![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What kind of glands are mammary glands?
|
- Accessory glands of the skin, specialized to secrete milk
- Compound tubuloalveolar glands |
|
|
How are mammary glands arranged?
|
- Each gland is arranged in 15-25 lobes
- Surrounded by varying amounts of adipose and CT (interlobular CT) |
|
|
How are the lobes in the mammary glands organized?
|
Lobes are subdivided into lobules that contain alveoli and ducts that are separated by a more cellular CT (intralobular CT)
|
|
|
What kind of duct opens onto the surface of the nipple to drain milk?
|
Lactiferous duct
|
|
|
Where is the milk generated before draining through the lactiferous duct?
|
Alveoli
|
|
|
What feature is seen in each lactiferous duct?
|
Terminal expansion called the Lactiferous Sinus, just deep to the surface of the nipple
|
|
|
What is the term for excessive development of the male mammary glands? What does this indicate?
|
Gynecomastia - indicates endocrinopathy
|
|
|
What are the age related breast stages in females?
|
- Pre-pubertal breast
- Puberty - Sexual maturity - Menopause |
|
|
What are the characteristics of the pre-pubertal breast?
|
Rudimentary, inactive lactiferous ducts and sinuses
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the breast during puberty?
|
Hormones stimulate the deposition of adipose tissue in female breasts and enhance the development of the lactiferous ducts and alveoli
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the breasts in the sexually mature female?
|
Glandular tissues undergo changes during each menstrual cycle
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of the breasts during menopause?
|
Atrophy of the glandular tissue, adipose tissue and interlobular connective tissue
|
|
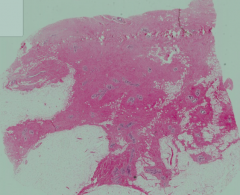
What stage of breast tissue is this? How can you tell?
|
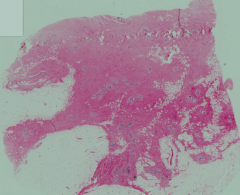
Human Pre-Pubertal Breast
- Major components of breast tissue are collagen and adipose tissue - Lobules of mammary gland contain undeveloped ductules and intralobular CT - Intralobular CT is much finer and less abundant than the interlobular CT |
|
|
What are the components of the mammary gland during the pre-pubertal stage?
|
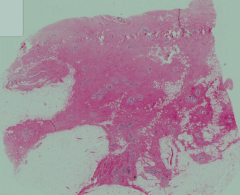
- Undeveloped ductules
- Intralobular CT |
|
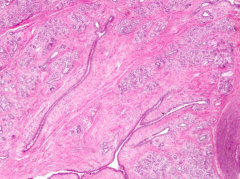
What stage of breast tissue is this? How can you tell?
|
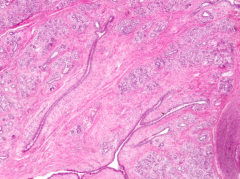
Sexual maturity - INACTIVE:
- Alveoli are not well developed - Dense fibrous CT and adipose tissue (interlobular CT) are abundant |
|
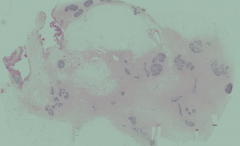
What stage of breast tissue is this? How can you tell?
|
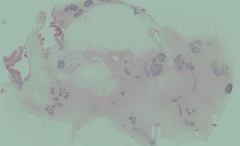
Sexual Maturity - INACTIVE:
- Predominant components are collagen and adipose tissue - Branching of the ductules has occurred |
|
What happens to the ductules of mammary glands once the pre-pubertal girl (picture) becomes sexually mature?
|
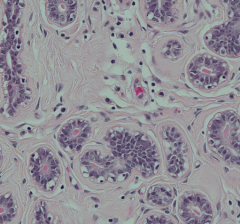
Branching of the ductules occurs
|
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the ductules in the mammary glands?
|
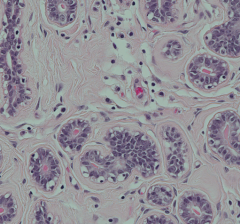
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- There are also flattened nuclei of Myoepithelial cells adjacent to the epithelium of the ducts |
|
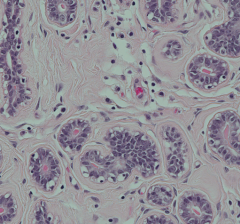
What kinds of cells are adjacent to the epithelium of the ducts of the mammary glands? How can you spot them?
|
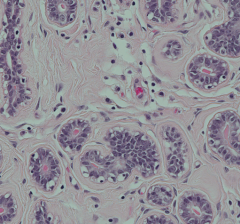
Myoepithelial cells - they have flattened nuclei and are adjacent to the simple cuboidal epithelium
|
|
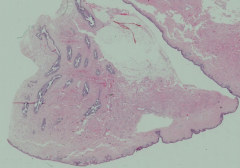
What is this structure?
|
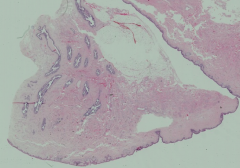
Nipple
|
|
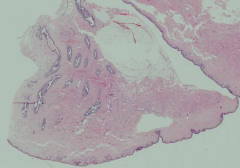
What are the structures that are cut in cross and longitudinal section?
|
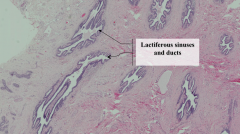
Lactiferous sinuses and ducts
|
|
|
What are the components of the human nipple?
|
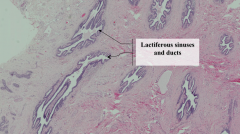
- Collagen and elastic tissue
- Stoma contains bundles of smooth muscle - Sebaceous glands are associated with skin that covers the nipple |
|
|
What kind of glands are found in the skin that covers the nipple? Is this skin thick or thin?
|
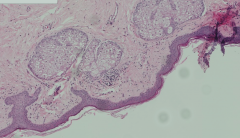
- Sebaceous glands
- Thin skin |
|
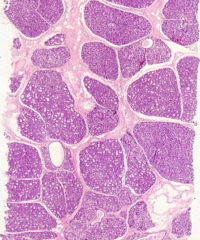
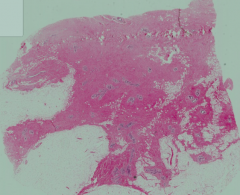
What stage of breast tissue is this? How can you tell?
|
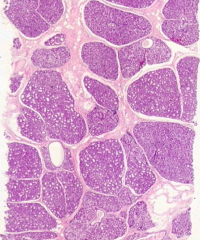
Human mammary gland during pregnancy
- Numerous, well-developed alveoli are seen in the mammary gland tissue - CT between lobules (interlobular) is reduced - Intralobular CT is more cellular than fibrous - Actively secreting alveolar cells have hypertrophied |
|
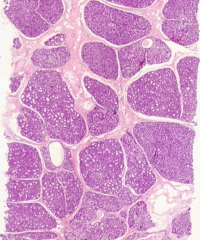
What leads to well-developed alveoli in the mammary gland tissue of pregnant women?
|
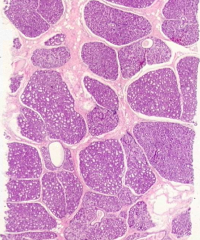
- Duct branching
- Alveolar growth in the terminal portions of the gland - CT between lobules is reduced |
|
|
What happens to the intralobular CT in pregnancy?
|
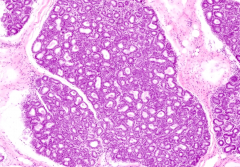
Intralobular CT is predominantly cellular, rather than fibrous, and includes plasma cells, lymphocytes, and eosinophils
|
|
|
Where might you find the secretory product of the alveolar cells during pregnancy?
|
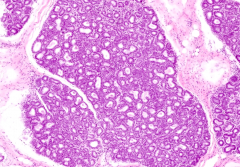
Lumen of some alveoli
|
|
|
What kind of WBCs are found in the intralobular CT of the mammary gland during pregnancy?
|
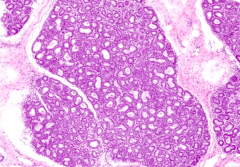
- Plasma cells
- Lymphocytes - Eosinophils |
|
|
What are the characteristics of the epithelium of the alveoli?
|
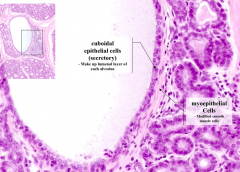
Two layers
- Cuboidal epithelial cells (secretory cells) - lumenal layer - Myoepithelial cells (modified smooth muscle cells) - outer layer |
|
|
What are smaller ducts lined with as compared to larger ducts?
|
Smaller ducts:
- Simple columnar or cuboidal epithelium Larger ducts: - Some may be Lactiferous ducts - Lined with stratified cuboidal epithelium |
|
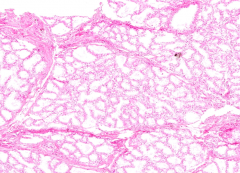
What stage of breast tissue is this? How can you tell?
|
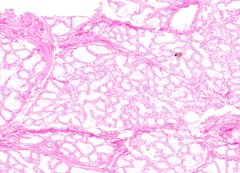
Mammary gland - LACTATING
- Interlobular CT is less abundant and more compressed than in an inactive mammary gland - CT within lobule (intralobular) is less abundant too |
|
|
What are the characteristics of alveolar cells in a mammary gland that is lactating?
|
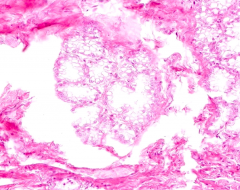
The large cells of the alveoli appear vacuolated because solvents remove lipid droplets in the apical cytoplasm during tissue processing
|
|
|
What happens to the lipids found in the alveoli of lactating mammary glands?
|
Apocrine Secretions: lipids are released into the lumen with a tiny amount of cytoplasm
|
|
|
Where is the protein component of milk synthesized? How is it secreted?
|
- Synthesized in rER
- Packaged into secretory granules and released by exocytosis = Merocrine Secretion |
|
|
What does the term Apocrine Secretion refer to?
|
Process of lipids being released into the lumen with a tiny amount of cytoplasm
|
|
|
What does the term Merocrine Secretion refer to?
|
Process of the protein product of milk being synthesized in rER, packaged into secretory granules, and released by exocytosis
|
|
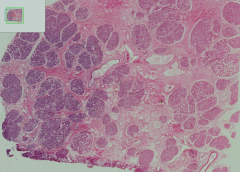
What stage of breast tissue is this?
|
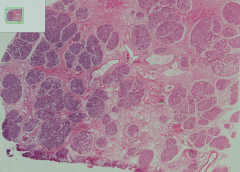
Section of breast in the lactation phase
|
|
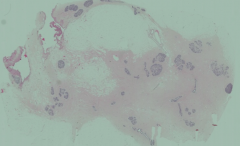
How does a lactating breast compare histologically to the inactive mature breast (this picture)?
|
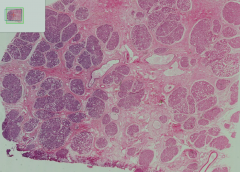
- In lactating breast (picture), alveoli are present and dilated
- Interlobular and intralobular CT have become compressed by the expanding mammary gland tissue |
|
|
What hormone regulates lactation? Source?
|
Prolactin from the lactotrophs of the adenohypophysis
|
|
|
Normally prolactin secretion is inhibited by what? How is this affected by suckling?
|
- Dopamine inhibits the release of prolactin
- Suckling blocks Dopamine release from the hypothalamus |
|
|
What stimulates the myoepithelial cells to contract? Source?
|
Oxytocin, released from neurohypophysis
|
|
|
What is the action of Oxytocin on the breast?
|
It facilitates ejection of the milk from the acinar cells by stimulating myoepithelial contraction
|
|
|
What do male patients with cirrhosis frequently exhibit related to the breast?
|
Gynecomastia
|
|
|
Why do male patients with cirrhosis often have gynecomastia?
|
- Diminished catabolism of androstenedione by the diseased liver means more substrate for the conversion of androgens to estrogens
- This results in higher circulating levels of estrogens and leads to mammary gland development in males |

