![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a. What is the period of pregnancy? b. what is the period of Gestation? c. What is the period for an embryo? d. What is the period for a foetus? e. What is the period for an infant? |
a. Fertilisation to birth b. Last Menstruation to Birth c. Fertilisation to week 8 d. week 9 to birth e. after birth |
|
|
Development: a. What occurs in week 1? b. What occurs in week 2? c. What occurs in week 3? d. What occurs during the Foetal period? (9-38) |
a. Fertilisation, Morula, Blastocyte, Implantation b. Bilaminar embryo, Placenta, Membranes, Gastrulation(begins) c. Gastrulation + Neurulation d. Brain grows, Neural connections made, loads of growth |
|
|
Describe the process of Gastrulation |
- Bilaminar Embryo (Inner cell mass = Epiblast + Hypoblast) turns into - Trilaminar Embryo (Inner cell mass = Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm) |
|
|
A Blastocyst contains which 2 things? |
- Embryoblast (inner cell mass) - Trophoblast (outer cell mass) |
|
|
Trophoblast develops to form which 2 things? |
- Syncytiotrophoblast: Invading cells - Cytotrophoblast: Proliferating cells (forms placenta) |
|
|
In a bilaminar embryo, the embryoblast contains which 2 things? |
- Epiblasts (on top) - Hypoblast (below) |
|
|
a. Which cavities are contained within a blastocyst? b. What do they border? |
a. - Amniotic Cavity - Yolk Sac cavity b. - AC: Epiblast - YSC: Hypoblast |
|
|
During the process of Gastrulation, what does the Epiblast become? |
- Ectoderm - Mesoderm - Endoderm |
|
|
a. What does the Ectoderm develop into? b. What does the Endoderm develop into? |
a. - Integumentary System - Brain - Spinal Cord - Pituitary Gland b. - Epithelial layer of: - Digestive System - Lungs - Pancreas - Bladder |
|
|
What does the Mesoderm develop into? |
- Musculoskeletal system - Cardiovascular system - Reproductive System - Excretory System |
|
|
What happens at the very beginning of Gastrulation? (2 layer ---> 3 layer) |
- Primitive streak occurs - On Epiblast of Embryonic Disc - Mainly on Longitudinal axis of body |
|
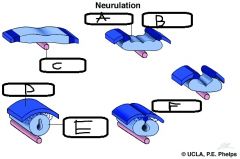
|
a. Neural Plate b. Neural Fold c. Notochord d. Epidermis e. Neural Tube f. Neural Groove |
|
|
a. Which layer(s) does the Epiblast develop into? b. Which layer(s) does the Hypoblast develop into? |
a. Ectoderm b. Endoderm |
|
|
Describe the steps in Invagination |
- Ectoderm pushes up into middle layer cells (Mesoderm) - Middle layer cells (Mesoderm) surrounds endoderm + ectoderm + inside border of Trophoblast cells |
|
|
a. What is neurulation? b. When can neurulation occur? |
a. Process by which Nervous System is formed by the Ectoderm Layer b. After the formation of the 3 germ layers |
|
|
a. Which cells develop to make the Notochord? b. What is the Notochord? c. What does the Notochord do? |
a. Mesoderm cells b. Cylindrical mass of cells which runs along the entire length of the developing embryo c. Induces and directs the thickening of the Ectodermal cells to form the Neural Plate |
|
|
- The central cells of the Neural Plate move outwards to form the __(a)__ and the __(b)__ - The continued movement of the central portion of the Neural Plate brings together the 2 __(c)__, forming the __(d)__ - Next to the fully formed (d) is the __(e)__ |
a. Neural groove b. Neural folds c. Neural folds d. Neural tube e. Neural crests |
|
|
a. What do Neural Crests give rise to? b. What does the Neural tube give rise to? |
a. Peripheral Nervous System b. Central Nervous System |

