![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The placenta has three main functions
3ct |
Metabolism
Transport of gases and nutrients Endocrine secretion |
|
|
|
Placental Metabolism
3ct |
synthesizes glycogen
cholesterol fatty acids which serve as sources of nutrients and energy for the embryo. |
|
|
|
Transport across the placental membrane is by one of the following four main transport mechanisms
4ct |
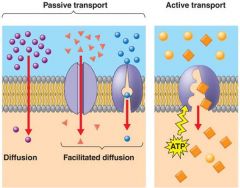
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion Active transport Pinocytosis (a process by which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells) |
|
|
|
Transport across the placental membrane is by
Oxygen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide |
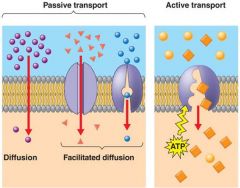
by simple diffusion.
|
|
|
|
Transport across the placental membrane is by
►Glucose, sodium ions choride ions- |
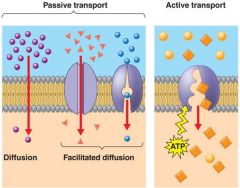
Facilitated diffusion
|
|
|
|
Transport across the placental membrane is by
►Amino acids |
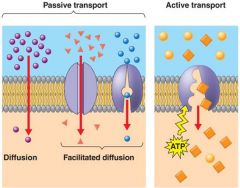
actively transported
|
|
|
|
a process by which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells. is called what =
|
Pinocytosis
|
►Pinocytosis: is a form of endocytosis in which small particles are brought into the cell which subsequently fuse with lysosomes to hydrolyze, or to break down, the particles)
Maternal Antibodies: IgG |
|
|
Other methods of placental transfer
Info *** |
►RBC can move across through microscopic breaks in the placental membrane
►Transport of cells across the placental membrane under their own power Maternal leukocytes and Treponema pallidum. ►Some protozoa such as Toxoplasma gondii infect the placenta by creating lesions and then cross the placental membrane through the defects that are created. |
|
|
|
Glucose produced by the mother and placenta is quickly transferred to the fetus by =
|
F. diffusion.
|
|
|
|
Among lipids only ____ ____ ____
acids are transported across the placenta. |
free fatty acids
|
|
|
|
T/F
Vitamins cross the placental membrane and are essential for normal development. |
T/F
|
|
|
|
______ ________
vitamins cross the placental membrane more quickly than fat-soluble ones. |
Water-soluble
|
|
|
|
Maternal Antibodies
Gamma globulins, such as the IgG class are readily transported to the fetus by |
pinocytosis
|
pinocytosis (is a form of endocytosis in which small particles are brought into the cell which subsequently fuse with lysosomes to hydrolyze, or to break down, the particles).
|
|
|
Maternal Antibodies
Passive immunity is conferred upon the fetus by the placental transfer of maternal antibodies. info |
.
|
|
|
|
Maternal antibodies confer fetal immunity to some diseases such as
3ct |
diphtheria
smallpox measles |
|
|
|
Maternal Antibodies
However, no immunity is acquired for |
pertussis (whooping cough)
varicella (chickenpox) |
|
|
|
Maternal Antibodies
Hemolytic disease of the newborn or erythroblastosis fetalis is what |
Rh positive fetus and Rh negative mother.
|
|
|
|
►Waste Products
Urea and uric acid pass through the placental membrane by simple diffusion and bilirubin is quickly cleared. |
.
|
|
|
|
►Waste Products
Most drugs and drug metabolites cross the placenta by simple diffusion, the exception being those with a structural similarity to amino acids, such as = |
methyldopa
So MD transported by…? |
|
|
|
►Waste Products
Fetal drug addiction may occur after maternal use of drugs such as heroin/morphine/cocaine and 50 to 75% of these newborns experience withdrawal symptoms. info |
.
|
|
|
|
Toxoplasmosis can cause
|
Encephalitis
It is caught from = |
Cat litter box
|
|
|
Toxoplasmosis
During the first few weeks post-exposure the infection typically causes |
a mild flu-like illness .
|
|
|
|
Toxoplasmosis
The parasite can cause encephalitis, and neurologic diseases, and can affect the heart, liver and eyes. |
pregnant women who newly contract the toxoplasmosis have a 40% chance of transmitting it to the fetus. Women who were first exposed to toxo more than six months before becoming pregnant are not likely to pass the infection to their children.
|
►Most infants have no symptoms at birth, but a small percentage may be born with eye (chorioretinitis) or brain damage(intracranial calcifications, brain abscess).
|
|
|
►Placenta as Endocrine Organ
The placenta produces both protein and steroid hormones as |
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Human placental lactogen (hPL) Estrone, estradiol (most potent), and estriol Progesterone |
|
|
|
What do these Placental Horones do
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) |
s a glycoprotein hormone that stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum.
|
|
|
|
What do these Placental Horones do
Human placental lactogen (hPL) |
is a protein hormone that induces lipolysis, thus elevating free fatty acid levels in the mother; it is considered to be the "growth hormone" of the fetus.
|
|
|
|
What do these Placental Horones do
Estrone, estradiol (most potent), and estriol |
are steroid hormones produced by the placenta, but little is known about their specific functions in either mother or fetus.
|
|
|
|
What do these Placental Horones do
Progesterone |
is a steroid hormone that maintains the endometrium during pregnancy, is used by the fetal adrenal cortex as a precursor for glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid synthesis, and is used by the fetal testes as a precursor of testosterone synthesis.
|
|
|
|
Placental hormones, and to a lesser extent increased fat deposits during pregnancy, seem to mediate =
|
insulin resistance during pregnancy.
Glucocorticoid (cortisol) and progesterone are the main culprits, but human placental lactogen, prolactin and estradiol contribute too. |
|

