |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Ventral part of the diencephalon Floor of the third ventricle Below the hypothamic sulcus |
|
|
|
Epithalamus |
In relation to the posterior part of the roof of the third ventricle Form the pineal gland |
|
|
|
Cells of the pineal gland |
Pinalocytes and astrocyte |
|
|
|
Cells of the pineal gland |
Pinalocytes and astrocyte |
|
|
|
Blood supply to the pineal gland |
Pineal arteries of the posterior choroidal arteries |
|
|
|
Nerve supply to pineal gland |
Superior cervical ganglion |
|
|
|
Foramen caecum |
Remittance of the thyroglossal duct |
|
|
|
Parathyroid production starts |
12th weeks |
|
|
|
Formation of the zones of the supra renal gland |
Zona glomerulosa proliferate to form the other two zones at 12 year its gully develops |
|
|
|
3rd pharyngeal pouch |
5th week thymus and inferior parathyroid gland |
|
|
|
Development of the hypothalamus |
Diencephalon 7thweek |
|
|
|
Mamilary body |
Short term memory |
|
|
|
Fornix |
Dives in the hypothalamus Divide the hypothalamus into a lateral and medial zone Then David it to a pre optic 1nucleus supra optic 4 nuclei tuberal 3 nuclei and mamilary region 2 nuclei anterioposterior Connects the hippocampus to the mamilary body |
|
|
|
Supraoptic nuclei |
Paraventricular Anterior nucleus Supraoptic Suprachiasmatic |
PASS |
|
|
Tuberal region nucleus |
Dorsomedial Ventromedial Arcuate (infundibulum) |
|
|
|
Mamilary nucleus |
Posterior Mamilary nucleus |
|
|
|
Pre optic region |
Pre optic nucleus Release GnRH |
|
|
|
Supraoptic region function |
Paraventricular and supra optic Water balance ADH and oxytocin Diebetes insipidus Corticotropin releasing hormone in response to stress Anterior nucleus Parasympathric activity Heat lost Suprachiasmatic nucleus Control melatonin Circadian rhythms |
|
|
|
Tuberal region function |
Dorsomedial Eating Too much stimulation cause obesity and savage behavior Ventromedial Satisfactory Destruction result in obesity Arcuate nucleus Hypothalmic releasing factors |
|
|
|
Mamilary region function |
Mamilary nucleus Hemorrhagic lesions Posterior nucleus Sympathetic Heat gain |
|
|
|
Cricothyroid muscle |
External laryngeal nerve Lengthen vocal cord and high pitch |
|
|
|
Cutting of the recurrent laryngeal nerve |
No abductors of the vocal cord |
|
|
|
Germ layer |
Endoderm- pouches Mesoderm- arches Ectoderm- cleft |
|
|
|
Cavernous sinus |
Between the supraorbital fissure and the foramen labrum Contain internal carotid artery Nerve 3 - occulomoter 4- tracular 5- maxillary and ophthalmic 6- abducent |
|
|
|
Posterior perferating substance |
Behind the mamilory body |
|
|
|
Rathicks pouch |
Persistent after birth cause cyst |
|
|
|
Lamina terminalis |
Represent the closing of the neural pore 24 days |
|
|
|
Vein to the posterior hypothalamus |
Inferior hypophysial vein |
|
|
|
Delphia nodes |
Infront thyroid |
|
|
|
Fascia covering the suprarenal glands |
Jarotors fascia |
|
|
|
Distence of the supra renal glands |
4cm |
|

