![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Symptoms:
• Incubation Period: 1-2 days • Fatigue/depression • Muscular aches and pains over whole body • General weakness Pathogenesis: • Incubation period: 1-2 days • Hemagluttinin protein helps the virus break into the cells, while the neuraminidase protein enables it to get out again |
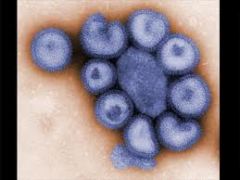
Influenza (Orthomyxoviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Tenderness • Hot, red swellings at site of infection Pathogenesis: • extremely common in the open environment and lives in the noses and skin of most people without causing any problems, but occasionally gets out of control and gets infected |
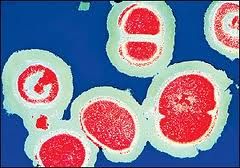
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Incubation period 10-21 days • Fever • Red, itchy rash over whole body • Blisters and scabs over whole body Pathogenesis: • Highly contagious |
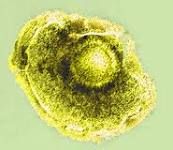
Chicken Pox (Varicella Zoster)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever • Vomiting • Nausea • Diarrhea • Itchy spot developing into an ulcer, at site of infection Pathogenesis: • Survives in soil and is easily picked up by grazing animals, then passed on to humans who work with them or eat their meat • Can jump to humans through a cut in the skin or through the lungs as we breathe |
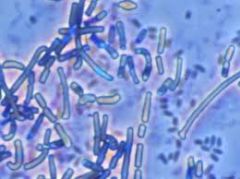
Anthrax (Bacillus Anthracis)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Headache drowsiness • Sensitivity to bright lights • Vomiting • Stiff neck • Rash over whole body Pathogenesis: • Most common: Haemophilus influenzae b (Hib), Group B Streptococcal bacteria, Escherichia coli, Listeria, and can tuberculosis |
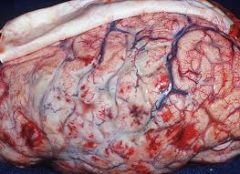
Bacterial Meningitis
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Insensitivity to pain • Loss of digits and limbs Pathogenesis: • Unconfirmed method of transmission |
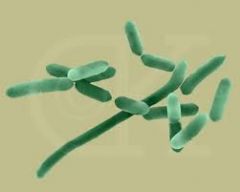
Leprosy (Mycobacterium leprae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Incubation period 7 and 17 days • Fever, headache • Initial spots in the mouth • Spots over the whole body, developing into sores Pathogenesis: • Can be coughed into the air or swallowed • Either through airborne droplets or feces |
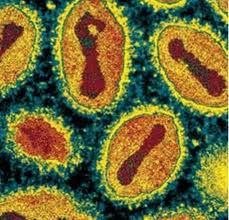
Smallpox (Variola) (Orthopoxvirus)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Headache, fever • Bleeding from eyes • Coughing and vomiting blood • General weakness • Sore throat • Organ failure • General muscle pain • Bloody diarrhea • Nausea • Red spots and bleeding under skin • Joint pain Pathogenesis: • Transmitted through infected blood and other bodily fluids |
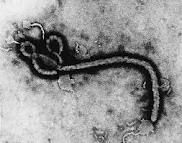
Ebola (Filoviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever, dizziness and confusion • Vomiting • Rash all over body • Sore throat • Destruction of organs, Organ failure • Diarrhea Pathogenesis: • Protein sticking that binds to cell walls • When the protein grabs a host cell, it triggers a process that causes the cell to draw it inside • Produce one or more pyrogenic (heat-producing) toxins that induce fever and shock |
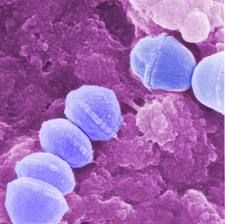
Group A Streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever • Gut pain, possible dilated or torn bowel • Diarrhea Pathogenesis: • Antibiotics killing off normal intestinal bacteria, allowing bacteria to thrive |
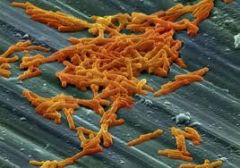
Clostridium Difficile
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Bad breath • Nausea • Flatulence • Stomach pain/Stomach ulcers Pathogenesis: • found in almost all patients with gastric inflammation, duodenal ulcers, or gastric ulcers |
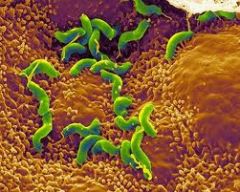
Helicobacter Pylori
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Nausea • Loss of appetite • General weakness • Inflammation of the liver • Possible liver cancer Pathogenesis: • Contaminated blood and other bodily fluids |
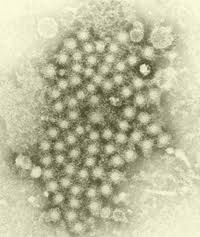
Hepatitis C (Flaviviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Gut damage • Diarrhea Pathogenesis: • Virus leaves the body through the feces, and poor hygiene enables it to move rapidly to other friends and family |
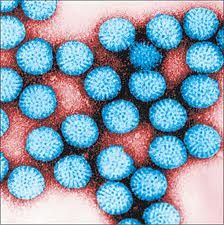
Rotavirus (Group A rotavirus)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Incubation period 2 – 10 days • Fever, extremely high temperature • Cough, sore throat • General lethargy • Collapsed lungs, breathing difficulties • Reduced white blood cell count Pathogenesis: • Unconfirmed mode of transmission |
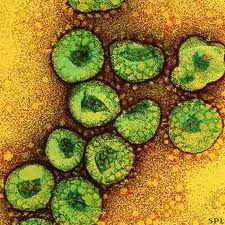
SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) (SARS-associated coronavirus) (Viverridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Face turns blue • Fluids from eyes and nose • Severe cough, coughing up phlegm • Possible collapsed lung Pathogenesis: • Bacteria binds to the outer layer of cells in the lungs and release a toxin that paralyzes the microscopic hair-like brushes that normally sweep the lungs • There is no way of clearing the mucus that the lungs constantly produces and bacteria less likely to be thrown out |
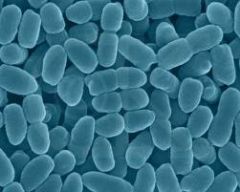
Whooping Cough (Bordetella sp.)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Headache, fever, chills • Blocked or runny nose, sneezing • Sore throat, cough Pathogenesis: • Of the people who become infected, 75% develop symptoms • 25% have the virus growing in their nose, but have no symptoms |
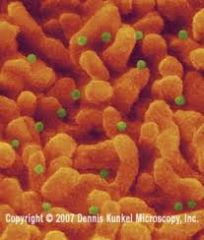
Rhinovirus (Common Cold) (Picornavirus)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Headache, delirium • General muscle pain • Paralysis • Breathlessness • Heart Palpatations Pathogenesis: • Unknown • It is strongly suggested that the disease was moving person to person as an airborne infection • Because of the pace of its attack and the nature of the symptoms, it was probably viral in nature |

English Sweating Sickness
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever, tiredness • Runny eyes, swollen eyelids, sensitivity to light • Possible pneumonia and bronchitis • Bright red, itchy rash all over body Pathogenesis: • Spread through fluids from an infected person’s nose and mouth, either directly or through droplets in the air |
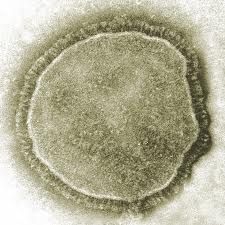
Measles (Morbillivirus)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever, fatigue • Possible facial scarring • Coughing • Deterioration of lungs • Chest pain • Appetite loss/Weight loss • Possible gut, bladder, and kidney problems • General muscle wastage Pathogenesis: • Colonies grow inside the lung, creating zones of dead and damaged tissues • Materials released from the bacteria trigger fevers and muscle wastage • As the region expand, they break into the airpipes and flood into the mucus • Each cough sends millions of bacteria into the air |
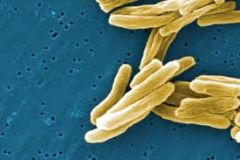
Tuberculosis (TB) (Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Incubation period 2 – 10 days • Confusion, hallucinations • Possible fits and fever • Breathing difficulties Pathogenesis: • Need to get into water droplets before moving into humans • Hot tubs and Jacuzzis are high risk |
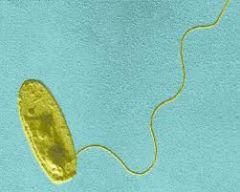
Legionnaires’ Disease (Legionnella pneumophila)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever • Nausea • Damage to fallopian tubes • Lower back pain • Bleeding between menstrual periods • Pain during intercourse • Possible abnormal discharge and pain when urinating Pathogenesis: • Transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex • Passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth |
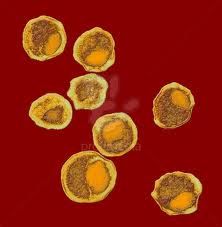
Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Weakened immune system, leading to infection with other diseases, especially TB Pathogenesis: • Transmitted through blood and semen • Attacks the immune system |
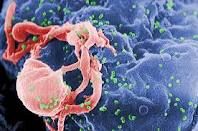
HIV/AIDS (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) (Retroviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Cold sores • Genital ulcers Pathogenesis: • Two types • Initial infection creates a “vesicle,” which is an inflating breakdown of skin cells • The cells in the base of the vesicle become infected with viruses and multiplies within • The roof of the vesicle degenerates, revealing an ulcer that heals (cold sores) |
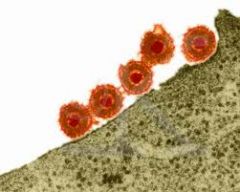
Herpes (Herpes Simplex Virus) (Herpesviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Insanity (tertiary) • Mouth ulcers (primary) • Genital ulcers (secondary) • Ulcers all over body (secondary) Pathogenesis: • Usually through sexual activity with other infected individuals • Mother to the fetus of her womb, or during delivery |
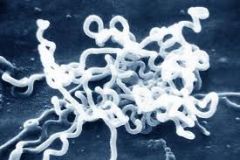
Syphilis (Treponema pallidum)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Fever • Arthritis • Joint pains • Pain on passing urine, discharge from the penis Pathogenesis: • Unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse with infected partner |

Gonorrhea (Nesseria gonorrhea)
|
|
|
Three Classifications of Antibiotics:
|
1. Natural
2. Semi-synthetic 3. Synthetic |
|
|
Two groups of Antibiotics:
|
1. bactericidal agents (kill bacteria)
2. bacteriostatic agents (impair bacterial growth) |
|
|
Etiology of Malaria Outbreak for Marines in 2003:
|
1. Failure of personal protective measures
2. Failure of compliance with mefloquine 3. P. falciparum with decreased susceptibility to mefloquine 4. Formulation of mefloquine |
|
|
Examples of Anthropogenic:
|
1. Deforestation and Incursion
2. Urbanization 3. Transportation of Pathogens and Vectors 4. Climate Change |
|
|
-Restriction of movement/seperation of sick infected person(s) with contagious disease
-Usually in a hospital setting, but can also be at home or in a dedicated isolation facility |
Isolation
|
|
|
-Restriction of movement/separation of well person(s) presumed exposed to a contagious disease
-usually at home, but can also be in a dedicated quarantine facility -individual(s) or community population/population level |
Quarantine
|
|
|
-Glycoprotein in influenza
-Viral attachment protein -Binds to sialic acid residues on cells -Serotype determinant -15 different molecules |
Hemagglutinin
|
|
|
-Serve as sources of vector infection
-Develop high titer viremia of "long" duration -Are available to the vector -Do not become ill |
Amplifying Hosts
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• fever, headache, muscle/joint/eye pain, nausea, rash, encephalopathy, seizures, coma, paresis • skin hemorrhages, leaky capillaries, low platelets, bleeding • circulatory failure Pathogenesis: • Transmitted to human in mosquito saliva • Virus replicates in target organ • Virus infects white blood cells and lymphatic tissues • Virus released and circulates in blood |
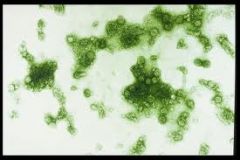
Dengue (Flaviviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Febrile, influenza-like illness with abrupt onset • Moderate to high fever, headache, sore throat, backache, myalgia, arthralgia, fatigue • Rash, lymphadenopathy • Acute aseptic meningitis or encephalitis Pathogenesis: • Transmitted to human in mosquito saliva |
Mosquito Borne Encephalitis (SLE, WN)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Debilitating fever, headache, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, muscle pain, rash • Joint pain Pathogenesis: • Circulates between mosquitoes and monkeys |
Chikungunya (Alphaviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Paroxysm: relapsing or periodic fever • Pattern of intermittent chills/fever Pathogenesis: • Mosquito transmission • Cytoadherence clogs capillaries in major organs |
Malaria (plasmodium spp.)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• Jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain • Symptoms usually last a couple weeks • Can take several months to a year to recover • Known as a “silent disease” as it is often asymptomatic Pathogenesis: • Transmitted through blood and bodily fluids • Also vertical transmission |

Hepatitis B (Hepadnaviridae)
|
|
|
Symptoms:
• 90% of cases, infection clears within 2 years • Those that don’t clear may experience: o Genital warts o Warts in your throat o Cervical cancer o Other cancers (vulva, vagina, penis, anus, and orpharynx) Pathogenesis: • Most common sexually transmitted infections • Transmitted through genital contact, vertical transmission is rare |
Human Papillomavirus (Papillomaviridae)
|

