![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The SELF
Erickson Theory Conflict #3: Initiative vs. Guilt |
Early childhood
Conscience developes Able to hear inner self i. self-observation ii. self-guidance iii. self-punishment CONFLICT: Freedom and opportunity supports INITIATIVE GUILT develops if child's enthusiasm and curiosity is squelched |
|
|
SELF understanding
SELF CONCEPT |
starts @ 18 mos - end of 2 yrs
Self description focuses on physical characteristics, physical actins, material possessions, called active dimension |
|
|
Piaget's view on Moral Reasoning Development
1st of 2 stages |
Heteronomous: 4-7 yrs old
child doesn't look at the intention..things are B&W. Rule broken means punishment. Rules have unchangeable properties, thus people can't change them |
|
|
Piaget's view on Moral Reasoning Development
2nd of 2 stages |
Autonomous: 10 yrs old
Child realizes rules are made by people and can be changed. Before judging an action need to look at intention |
|
|
What is moral development?
|
involves thought, feelings, and behaviors regarding rules and conventions.
It involves INTERpersonal and INTRApersonal components. |
|
|
Moral behavior and self control
|
Self control is an important aspect of understanding children's moral behavior. to achieve self control, they must learn to be patient and delay gratification
|
|
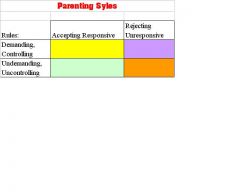
What are the parenting styles
|
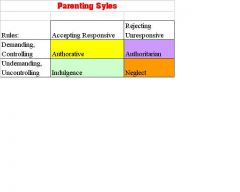
Authorative
Authoratarian Indulgent Neglect |
|
|
What will children by like under
AUTHORATIVE parenting style |
Cheerful, self-controlled, self-reliant, achievement oriented, cooperate w/adults, cope well under stress
|
|
|
What will children by like under
AUTHORITARIAN parenting style |
anxious about themselves and w/others, FAIL TO INITIATE activites, weak communication skills
|
|
|
What will children by like under
INDULGENCE parenting style |
may be impulsive, aggressive,domineering,non-compliant, never learn self-control, rarely learn to respect others, have difficulty controlling their behaviors, have difficulties w/peer relationships
|
|
|
What will children by like under
NEGLECT parenting style |
Often are immature, may be alienated from the family, socially incompetent, poor self-esteem, poor self-control, don't handle independence well
|
|
|
PEER RELATIONS
what are their functions |
- one of the most important func is to provide a source of info and comparison outside family.
Thus, GOOD peer relations can be necessary for normal social development |
|
|
PLAY FUNCTION
|
It's engaged for its own sake
However, it also -increases affiliation w/peers -advances cognitive development -increases exploration -provides safe haven to explore and learn -increase conversation and interaction -practice roles they will probably assume later in life |
|
|
PLAY THERAPY
|
-Allows child to work off frustrations
-Thru play, child can be analyzed for conflicts and coping issues -child feels less threatened in play, thus can express true feelings |
|
|
PARTEN's Classifications of play
|
play in childs SOCIAL world:
1-Unoccupied play 2-Solitary play 3- Onlooker play 4- Parallel play 5- Associative play 6- Cooperative play |
|
|
PARTEN's Classifications of play
Define: Unoccupied |
Stands alone in 1 spot, looks around the room, or performs random movements that don't seem to hav a goal.
|
|
|
PARTEN's Classifications of play
Define: Solitary |
child plays alone and independently of others
|
|
|
Mildred PARTEN's (1932) Classifications of play
Define: Onlooker |
when the child watches other children play. May ask questions/talk to kids, but won't participate.
|
|
|
PARTEN's Classifications of play
Define: Parallel |
Child plays separately from others, but with toys like those the others are using or in a manner that mimics their play
|
|
|
PARTEN's Classifications of play
Define: Associative |
involves social interaction with little or no organization (no rules)
Children are more interested in each other than the activity: borrowing/lending toys, follow each other in lines, etc |
|
|
PARTEN's Classifications of play
Define: Cooperative |
Social interaction in a group with a sense of group identity and organized activity (phototype for play in middle childhood).
|
|
|
Bergen's types of play
Contemporary look at play 5 types |
Emphasized on cognitive and social aspects
1-sensorimotor and practice 2-Pretense/Symbolic play 3-Social Play 4-Constructive Play 5-Games |
|
|
Bergen's types of play
Define Semimotor and Practice Play |
Semimotor: (infant stage: 9-24 mos.) pleasure from exercising their existing sensorimotor schemas
Practice play used to master new new skills/behaviors. Semimotor and Practice go hand-in-hand. But Practice play will stay throught life, where semimotor confined to infancy. |
|
|
Bergen's types of play
Define Pretense/symbolic play |
from 9-30 mos. child transforms objects to symbols. Imagination peaks at 4-5 yrs and then gradually declines
|
|
|
Bergen's types of play
Define Social Play |
interact w/peers, rough 'n tough play...increasing dramatically during preschool years
|
|
|
Bergen's types of play
Define Constructive Play |
Most common type of play in preschool years.
Combines semimotor, repetitive activities w/sympolic representation of ideas. They engage in self-regulated creatoin or construction of a product or problem solution. Constructive play increases as symbolic play increases adn sensorimotor play decreased in preschool yrs. |
|
|
Bergen's types of play
Define Games |
Highest Level
include rules and are engaged-in for pleasure. Competition w/one another. The meaningfulness of challenge emerges in elementary school. |

