![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the principle of antithesis
|
opposite messages are signalled by opposite movements and postures. i.e. aggression in cat raises back vs submission, like stretching
|
|
|
the common sense view theory of emotion
|
the emotional feelings cause the emotional response:
1. Perception of the emotion-eliciting event (e.g. see a bear). 2. Subjective feelings of emotion (e.g. fear). 3. Behavioral and adaptive physiological responses (e.g. trembling, sweating and running away). |
|
|
James- Lange Theory of emotions
|
1. Perception of emotion-eliciting event (e.g. see a bear).
2. Appropriate set of physiological responses are triggered (e.g. sweating, trembling, increased heart rate). 3. The emotional event also triggers adaptive behaviours (e.g. clench fists, run away). 4. The brain receives feedback from the peripheral nervous system which constitutes our feelings of emotion. |
|
|
walter cannons problems with james lange theory (2)
|
1. The internal organs (or viscera) are relatively insensitive and do not respond quickly enough to account for our
emotional feelings. 2. Cutting the sensory nerves between the internal organs and the central nervous system does not abolish emotional behaviour in animals. |
|
|
what support is there for the james lange theory
|
- Studied paraplegics who had spinal cord surgery at different levels.
- Patients were asked about their emotional feelings. - Those with highest transections (i.e. surgery high up the spinal cord) showed less intense emotional feelings. - Other subjects showed angry behaviour (the emotional response) without feeling angry. - Thus, the emotional experience lacked the intensity that was experienced before the surgery. |
|
|
The Papez Circuit
|
- sensory pathway can be divided into two different streams: thought and feeling
- pathway can be transmitted upstream or downstream - pathway from hypothalamus to cingulate cortex involved in subjective emotional experience - pathway back to hypothalamus involved in expression of emotion |
|
|
Kluver-Bucy Syndrome
|
temporal lobe lesions of amygdala showed:
reduced fear, hypersexuality, hyperorality, hyper aggression |
|
|
Know the structure of the limbic system and their functions (septum, amygdala, mammilliary bodies, fornix, cingulate cortex, hippocampus)
|
see image
|
|
|
Central nucleus of amygdaloid complex
|
-activation of this area elicits a variety of emotional responses
- particularly important for expression of emotional responses to adverse stimuli - neural activity here increases in presence of threatening things -lesions to this area result in no fear to threats and less stress. stimulation results in the opposite |
|
|
medial nucleus in amygdaloid complex
|
has many subnuclei which receive sensory input info and relay it to basil forebrain and hypothalamus. Involved in reproductive functions
|
|
|
lateral nucleus of amygdaloid complex
|
receives info from prefrontal cortex, thalamus, and hippocampus, and projects to the basil ganglia (nucleus cumbers), basal/accessory basal regions of amygdala and dorsomedial thalamus,
|
|
|
Basal forebrain is important in product of...
|
ACh
|
|
|
Look over the brain regions the central nucleus sends output to which control various emotions
|
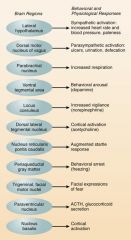
|
|
|
extinction
|
Extinction is NOT the same as forgetting. In extinction, the animal learns that the CS is longer followed by an aversive stimulus. Therefore, the CR expression is inhibited.
|
|
|
monkeys with amygdala lesions react how?
|
show no fear when presented with a snake real or fake and had no problem reaching over it to get food
|
|
|
people with amygdala lesions/damage...
|
-fail to acquire conditioned emotional responses
- seeing words that denote threatening stimuli usually increases amygdala activity |
|
|
aggressive behaviours, threat behaviours, defensive behaviours, submissive behaviours, predation
|
biting, hissing, species- typical; warn adversary to leave or will become target; shown by threatened animal; animal accepts defeat; one species attacks another for food usually
|
|
|
Stimulating the Pariaqueductal Gray Matter (PAG) in the midbrain...
|
elecits predatory and defensive behaviour
|
|
|
Role of 5HT in impulse control of monkeys
|
high levels of serotonin metabolite 5-H1AA indicates elevated serotonin activity. Monkeys with LOW levels of 5-HH1AA were risk takers and aggressive- usually died early or were killed
|
|
|
Role of serotonin in impulse control of humans
|
low levels of serotonin metabolite 5-H1AA (=low levels of serotonin) is associated with assault, aggression, and areon.
-SSRIs decrease aggressiveness -serotonin transporter has 2 alleles, long and short. if you have at least one short one you will more likely show high anxiety levels |
|
|
prefrontal cortex's role in emotions
|
prefrontal cortex plays large role in regulating our emotions and avoiding impulsive behaviours
|
|
|
Ventral Prefrontal Cortex (PFv) - (parts, locations)
|
Parts: consists of the orbital prefrontal (PFo) cortex and the ventromedial prefrontal (PFvm) cortex.
Locations: - The PFo is located at the ventral surface of the frontal lobe and covers the brain above the eye orbits. - PFvm lies adjacent to PFo. It occupies the medial extent of the ventral surface. |
|
|
Functions of the PFv (3)
|
a) exchanges info about environment and future planning with the amygdala, hippocampus, ventral tegmental area (dopamine!) and olfactory system
b) has inhibitory connections with the amygdala which are responsible for suppressing emotional responses in social situations - PHINEAS GAGE c) Patients with PFv damage make decisions that are rewarding in the short term but lead to detrimental effects in the long term (e.g. gambling) |
|
|
Iowa Gambling Task
|
Subjects were given a stake of $2000 play money and were instructed to win as much as possible. Subjects had to draw cards from one of four decks. Two were good decks and two were bad decks.
- Selecting cards from the ‘good’ decks lead to low rewards but low penalties. - Selecting cards from the ‘bad’ decks lead to to high rewards but high penalties. - Control subjects showed changes in skin conductance associated with ‘emotional stress’ just before they chose a card from the bad deck. - Control subjects eventually shifted their responses from bad decks to good decks. That is, they let their emotional response guide their choice behaviour. - Patients with PFv damage (especially PFo damage) did not show signs of stress ‘before’ they selected from the ‘bad’ deck but showed autonomic changes ‘after’ they made a choice that cost them money- they realize their mistakes and feel emotional responses when it is too late. - Patients with amygdala damage failed to show any emotional changes before or after the choice of cards. - Thus, emotional responses are important in guiding our decisions. |
|
|
psychopaths and emotional response
|
Subjects were presented with a picture of a man’s face paired with a painful stimulus.
- Control subjects show autonomic signs of emotional conditioning (e.g. galvanic skin response) and activation of the amygdala, PFo and PFvm and insula. - Psychopathic subjects fail to develop a conditioned emotional response and little sign of brain activation. |
|
|
Facial expression of emotion
|
- innate
- Ekman and Friesen (1971) showed that an isolated tribe in New Guinea were able to recognize and produce emotional expressions by westerners. |
|
|
role of amygdala in emotion (4)
|
- Damage to the amygdala impairs the ability to recognize facial expressions of fear.
- Increased amygdala activity when people view fearful faces, not happy faces. - involved in recognition, not expression- patient had lesion to amygdala and can regocnize and produce all emotions except fear- even seeing a picture of herself being fearful - viewing fearful eyes activates amygdala |
|
|
which regions input enable facial recognition?
|
- Superior colliculus and pulvinar input to the amygdala enable facial recognition (not input from the visual association area!).
- Patients with damage to the visual cortex, who have no conscious awareness of looking at a person’s face, show activation in the thalamus, superior colliculus and the amygdala when viewing fearful faces. |
|
|
amygdala lesions and eye movements for emotion recognition
|
Control subjects spontaneously look at and examine the eyes of a face to detect the emotional state of the person they are interacting with, but patient with lesion doesn't look at eyes ( she can do so if trained and can then recognize emotion but must be told to)
|
|
|
When are neurons in Superior Temporal Sulcus (STS) activated?
|
- Neurons in a monkeys’ superior temporal sulcus (STS) increases firing rate when it looks at photographs of another monkey or human ‘gazing’ in a particular direction for example when the gaze is up.
- gaze direction is informative - lesions of this do NOT impair ability to recognize faces, only gazes |
|
|
Somatosensory cortex and emotion recognition
|
- activity in somatosensory cortex increases during emotion recognition
-Patients who are unable to recognise and identify facial expressions of emotions typically have severe damage to the somatosensory cortex. - - This suggests that when we see a facial expression of an emotion, we unconsciously imagine ourselves making that expression. That is, we imitate what we see. |
|
|
facial expressions of emotion; volitional facial paresis vs. emotional facial paresis
|
- involuntary, we innately imitate them (babies imitate facial expressions at 36 hours)
- People with volitional facial paresis are unable to voluntarily control facial muscles but can express genuine emotion with those muscles (caused by damage to the face portion of PMC). The reverse is true of people with emotional facial paresis (caused by damage to the insular region of premotor cortex). |
|
|
Roles of the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (PFvm)
|
- courage and overcoming fear
- inhibiting CR after extinction has taken place - making emotional (vs utilitarian) responses to moral situations/ decisions - jokes activate PFvm |
|
|
Affective Blindness
|
person who cannot see can identify facial expressions
|
|
|
which cortex is activated at disgust?
|
insular- both at feeling disgust oneself as well as seeing disgust. Hearing sounds like "yuck" can also activate it like seeing it
|
|
|
which hemisphere lesion would impair emotion expression? stimulating emotional expression like a smile causes activity where?
|
right hemisphere; autonomic nervous system
|

