![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
141 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the avergae age of menarche?
|
13 years old
|
|
|
What is the average age of menopause?
|
51 years old
|
|
|
How long is a normal menstrual cycle?
|
28 days ( ranges from 21-35 days)
|
|
|
How long is the normal duration of a period?
|
2-7 days
|
|
|
What is the normal blood loss for a period?
|
<80 cc
|
|
|
Define dysfunctional uterine bleeding
|
any abnormal uterine bleeding pattern without obvious cause
|
|
|
Define menorrhagia
|
prolonged (>7 days) or excessive (>80cc) uterine bleeding at regular intervals
|
|
|
Define metorrhagia
|
uterine bleeding at irregular frequent intervals in variable amounts
|
|
|
Define menometorrhagia
|
prolonged uterine bleeding at irregular intervals
|
|
|
At what phase and around what day of your cycle does a woman's body temperature rise about 1 degree C?
|
ovulation
|
|
|
Which hormones peak with ovulation?
|
LH
and FSH |
|
|
Which hormone level is highest with ovulation?
|
LH
|
|
|
which hormone peaks just before ovulation?
|
estradiol
|
|
|
Which hormone has the highest level during the luteal phase?
|
progesterone
|
|
|
which hormone has the highest levels (of all the hormones, not highest level for that hormone ever) during the follicular phase?
|
estradiol
|
|
|
around what day of the menstrual cycle is ovulation?
|
about day 13-15
|
|
|
Describe all the hormones and how everything works in the normal menstrual cycle
|
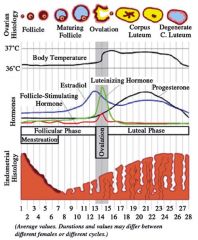
|
|
|
What causes anovulatory bleeding?
|
hypothalamic-pituitary axis disruption or immaturity
|
|
|
What are the undelying causes of anovulatory bleeding?
|
1. perimenacrhal females
2. psychological or physical stress 3. rapid changes in weight/ eating disorders 4. excessive exercise 5. hypothyroidism 6. hyperprolactinemia 7. PCOS |
|
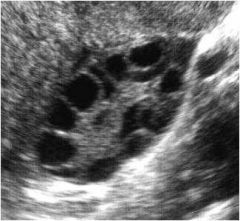
What is this showing?
|
PCOS
|
|
|
explain what happens to a person with PCOS's hormones
|
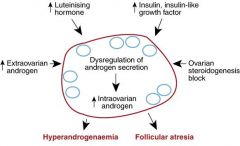
|
|
|
Which hormones are up-regulated in PCOS?
|
LH
insulin like growth factor extraovarian androgen |
|
|
What do excesses in LH, insulin like growth factor, and extraovarian androgen along with the effects of ovarian stereogeneis block lead to?
|
dysregulation of androgen secretion which leads to an increase in intraovarian androgen
|
|
|
What effects does the dysregulation of androgen secretion and increase in intraovarian androgen lead to?
|
hyperandrogenemia
follicular atresia |
|
|
are most fibroids symptomatic or asymptomatic?
|
asymptomatic
|
|
|
Which type of uterine fibroids tend to cause the most bleeding abnormalities?
|
submucosal fibroids
|
|
|
What are three causes of disorders of hemostasis in the female uterus?
|
perimenarchal females
inherited systemic disorders of hemostasis anticoagulant medications |
|
|
List 2 inherited systemic disorder of hemostasis that cause lead to abnormal uterine bleeding
|
von wildebrand disease (13% of women with menorrhagia have this)
hemophilia |
|
|
13% of women with von wildebrand disease have ___________
|
menorrhagia
|
|
|
List 4 anticoagulant medications that can lead to abnormal uterine bleeding
|
heparin
lovenox coumadin aspirin |
|
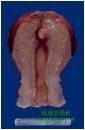
What is this?
|
a uterus with a submucosal fibroid
|
|
|
What are 3 medical treatments for abnormal uterine bleeding? (general)
|
estrogens
estrogens and progestins progestins |
|
|
With abnormal uterine bleeding, how can you treat an acute event with estrogen?
|
25 mg conjugated equine estrogen IV q4 hours until bleeding is controlled
then start a monophasic OC or progestin |
|
|
With abnormal uterine bleeding, how can you treat it using estrogens and progestin?
|
multidose monophasic OC regimen
1 PO tid x7 days, then daily for 3-6 weeks |
|
|
With abnormal uterine bleeding, how can you treat it using progestin? (one way)
|
medrocyprogesterone 60-120 mg q day until bleeding has stopped for 7 days
then: 20-40 mg q day for 3-6 weeks |
|
|
With abnormal uterine bleeding, how can you treat it using progestin? (the other way)
|
Norethindrone acetate 5-15 mg q day until bleeding has stopped for 7 days
then: 5-10 mg d day for 3-6 weeks |
|
|
What is the #1 rule with acute pelvic pain??
|
Pregnancy test!!!
|
|
|
What are the key points in acute pelvic pain?
|
pregnancy test
trust your clinical evaluations and impressions avoid pain meds prior to evaluation be systematic |
|
|
What are the important causes of pelvic pain?
|
ectopic pregnancy
ovarian torsion PID & tuboovarian abscess endometriosis ovarian cysts degenerating fibroids |
|
What is this?
|
endometriosis
|
|
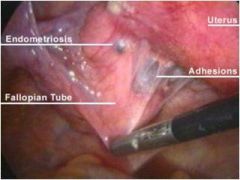
note the anatomy
|
delicious
|
|
What is this?
|
endometriosis
|
|
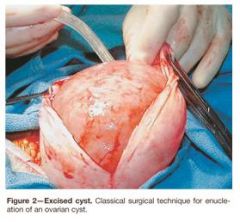
What is this?
|
ovarian cyst
|
|
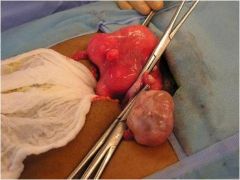
What is this?
|
ovarian cyst
|
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for acute pelvic pain?
|
important causes already listed + adhesions
+ (this is what is actually on his slide) ovarian lesions -benighn psysiologic ovarian cysts -benign pathologic cysts -solid ovarian lesions (rarely a source of pain) -ovarian torsion hydrosalpinx |
|
|
List 3 examples of benign physiologic ovarian cysts
|
follicular cysts
luteal cysts hemorrhagic cysts |
|
|
What can the rupture of a hemorrhagic cyst result in?
|
bleeding and free fluid
|
|
|
What are 4 examples of benign pathologic cysts?
|
serous and mucinous cystadenoma
endometrioma tubo-ovarian abscess dermoid cyst |
|
|
What type of ovarin lesion rarely is a source of pain?
|
solid ones
|
|
|
What is the key phrase with ovarian torsion that should clue you in on it's presence?
|
pain out of proportion to exam
|
|
|
What often accompanies ovarian torsion?
|
large ovarian lesions
|
|
|
What does US show with ovarian torsion (may show)?
|
lack of blood flow to ovary on US color flow study
|
|
|
Because ovarian torsion is a TRUE EMERGENCY, ______________________________
|
do NOT delay surgical intervention if it is suspected!
|
|
|
What are some additional differential diagnoses for acute pelvic pain?
|
1. appendicitis
2. UTI 3. cholecystitis 4. diverticulitis 5. inflammatory bowel disease 6. irritable bowel syndrome 7. musculoskeletal causes |
|
|
How do you treat oravian cysts and masses?
|
pain control
immediate surgical management if necessary |
|
|
When do you need to treat ovarian cysts with immediate surgical management?
|
1. hemorrhage
2. bowel obstruction 3. ureteral obstruction 4. uncontrolled pain 5. suspect torsion |
|
|
How do you treat ovarian torsion?
|
with immediate surgery! the ovary can often be preserved.
|
|
|
What is PID?
|
a generalized term that refers to infection and inflammation of the upper GI tract and pelvis
|
|
|
What can be included in PID?
|
endometritis
salpingitis tubo-ovarian abscess peritonitis |
|
|
Describe acute salpingitis
|
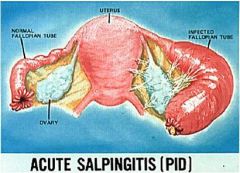
|
|
|
With PID ___% have lower abdominal pain
|
90
|
|
|
With pid, 90% have ____________
|
lower abdominal pain
|
|
|
With PID ___% have mucopurulent cervical discharge
|
75%
|
|
|
With PID, 75% have _____
(symptom) |
mucopurulent discharge
|
|
|
With PID, __% have a SED rate >15
|
75%
|
|
|
with PID, 75% have _______
(lab value) |
a SED rate >15
|
|
|
with PID, __% have WBC >10,000
|
50%
|
|
|
with PID, 50% have _____________
|
WBC >10,000
|
|
|
Many individuals with PID are ______________
|
asymptomatic
|
|
|
What is the Gold Standard for diagnosing PID?
|
lapraoscopy
|
|
|
List 6 diagnostic tests you can consider in PID.
|
1. UhCG
2. CBC with diff 3. vaginal culture 4. gonorrhea and chlamydia DNA probe 5. pelvic US 6. culdocentesis |
|
|
What is the outpatient treatment for PID?
|
ceftriaxone 250 mg IM single dose plus doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 14 days with or without metronidazole 500 mg PO BID x14 days
or ofloxin 400 mg PO BID x 14 days plus metronidazole 500 mg PO BID x 14 days |
|
|
What are the drugs used in the 3 possible regimens to treat inpatient PID?
|
1. cefoxitin or cefotetan IV +
doxy IV 2. clindamycin IV +gentamycin loading dose + regular dose 3. ampicillin/sulbactam IV + doxy IV |
|
|
This is a possible inpatient treatment for PID:
Cefoxitin ___ q____ IV OR cefotetan _____ q ___ IV +doxy ____ q____ IV |
2g, 6 hours
2 g, 12 hours 100mg, 12 hours |
|
|
This is a possible inpatient treatment for PID:
clindamycin ___ q ____ IV + gentamicin _____ loading does followed by ______ q _____ |
900 mg, 8 hours
2 mg/kg, 1.5 mg/kg, 8 hours |
|
|
This is a possible inpatient treatment for PID:
ampicillin/sulbactam ______ q ____ IV + doxycycline ______ IV q ___ |
3g, 6 hours
100 mg, 12 hours |
|
|
What are 6 complications of PID?
|
1. pelvic adhesions
2. chronic PID 3. infertility 4. hydrosalpinx 5. ectopic pregnancy 6. chronic pelvic pain |
|
|
Ectopic pregnancies account for ____% of all first time pregnancies and ____% of all pregnancy related deaths
|
2%
6% |
|
|
What is the leading cause of maternal death in the first trimester?
|
ectopic pregnancy
|
|
|
Define an ectopic pregnancy?
|
implantation of the fertilized egg outside of the uterus
|
|
|
What are possible locations for an ectopic pregnancy?
|
abdomen
cervix ovary uterine cornua fallopian tube |
|
|
What is the most common location for an ectopic pregnancy?
|
the fallopian tube (97%)
|
|
|
What is the #1 cause of ectopic pregnancy?
|
abnormal fallopian tube!
ie: tubal sx PID pervious ectopic pregnancy in utero exposure to DES |
|
|
_____ of all pregnancies after tubal ligation are _________
|
1/3
ectopic |
|
|
What are the risk factors for an ectopic pregnancy?
|
infertility
use of ART previous pelvic/abdominal surgery smoking |
|
|
all reproductive age women who present with bleeding or pain should have a ______________-
|
urine pregnancy test
|
|
|
At what HCG hormone level should you see a gestational sac in the uterus?
|
Quantitative HCG >1500-2000 mlU/ml
|
|
|
What is diagnostic of ectopic pregnancy?
|
pain/bleeding + HCG over 2000 + no sac in uterus on ultrasound
or pain/bleeding + blood in abdomen + no sac in uterus |
|
|
What percent of pregnancies are complicated by per-gestation diabetes?
|
5-10%
|
|
|
DKA in pregnancy is different because _____________
|
it presents at lower levels of hyperglycemia
|
|
|
What are the symptoms od DKA in pregnancy?
|
abdominal pain
nausea/emesis altered sensorium |
|
|
In what trimester of pregnancy is DVT more common?
|
none- it has an equal frequency of occurance in all 3 trimesters
|
|
|
When is a pulmonary embolism more common during pregnancy?
|
in the post-partum period
|
|
|
What tests can you order for DVT and PE in pregnancy?
|
room air ABG
spiral CT scan |
|
|
How do you treat thromboembolism in pregnancy?
|
heparin
|
|
|
How many pregnancies does hypertensive disease complicate?
|
12-22%
|
|
|
preeclampsia/eclampsia/ (hypertensive disease?) is responsible for ___ of maternal deaths in the USA
|
17.6%
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic criteria for preeclampsia?
|
SBP >140, DBP >90 after 20 weeks gestation in previously normotensive woman
+ proteinuria defined as 300 mg or more in 24 hours |
|
|
What is the treatment of preeclampsia
|
delivery!
|
|
|
define eclampsia
|
new onset of grand mal seizures in a woman with preeclampsia
|
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis for eclampsia?
|
bleeding AV malformation
ruptured aneurysm idiopathic seizure disorder |
|
|
How is eclampsia treated?
|
medical stabilization with magnesium sulfate, valium, and anti-hypertensives
+ delivery of fetus |
|
|
How do you manage the injured pregnant woman?
|
-evaluation and stabilization of maternal vital signs
-ABC -displacement of uterus after 20 weeks -secondary survery with fetal evaluation |
|
|
In pregnancy, there is a ______ increase in ________ at the expense of __________
(respiration) |
30-40%
tidal volume expiratory reserve volume |
|
|
What happens to the diaphragm in pregnancy?
|
it is elevated
|
|
|
What happens to minute ventilation in pregnancy?
|
it increases
|
|
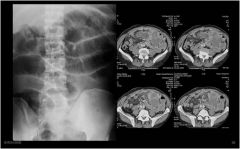
What is going on here?
|
small bowel obstruction
|
|
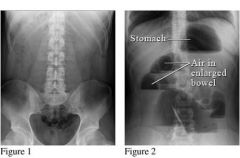
What is going on here?
|
the pic on the left is normal
the pic on the right is an obstructed bowel showing trapped air |
|
|
What is a hypersensitivity reaction?
|
a response to an exogenous antigen
|
|
|
What are some possible clinical manifestations of a hypersensitivity reaction?
|
itching, hives
angioedema vasodilation and cardiovascular collapse |
|
|
How are hypersensitivity reactions classified?
|
based on immunologic mechanism
|
|
|
What are the steps of a type I hypersensitivity reaction? explain what happens.
|
-initial sensitization (formation of IgE)
-secondary exposure (release of vasoactive amines (histamine)- basophils & mast cells) which leads to recruitment |
|
|
What type of hypersensitivy reaction is true anaphylaxis?
|
type I
|
|
|
explain the steps of a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
|
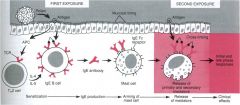
|
|
|
List the primary mediators of a type I hypersensitivity reaction
|
biogenic amines
chemotactic mediators enzymes proteoglycans |
|
|
What biogenic amines are primary mediators in a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction?
|
histamine
|
|
|
What do chemotactic mediators do as primary mediators of a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction?
|
attract eosinophils and neutrophils
|
|
|
List the secondary mediators in a type I hypersensitivity reacion
|
leukotrienes
prostaglandin D2 platelet activity factor cytokines |
|
|
What do leukotrienes do as secondary mediators in a type I hypersensitivity reaction?
|
increase vascular permeability and smooth muscle contraction
|
|
|
What dose prostaglandin D2 do as a secondary mediator in a type I hypersensitivity reaction?
|
causes bronchospasm
|
|
|
What do cytokines do as secondary mediators in a type I hypersensitivity reaction?
|
-recruit inflammatory cells
-activate B cells |
|
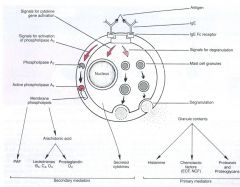
|
apparently that picture is important
|
|
|
What are the 3 mechanisms for a type II hypersentitivity reaction?
|
-antibody mediated
-antibody-dependent cell-mediated toxicity -antibody mediated cellular dysfunction |
|
|
With type II hypersensitivity reactions, the antibody mediated mechanism is ___________
|
complement dependent
|
|
|
a transfusion reaction is an examples of a __________-
|
type II hypersensitivity reaction
antibody mediated |
|
|
parasites cause _____________ reactions that are ____________________
|
type II hypersensitivity
Ab-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity |
|
|
Myasthinia grave is an example of this type of hypersensitivy reaction
|
type II hypersensitivity
Ab- mediated cellular dysfunction |
|
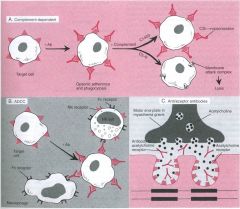
What type of reaction is this demonstrating?
|
type II hypersensitivity
|
|
|
What is a type III hypersensitivity reaction?
|
immune complex-mediated
|
|
|
describe how a type III hypersensitivity reaction takes place
|
Ab-Ag complexes are formed
deposited in tissues there is an inflammatory reaction |
|
|
What are some possible examples of a type III hypersensitivity reactions that may be post-infectious?
|
glomerulonephritis
endocarditis |
|
|
What are two examples of type III hypersensitivity reactions?
|
SLE
RA |
|
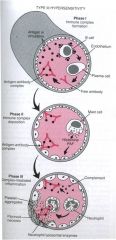
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is this picture illustrating?
|
type II hypersensitivity
|
|
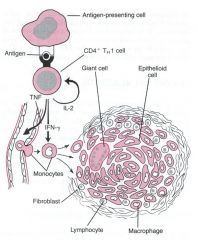
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is this picture demonstrating?
|
type IV
|
|
|
type IV hypersensitivity reactions are _______________
|
cell-mediated
|
|
|
IN general, what happens in a type 4 hypersensitivity reaction?
|
- sensitized T- lymphs
-delayed CD4 (8-12 hour, peak 24-72 hours. granuloma formation) -direct C48 -response to intracellular microbes |
|
|
granuloma formation is associated with ______ in the type IV hypersensitivity reaction
|
CD4
|
|
|
When does CD4 come into play in a typ IV hypersensitivity reaction?
|
8-12 hours, peaks at 24-72 hours
|
|
|
A type IV hypersensitivity reaction can occur in response to intracellular microbes, especially ______________
|
mycobacterium tebuerculosis
|
|
|
What is non-immunologic anaphylaxis?
|
a suddne, massive mast cell or basophil degranulation without antibodies present
|
|
|
List 4 examples of non-immunologic anaphylaxis
|
Red man syndrome (vanco)
opiates cold urticaria ACE inhibitors |

