![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osteoporosis: Menopause & aging effects
|
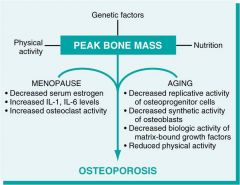
|
|
|
osteogenesis imperfecta
|
brittle bone dz
*abnormal dev of type 1 collagen *multiple bone fractures, blue sclear, hearing loss, dentinogenesis imperfecta, scoliosis, short stature *subtypes: OI type 1: compatible w/ life OI type 2: perinatal lethal OI type 3: progressive & deforming but compatible w/ survival *OI type 4: compatible w/ survival |
|
|
Osteopetrosis
|
marble bone dz & albers schonberg dz
*rare bone disorder w/ reduced bone resorption & diffuse symmetric skeletal sclerosis due to impaire formation/fxn oclasts. *stonelike/brittle bones *mutation interfere w/ acidification of oclast resorption pit needed to dissolve Ca hydroxyapatite in matrix *No medullary canal on bones. Bulbous ends of long bones (erlenmeyer flask deformity). small neural foramina--> compressed nerves *primary spongiosa fills medullary cavity interfereing w/ hematopoietic bone marrow & prevent formation of mature traveculae. deposited bone not remodeld & woven into archeture. These lead to brittle bones *dep on subtype: oclasts inc dec or normal |
|
|
Infantile Malignant osteopetrosis
|
*fracture anemia, hydrocephaly--> postpartum mortality
*if child survives: Cranial nerve defects, inadequate bone marrow--> severe infx. Extramedullary hematopoiesis --> hepatosplenomegaly. *milder forms may not be detected until adolescence or young adulthood. |
|
|
Osteoporosis
|
* Dec in bone mass. Structural change--> bone fragility.
*loss of horizontal trabeculae & thick vertical trabeculae *GENETICS: RANKL, OPG, RANK--> regulate oclasts. MHC locus & estrogen receptor *AGE: oblasts in elderly= dec prolif & biosynth *Dec weight bearing exercise & adolescents w/ dec Ca+ diet *HORMONE: decade after menopause: estrogen dec--> +CK--> inc RANKL & dec OPG--> inc oclasts--> yearly inc lost bone mass |
|
|
Osteomalacia
|
* Rickets
*children w/ open epiphyseal plates--> shape deformity on xray *accum unmineralized bone by defective mineralization. * dec Vit D--> Dec serum Ca/P |
|
|
Paget's :)
|
* >55yo, England/Australia/ N. Europe
*affect L-S spine, pelvis, femur, skull *Cause: uncertain, genetic & env connection *15% have family hx. *mut in SQSTM1 gene (inc + by RANK--> inc oclast & inc susceptibility to dz *may dev secondary osteosarcomas/ fibrosarcomas *osteolytic phase: marrow replaced by CT w/ oclasts *mixed phase: bone resorption & bone formation *osteosclerotic phase: irreg bone deposition--> mosaic pattern *usu asymp. Serum alkaline Phosphatase inc. hypervascular bone lesions: warm skin, inc CO. enlarged head: headache, visual disturb, deaf. Transverse fractures of long bones |
|
|
Osteomyelitis
|
*Bacterial: STAPH AUREUS. e. coli, klebsiella or proteus.
*salmonella: sickle cell pt * h influenza: newborns *pseudomonas: IVDA *TB: pott's dz * hematogenous spread. direct extension from joint/tissue. traumatic implantation from surgery/trauma *Acute: Nphil inflam, necrosis, sub periosteal abscesses, disrupt blood supply, spread to joint capsule *Chronic: sequela of Acute infx. Sequestrum = residual necrotic bone Involucrum= rim of reactive bone Brodie's Abscess: abscess surrounded by sclerotic bone *bacteria may be present in sequestered area |
|
|
Osteomas
|
* 40-50y, M>F
*exophytic lesion of dense mature bone on flat bonse of skull/face. may protrude into sinuses *assoc w/ Gardner's Syndrome. *cosmetic problems. not malignant |
|
|
Osteoid Osteoma
|
* M>F, 10-30yo
*femur, tibia in metaphysis *painful, relieved by aspirin, central radiolucent nidus. *high levels of prostaglandins |
|
|
Osteoblastoma
|
*sim to osteoid osteoma
*large central nidus *spine, large bones of legs. * PAINLESS *may be diff to distinguish from osteosarcoma |
|
|
osteosarcoma
|
*most common primary bone malignancy (except hematopoietic lesions)
*M: F = 3: 2, usu 10-25y w/ 2nd peak >40y *metaphysis, lower femur, upper tibia *malignant cells form osteoid. Extend from marrow to cortex to soft tissie to epiphysis to joint *Codman's triangle: elevation of periosteum. *may have satellite nodules *destroy preexisting bone/grow around it. *met via blood to Lung or other bones. Regional LN not involved *predispositions: Paget's Dz (>50yo), Radiation: 10yr post, Chemo: children w/ retinoblastoma. Trauma does not cause but brings attention to it. |
|
|
Osteochondroma
|
* exostoses
*10yo, M>F *metaphysis, lower femur, upper tibia, humerus. *grow in opposite direction of joint. cap of cartilage w/ bone underneath. *asymp. spont regress. Rare malig transform if single. If multiple = Garder's syndrome & inc malig. |
|
|
Chondroma
|
*common benign lesions
* Xray = popcorn like densities *small bones: hands, feet, phalanges *usu not painful. *lobules of hyaline cartilage, may have calcification *syndromes w/ mult chondromas= inc risk malig 1. Ollier's dz: U/L chondromas & ovarian tumors 2. Maffucci's syndrome: chondromas & soft tissue hemangiomas |
|
|
chondroblastoma
|
*10-20yr, M>F
*painful *Epiphyseal: distal femur, proximal humerus. Very cellular. Rarely aggressive *immature cartilage=chicken wire pattern |
|
|
chondromyxoid fibroma
|
* young adults, long bones, small bones of feet
* xray: well defined lytic lesion *solid yellowish to tan. reselmble low grade chondrosarcoma *recur if not completely removed |
|
|
Chondrosarcoma
|
*30-60yo = pelvis, ribs, shoulder
*In children = extremities *xray: osteolytic lesions w/ calcification *2+ nuclei per cell. permeate Bone marrow *must correlate w/ xray. better prognosis than osteosarcoma. Recurrence may occur up to 20y later. Met to lung, usu not LN via blood |
|
|
Giant cell tumor
|
* F> M, 20-30y, Asian>western
*most at metaphyseal-epiphyseal jxn. Ends of bones: lower femur, upper tibia, lower radius. *xray = lytic w/o sclerosis *solid, tan --> brown w/ hemorrhage *giant cells in spindled stromal cells. *all potentially malignant. Met to lung. Radiation tx may induce malig. |
|
|
Ewings Sarcoma
|
* 5-20yo
*long bones, pelvis, ribs, vertebrae *common bone malig in children *t (11:22) translocation *arise in medullary cavity. involve entire bone. *xray: onion skin layering of new bone *Gross= white, fleshy *micro: sheets of small uniform cells separated by strands of fibrous stroma. "small blue cell tumor *met to lungs, other bones, cns, LN |
|
|
chordoma
|
*M>F, 40-50 yo
* malignant, destroys bone * Gross: gelatinous, soft, hemorrhage *micro: cells grow in cords & lobules separated by mucoid matrix *physaliferous cells: large tumor cells w/ bubbly cytoplasm *met late to skin, bone. *vertebral bodes, discs, sacrum. sphenooccipital area in kids |
|
|
fibrous dysplasia
|
*uncommon benign tumor like lesion of bone
1. monostotic: most common, teens, ribs, tibia, femur. 2. polystotic: craniofacial area, pelvis, femur. 3. polystotic w/ endocrine abnorm: least common 4. McCune-Albright syndrome: UL bone lesions, cafe au lait spots, precocious puberty *lesions circ &radiolucent. Prolif of fibroblasts & collegen w/ islands of woven bone. may fracture. asymp |
|
|
Adamantinoma
|
*tibia femur ulna fibula
* in jaw = ameloblastoma *poorly defined lytic lesion. sclerosis outlining lucent areas. spindle cells surround basaloid cells. *low grade malig: local recurrence, rare LN met |
|
|
Plasma cell myeloma
|
most common primary tumor of bone skull spine & ribs
|
|
|
Malignant lymphoma
|
patchy cortical & medullary involvement
most = large cell type |
|
|
hemangioma
|
common
skull, vertebrae, jaw |
|
|
Metasteses
|
*most common of all malig tumors of bone
*mostly from breast, lung, prostate, *70% in axial skeleton, 30% in extremities. *usu osteolytic *osteoblastic: prostate, bone *painful |
|
|
osteoarthritis
|
*enlargement &disorganization of chondrocytes
*splitting of articular surface, erosion of articular cartilage, eburnation of underlying bone, *osteophytes: bony excrescences on bone margins *clinic: hips knees lumbar cervical vert. prox/dist interphalangeal joints of fingers. first carpometacarpal joints, first tarsometatarsal joints. most <50yo = asymp. deep aching pain |

