![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define employment relations |
The relationship between employers and employees over terms and conditions of employment and work, which when settled becomes both a binding agreement in law and an informal understanding between people. |
|
|
What are the implicit and explicit employment relations? |
I - Psychological contract, expectations
E - Employment contract |
|
|
What are the 10 minimum entitlements of the NES? (National Employment Standards - Fairwork) |
Max hrs per week, requests for work flexibility, potential leave, annual leave, careers leave and compassionate leave, community service leave, long service leave, public holidays, termination/redundancy pay, fair work information statement |
|
|
Define Employee |
Someone who provides labour and/or expertise in exchange for a wage or salary. |
|
|
Define awards and agreements and their relationship with pay |
minimum conditions at work can come from registered agreements, awards or legislation. |
|
|
Define employee voice |
A whole variety of process and structures which enable and at times empower, employees, directly and indirectly to contribute to decision making in the firm (Boxall and Purcell, 2013) |
|
|
Define Trade Unions |
Act as collective agents to protect and improve member wages and conditions through collective bargaining and other means. Provide members with a form of indirect employee voice in the workplace. |
|
|
Define Employer |
A person or organisation who offers wages or salary in return for labour and or expertise. |
|
|
Define each of the contemporary business problems. |
Corporate strategy - continuous need for alignment, strategy, people, structure. Technological advancements - increased computing power and network growth are driving changes after and altering many workplaces Competition - global markets, multiple competitors, increased rate of change. Flexibility - job sharing, flexitime, telework Social friends - social networked, ageing population, cultural diversity. |
|
|
Define managerial prerogative |
Authority to exercise discretion in areas of the organisation |
|
|
What is the McGregor theory X and theory Y? |
Theory X sees workers as: having little ambition, disliking work and avoiding responsibility. Theory Y sees workers as: self directed, enjoying work, accepting responsibility. |
|
|
What are the leadership styles? |
MANAGEMENT HAS MOST KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS Autocratic style Paternalistic style Participative style Delegative style Free reign style EMPLOYEES HAVE THE NEEDED KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS |
|
|
What leadership style should be used? |
Situational leadership style is best, however one size does not fit all. |
|
|
Define employability |
To make oneself employable means to develop the personal and professional capacity to maximise ones employment potential. |
|
|
Define professional identity |
Ones professional self concept based on attributes, beliefs, values, motives and experiences. |
|
|
Define Personality |
Refers to the individual differences in characteristics patterns of thinking, feeling and behaving. |
|
|
Define values |
Broad preferences concerning appropriate courses of action or outcomes. |
|
|
Explain person-organisation fit |
Comprises an alignment of your personality, values, knowledge and experience with the organisation and the job position you are applying for. Knowledge, willingness to learn, adaptability, interpersonal skills. |
|
|
Define self-management |
- documenting personal vision and goals - evaluating+monitoring own performance and progress, review when necessary. - having confidence and articulation of abilities, ideas, visions - take responsibility for growth, development and career choices. |
|
|
What is social capital? |
social life networks. Your social capital is Facebook, linkedin, twitter, instagram, Pinterests etc. The significance is the outcome: the stronger the ties the more valuable the network (professional information, professional solidarity, the power of influence) |
|
|
What is networking? |
- Meeting key people - Access to a wealth of resources - Participation in blogs/share and receive information - Become a member of professional groups - Access potential jobs |
|
|
Define Human Resource management (HRM) |
The effective use of human resources in order to enhance organisational performance. |
|
|
What are the 3 key elements of HRM? |
Attracting - planning, recruitment, selection Developing - training, learning and development, career planning and development. Maintaining - retention performance review and management remuneration. |
|
|
Define HR planning |
Pprocess of analysing and identifying the need for and availability of, human resources so that the organisation can meet its objectives. |
|
|
What is HR Planning? |
Having the right person at the right time with the right skills and capabilities in the right place |
|
|
Define recruitment |
The process of encouraging and attracting a pool of qualified and experienced candidates to apply for a position. |
|
|
What are two things to consider when recruiting? |
1. Does a new job need to be created? 2. Does the job already exist? (internal promotion, temporary leave) |
|
|
Preparing for recruitment, define job analysis? |
Process of collecting and analysing detailed information about tasks, content and responsibilities. |
|
|
Define job description |
Describes the activities to be done, identifies the tasks, duties and responsibilities of a job. It describes what is done, why it is done, where it is done and how it is down. |
|
|
Define person specification |
Includes attributes specific to the person, including the knowledge, skills and abilities needed to perform a job satisfactorily. |
|
|
What does job specification include? |
Training, qualification, KSAO's and experience. |
|
|
Define selection process |
Process of selecting the most suitable applicant for a position. The most common selection techniques are: reference checks, interviews and or personality tests. |
|
|
What are selection methods? |
Practicability - cost effective, ensure the selection method is appropriate for the position Sensitivity - ensure selection methods are based on job-related factors only Reliability - consistency in approaches Validity - does the method measure what it is meant to ? |
|
|
What are the different types of interviews? |
Single or panel Structured - standardised job related questions with pre-determined scores for different answers Unstructured - non-standardised questions that differ across interviews Behavioural - past behaviour predicts future behaviour Situational - responses to specific job related scenarios |
|
|
How to shortlist? |
- agree on candidates that best match criteria - remove applicants that do not meet criteria - agree on a set of questions based on selection criteria - determine a preliminary list of candidates to be interviewed - Decide whether to obtain referee reports before or after interviews |
|
|
Define learning organisations |
- Where focus is on acquisition sharing and utilisation of knowledge to survive and prosper. - Represents a strategic orientation that promotes critical capability to compete. |
|
|
Define performance management |
Process and control function used within an organisation to improve and manage the performance outcomes of individuals, teams and the organisation. |
|
|
Define strategic management |
Signals to managers and employees what is important |
|
|
What are the 4 key elements to the performance management process |
1. Orientation/induction and socialisation 2. Performance appraisals - reviewing performance 3. Reinforcing performance standards 4. Managing performance - coaching, counselling, discipline |
|
|
What are the aims of a performance appraisal? |
Reward positive performance, Enhance career development, Determine key performance objectives against strategic objectives. |
|
|
What is content (intrinsic) motivation?
|
Theories of motivation, emphasise human needs and what motivates. e.g. cars, childcare, medicare |
|
|
What is process (extrinsic) motivation? |
Emphasise relationships among dynamic variables and actions required to influence behaviour and actions. |
|
|
What are modern content theories? |
Focussed on the nature of human needs, concerned with what factors motivate people, focused mainly on intrinsic needs. |
|
|
What is Maslows hierarchy of needs? |
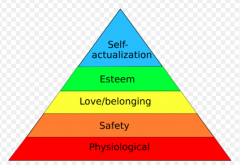
Needs theory (Maslow) - higher and lower needs - move up hierarchy in order - move to next level only when all needs at current low level are met. |
|
|
What is Herzberg two factor theory? |
Motivation factors - Intrinsic - and related to satisfaction, achievement, growth, responsibility Hygiene factors - Extrinsic - and related to dissatisfaction - salary, work conditions, company policies. |
|
|
Define workplace negotiations |
Joint examination of the opposing claims of employer and employee to resolve or avert conflict by reaching a solution that is acceptable to both parties. |
|
|
What are the two types of power in negotiations? |
Formal or positional power - coercive, reward, legitimate Informal or personal power - expert, information, referent |
|
|
What are the negotiating styles and their characteristics? |
ACCOMMODATING - learn and establish social and business relationships e.g. new job COMPROMISING - temporary settlements to complex/time pressure e.g. salary negotiation COMPETING - quick, decisive action, vital to company welfare e.g. QLD health reforms AVOIDING - issue is trivial, more important issues are pressing e.g. politics COLLABORATING - learn, fin solution, gain commitment e.g. partnership. |
|
|
What are the five stages of negotiation? |
1. Preparation and planning 2. Definition of ground rules 3. Clarification and justification 4. Bargaining and problem solving 5. Closure and implementation |
|
|
Define work ethics |
Group of moral principles, standards and behaviour, or set of values regarding proper conduct in the workplace. |
|
|
Define workplace health and safety |
Promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social wellbeing of workers in all occupations. |
|
|
What are employee responsibilities? |
- Take reasonable care of self and others - Cooperate with employer to comply with WHS - Not act recklessly |
|
|
What are employer responsibilities? |
- Employee health, training and supervision of employee safety - Engage WHS qualified professionals - Keep records and monitor workplace conditions - Hazard information, safe work systems |
|
|
What are the modern workplace trends? |
Gen Z internships, more millenials as leaders, honesty, wider skills gap, mobile hiring, social media, succession planning, women in power positions, non-traditional career paths. |
|
|
What is an explicit employment relationship? |
EMPLOYER - job advertisement, job description, letters of offer, acceptance, HR policies and practices. EMPLOYEE - job advertisement, job description, letters of offer/acceptance, application and CV. |
|
|
What are some examples of unpaid work? |
- Student placements - Unpaid internships - Work experience |

