![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the natural androgen?
|
- Testosterone
- Dehydroepiandrosterone - Androstenedione - Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) |
|
|
What are the non-natural androgens?
|
- Testosterone esters (Cypionate)
- 17-Alkylated Androgen (Stanozolol) |
|
|
What are the Anti-Androgens?
|
- Flutamide
- Finasteride |
|
|
What are the drugs used for impotence?
|
- Alprostadil
- Sildenafil - Vardenafil - Tadalafil |
|
|
How does Testosterone mediate its effects directly and indirectly?
|
- Direct: binds androgen receptor
- Indirect: conversion to DHT and then binding to the androgen receptor |
|
|
What can Testosterone be converted to?
|
- 5α-Reductase: T → DHT
- Aromatase: T → Estradiol |
|
|
What are the types of 5α-Reductase? Location?
|
- Type 1: non-genital skin, liver, and bone
- Type 2: urogenital skin in men and genital skin in men and women |
|
|
What is the other name for the androgen receptor? What kind of receptor is it?
|
- NR3A = Androgen Receptor
- Member of the Steroid Nuclear Receptor family |
|
|
What happens to the Androgen Receptor when there is no ligand?
|
- Androgen receptor is located in the cytoplasm
- Associated with Heat Shock Protein complex |
|
|
What happens to the Androgen Receptor when there is ligand (T or DHT)?
|
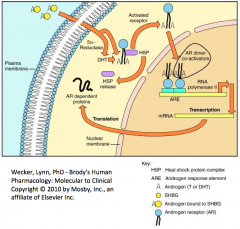
- T or DHT binds to the ligand-binding domain
- Androgen receptor dissociates from the Heat Shock Protein complex - Receptor dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus - Dimer then binds via the DNA-binding domain to androgen response elements on certain responsive genes - Ligand-receptor complex recruits coactivators and acts as a transcription factor complex, stimulating or repressing gene expression |
|
|
What accounts for the varying action of androgens in different tissues?
|
- Higher affinity with which DHT binds to and activates the androgen receptor compared to T
- Tissue-specific transcription factors (both activators and repressors) |
|
|
What percent of the circulating estradiol in men is from testosterone conversion via Aromatase?
|
85% of circulating estradiol is converted from T
|
|
|
What happens in men that do not express Aromatase?
|
- Epiphyses do not fuse and long-bone growth continues indefinitely
- Osteoporosis |
|
|
How does an aromatase deficiency compare to an estrogen receptor defect?
|
- Both cause bone abnormalities (eg, epiphyses don't fuse, long bone growth continues indefinitely, and osteoporosis)
- Only aromatase deficiency can be corrected with administration of estradiol - Estrogen-receptor defect will not be corrected by administration of estradiol |
|
|
What is important for the regulation of epiphyseal growth plate closure?
|
Testosterone conversion to estradiol
|
|
|
What happens when you take Testosterone orally? Why?
|
- Testosterone can not be taken in sufficient amounts orally to maintain normal serum T concentrations in hypogonadal men
- This is because T has a high first pass effect |
|
|
What pharmacologic preps are there for Testosterone?
|
- Testosterone patches, gels, and buccal tablets
- Testosterone esters (Cypionate) - 17α-Alkylated compounds (Stanozolol) |
|
|
What drug is a Testosterone ester? How is it administered? How is it different from regular T?
|
Cypionate
- Injected IM - Esterify a fatty acid to the 17-hydroxyl group of T making it more lipophilic than T |
|
|
How is Cypionate different from Testosterone? Effect?
|
- Testosterone esterified with a fatty acid to the 17 hydroxyl group
- This makes the compound more lipophilic - Ester hydrolyzes in vivo and results in serum testosterone concentrations that range from higher than normal in the first few days after the injection to low normal just before the next injection |
|
|
Which drug has an ester that is hydrolyzed resulting in slow testosterone release?
|
Cypionate
|
|
|
What drug is a 17α Alkylated compound?
|
Stanozolol
|
|
|
How is Stanozolol administered? How is it modified from Testosterone?
|
- Oral
- Add an alkyl group to the 17 position of testosterone |
|
|
What is the effect of the 17α-alkyl group on Testosterone (Stanozolol)?
|
Slows hepatic catabolism, less androgenic than testosterone itself
|
|
|
What is the side effect of Stanozolol?
|
Hepatotoxicity
|
|
|
What are the therapeutic uses of androgens?
|
- Male hypogonadism
- Testosterone deficiency |
|
|
What is the most important aspect of monitoring the efficacy testosterone treatment?
|
Measuring serum testosterone concentration
|
|
|
What is the goal of testosterone therapy?
|
Mimic as closely as possible the normal serum testosterone concentration
|
|
|
What are the undesirable effects of testosterone therapy?
|
- Acne
- Gynecomastia - More aggressive sexual behavior |
|
|
When administering testosterone to testosterone deficient boys at the type of puberty, what do you need to consider?
|
- Consider the epiphyseal closure and permanent cessation of linear growth
- Height and growth hormone status of the patient must be considered - Boys who are short because of GH deficiency should be treated w/ GH before their hypogonadism is treated with T |
|
|
What are some other (non-FDA approved) uses of testosterone?
|
- Male senescence
- Women with low serum T - Muscle wasting d/t AIDS - Blood dyscrasias - Angioedema - Improve athletic performance |
|
|
What is male senescence? Why would you treat with T?
|
- Men whose serum levels of T are decreased due to age
- Use T to increase bone mineral density and lean mass and decrease fat mass |
|
|
When would you use T in women?
|
- Women with low serum T
- Possibly increase bone mineral density, fat-free mass, and sexual function |
|
|
Why would you use T in AIDS patients?
|
To treat muscle wasting associated with AIDS, which is often accompanied by hypogonadism
|
|
|
What blood dyscrasias would you use T to treat? When?
|
- Hemolytic anemia and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Use androgens (such as danazol) as adjunctive treatment when they are refractory to first-line agents |
|
|
What causes Angioedema? How would you treat?
|
- Caused by hereditary impairment of C1-esterase inhibitor or acquired development of antibodies against it
- 17-alkylated androgens like Stanozolol, stimulates hepatic synthesis of the esterase inhibitor |
|
|
What forms of testosterone are abused by athletes?
|
Testosterone precursors:
- Androstenedione - Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) |
|
|
What are the most commonly detected anabolic-androgenic steroids in competitive athletes?
|
- Tesosterone
- Stanozolol - Androstenedione - Dehydroepiandorsterone (DHEA) |
|
|
How effective are anabolic steroids in athletes?
|
- Men who receive testosterone increased muscle strength compared to those who took placebo
- Men who exercised simultaneously experienced even greater increase in muscle strength |
|
|
What are the effects of anabolic steroid abuse?
|
- Suppress gonadotropin secretion, suppressing endogenous testicular function
- Decreases endogenous testosterone and sperm production, decreasing fertility - Diminishes testicular size - Decreases HDL and increases LDL |
|
|
What are the side effects of anabolic steroid abuse?
|
- Decreased fertility
- Erythrocytosis - Diminished testicular size - Gynecomastia (except DHT) - Hepatotoxicity (17-alkylated androgens) - Decreased HDL and increased LDL - Psychological disorders - Sudden death d/t cardiac disease - Stunting of linear growth (in those who have not yet close their growth plates) - Women get virilization: facial and body hirsutism, male pattern hair loss, and acne - Phallic enlargement in boys and clitoral enlargement in girls |
|
|
Does fertility return after stopping anabolic steroid abuse?
|
Testosterone and sperm production usually returns to normal within a few months of discontinuation, but may take longer
|
|
|
Which form of T does not cause gynecomastia when taken in excess? Why?
|
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) - has a modification so that it can't be aromatized
|
|
|
What are the inhibitors of testosterone secretion?
|
Leuprolide = GnRH analog
|
|
|
What is the action of Leuprolide?
|
- GnRH analog that inhibits Testosterone secretion by inhibiting LH secretion
- Transient stimulation of gonadotropin secretion, which then down-regulates GnRH receptor and inhibits gonadotropin secretion |
|
|
What is Leuprolide used for?
|
- Treatment of advanced prostate cancer
- Management of endometriosis - Treatment of anemia caused by uterine fibroids - Central precocious puberty |
|
|
What are the side effects of long acting GnRH analogs (Leuprolide)
|
- Suppression of gonadal steroidogenesis including hot flashes and decreased bone density
- Vaginal dryness and atrophy in women - Erectile dysfunction in men |
|
|
What is the androgen receptor antagonist?
|
Flutamide
|
|
|
What is the effect of Flutamide?
|
- Androgen receptor antagonist
- When used alone, increases LH secretion, which stimulates higher serum T concentration |
|
|
With what should Flutamide be used? Function?
|
In conjunction with a GnRH analog (Leuprolide) for:
- Metastatic Prostate Cancer |
|
|
What are the uses of Flutamide?
|
- Metastatic prostate cancer with a GnRH analog (Flutamide)
- Hirsutism in women (off label) |
|
|
What are the side effects of Flutamide?
|
- Galactorrhea (9-42%)
- Breast tenderness - Gynecomastia - Hot flashes - Impotence - Decreased libido - Tumor flare * Black box warning of HEPATIC FAILURE |
|
|
What is the 5α-reductase inhibitor drug?
|
Finasteride
|
|
|
What is the action of Finasteride?
|
5α-Reductase Antagonist, especially Type II
- Blocks the conversion of T to DHT, especially in male external genitalia |
|
|
What are the uses of Finasteride? Side effects?
|
Uses
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia - Male Pattern Baldness Side Effects - Impotence - Decreased libido |
|
|
What drugs are used for impotence?
|
- Alprostadil
- Sildenafil - Vardenafil - Tadalafil |
|
|
How is Alprostadil administered? Use?
|
- Intracavernous injection or urethral suppository
- Used for treatment of impotence - Erection will last 1-3 hours and is sufficient for sexual intercourse |
|
|
What are the side effects of Alprostadil?
|
- Penile pain
- Urethral burning |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil?
|
Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors:
- Nerves and vascular endothelial cells in the corpus cavernosum produce NO during sexual arousal - NO stimulates formation of cyclic GMP, which relaxes smooth muscle of the corpus cavernosum and penile arteries - Causes corpus cavernosum engorgement and erection - Cyclic GMP accumulation is enhanced by inhibiting the cGMP specific PDE5 |
|
|
What is the use of Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil?
|
Improves erectile function (penile engorgement) in patients with erectile dysfunction
|
|
|
What is the time to onset of action and duration of the PDE5 inhibitors?
|
Tadalafil has a longer time to onset of action and duration (36 hours) than other PDE5 inhibitors (2-4 hours)
|
|
|
What happens in men taking anti-anginal therapy AND PDE5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction?
|
Combination of Sildenafil and other PDE5 inhibitors with organic nitrate vasodilators can cause extreme hypotension
|
|
|
What are the side effects of Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil?
|
- Extreme hypotension in patients also taking nitrate vasodilators
- Headache - Flushing - Rhinitis - Dyspepsia - Sildenafil and Vardenafil can cause visual disturbances |
|
|
How can Sildenafil and Vardenafil cause visual disturbances?
|
They can also weakly inhibit PDE6, the enzyme involved in photoreceptor signal transduction causing visual disturbances (changes in the perception of color hue or brightness)
|
|
|
How are PDE5 inhibitors (Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil) metabolized? Implications?
|
CYP3A4 - toxicity may be enhanced in patients who receive other substrates of this enzyme (including macrolide and imidazole antibiotics, some statins, and antiretroviral agents)
|
|
|
When are PDE5 inhibitors contraindicated?
|
In patients taking organic nitrate vasodilators and should be used in caution in patients taking adrenergic receptor antagonists
|
|
|
What hormone is responsible for male pattern balding? What drug can treat this?
|
- DHT is responsible for it
- Finasteride can treat it |
|
|
What hormone is responsible for prostate hyperplasia?
|
DHT
|

