![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an atomic number? Element?Electron Configuration?
|
the number of protons in an atom of an element
a substance made from one kind of atom, with unique chemical properties the arrangement of electrons in an atom. |
|
|
What do atoms in a row & columns have in common?
|
Their atoms have the same number of
occupied shells. Their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. |
|
|
What are the correct atomic number and mass for boron?
|
5 and 11
|
|
|
Use your periodic table to identify the element that has atoms that contain 19 protons and 20 neutrons?
|
Potassium (K)
|
|
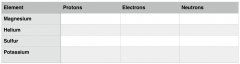
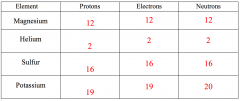
Use your periodic table to work out the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in some different elements. Fill out the table below.
|
|
|
|
How to work out the number of sub atomic particles in sulfur.
|
The atomic number is the number of protons. This is equal to the number of electrons in an atom. If I subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass, I get the number of neutrons.
|
|
|
Describe two ways in which you can use the electron configuration 2.8.5 to identify an element on the periodic table.
|
(i)The number of digits tells me the period. The last digit tells me the group.
(ii) Adding together the total number of electrons (2 + 8 + 5 = 15) gives me the number of protons, which is the atomic number. The elements are arranged in order of their atomic number so then I find element 15. |
|
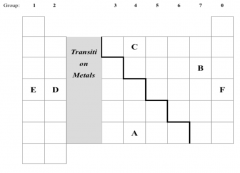
Which letter in the diagram corresponds to the position of potassium in the periodic
table? (b) Shade the letter for the element that exists as a diatomic molecule. (c) Which letters in the diagram represent elements in the same group? (d) State two letters in the diagram which represent elements in the same period? (e) In any relevant empty square, write the correct chemical symbol for an element in the same group as helium. |
E
Shade square B. C and A Two of: D, E or F. Any square in the last group (group 0 / noble gases) |
|
|
Is aluminium a metal or non-metal?
How did you use the periodic table to help you decide? |
A metal
It is on the left-hand side of the periodic table / of the “staircase”. |
|
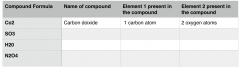
Fill the table above.
|
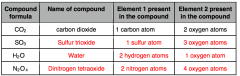
|
|
|
What are valence electrons? The atomic number of an element?A covalent bond?
|
the outermost electrons in an atom
is the number of protons in (the nucleus of) its atoms a pair of valence electrons shared between two non-metal atoms |
|
|
What is an ionic bond?
|
A strong electrostatic attraction between two ions of opposite charge.
|
|
|
State two characteristics of a chemical change
|
1. A new substance is made.
2. An energy change takes place (net energy is released or absorbed) |
|
Fill out the table
|
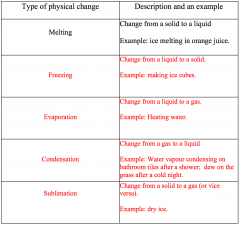
|
|
|
What is the boiling point of a substance?
|
The maximum rate of evaporation. Vapor bubbles can be seen forming in the liquid, i.e. the liquid is turning to gas within the liquid.
|
|
|
We know a chemical change has taken place (happened) when:
|
A new substance has been made.
An energy change has taken place It's not easily reversible |
|
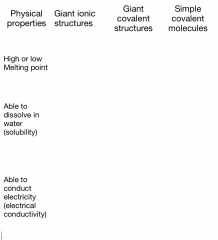
How do the chemical bonds and structure of a substance affect its physical properties?
|
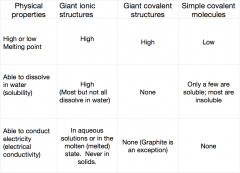
|
|
|
Describe the particle structure of a metal and explain how this kind of bonding keeps the structure together.
|
Metal atoms have loosely held valence electrons which can move freely between metal atoms in a piece of metal. The attractions between the valence electrons and the nuclei of the atoms are called metallic bonds. The electrons are described as delocalized because they do not belong to any particular atom but can move between them.
The atoms are arranged in layers, which can slide over each other when a force is applied. |
|
|
Magnesium has a higher melting point than sodium. In other words, more energy is needed to separate the particles in the solid state so that it becomes a liquid. Think about the structure of metals and suggest a reason for this.
|
Magnesium has two valence electrons but sodium has only one. Therefore there are more attractions between the valence electrons and the nuclei, causing stronger bonds.
|
|
Use periodic table to fill the table
|
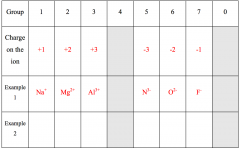
|

