![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
173 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
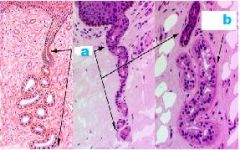
What type of gland?
|
-Sweat Gland
a. Duct b. Secretory Region |
|
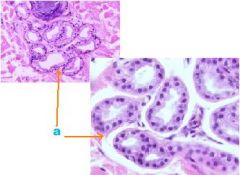
What type of glands?
|
a. secretory region of sweat glands
|
|
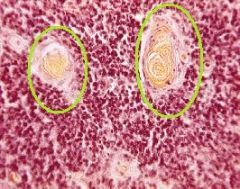
What are these?
Where are they Located? |
Thymic (Hassall's)Corpuscles located within the Medulla of the Thymus
|
|
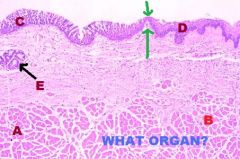
|
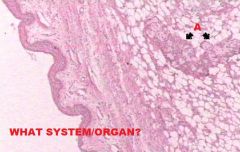
Respiratory System
Larynx A. False Vocal Cords (Skele m. however) B. Vocal Muscle (Skele m.) C. Respiratory Epithelium (Covering vestibular folds) D. NKSS (covering TVC) E. Mixed Gland in Vocal Fold (no glands or Lymphatics in TVC!) Green arrows where Pulmonary Epith becomes NKSS; FVC->TVC cranially |
|
|
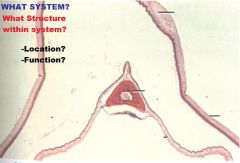
Respiratory System
Larynx-False Vocal Cord A. Gland (NO GLANDS IN TVC !!!) |
|
|
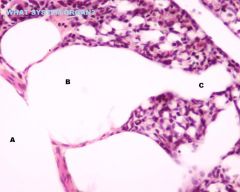
Avian Respiratory System
-Syrnx -located at bifurcation of trachea into 2 principal bronchi -For Voice production in birds |
|
|
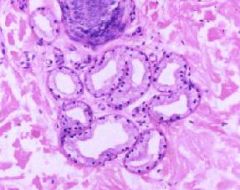
Avian Respiratory System
Lung A. Lumen of Parabronchus B. Air Vesicle C. Air Capillary |
|
A. What organ/part?
B. What tissues? C. What type of Glands? |
A. External Ear Canal
B. Elastic Cartilage->Bone C. Apocrine Sweat Glands |
|
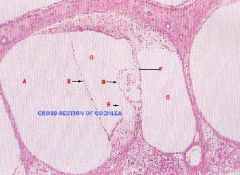
|
A. Scala Vestibuli
B. Vestibular Membrane C. Cochlear Duct (Scala Media) D. Organ of Corti E. Tectorial Membrane F. Basilar Membrane G. Scala Tympani |
|
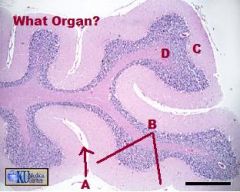
|
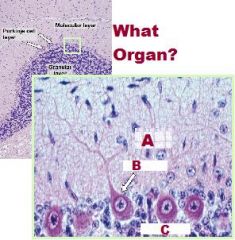
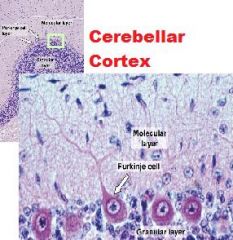
-Cerebellum
A.Sulcus B.Folium (Folia pl) C. Grey Matter (Cortex) D. White Matter (Medulla) |
|
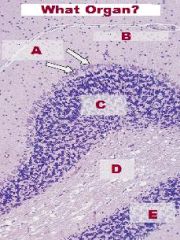
|
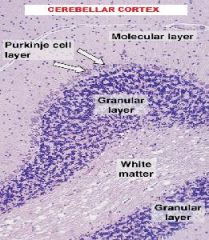
|
|
|
|
|
|
Choroid Plexus
|
|
|
-Choroid Plexus
-Produce CSF A. Capillary B. Invaginations pia into ventricles –Loose CCT (highly vascular) covered with simple cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
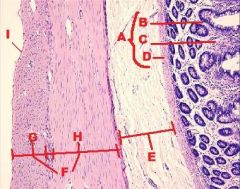
Digestive System
A. Mucosa (Mucous Membrane) B. Epithelium C. Lamina Propria D. Muscularis Mucosae E. Submucosa F. Tunica Muscularis G. Inner Circular Layer H. Outer Longitudinal Layer I. Serosa |
|
|
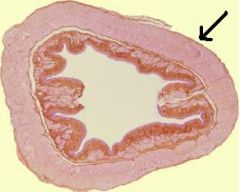
Digestive System-ESOPHAGUS
Adventitia (CCT) covers organs outside body cavity (Serosa=Mesothelium=CCT + Simple squamous epithelium); covers organs within body cavity) |
|
|
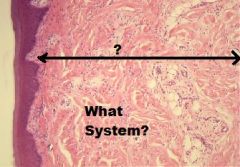
Digestive System
Lamina Propria/Submucosa (Blended sometimes) |
|
|
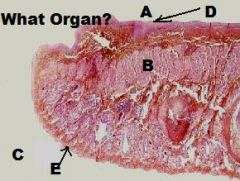
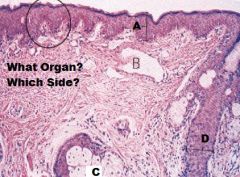
Lip
A. Oral Cavity Side B. Buccal Muscle C. Integument Side D. NKSS E. KSS + Adnexa |
|
|
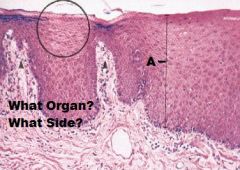
LIP
INTEGUMENT SIDE A.KSS B.Blood Vessel C.Sebaceous Gland (mixed) D. Hair Follicle |
|
|
Lip/Oral Cavity Side
A. NKSS |
|
|
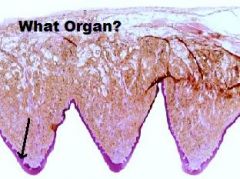
Hard Palate
Mucosa (KSS) |
|
|
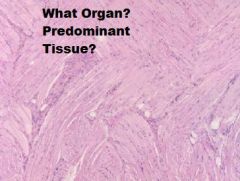
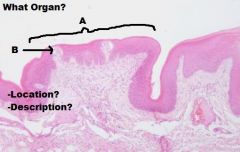
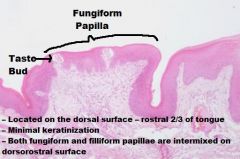
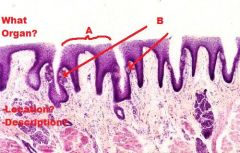
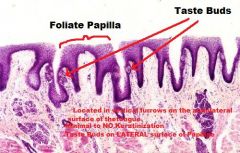
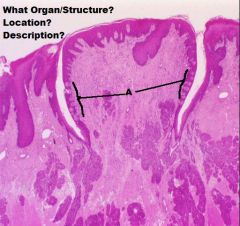
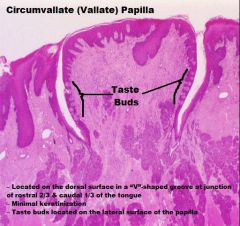
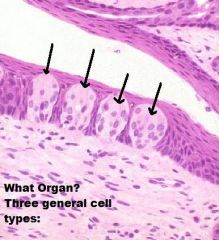
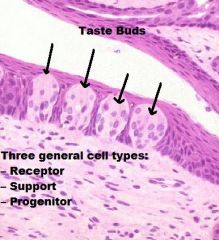
TONGUE
A. Mucosa (KSS usually) B. Lamina Propria/Submucosa (NO MUSCULARIS MUCOSA!) C. Mixed Glands D. Skeletal Muscle (3 Planes) E. Unilocular Adipose Tissue |
|
|
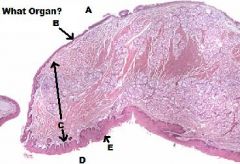
TONGUE
Skeletal Muscle (In 3 Different Planes, UNIQUE!!) |
|
|
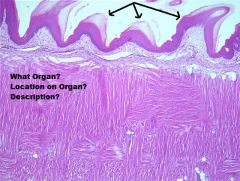
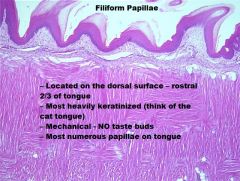
-Soft Palate
A. Nasopharynx Side B. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium with Cilia & Goblet Cells C. Lamina Propria/ Submucosa +CCT+Mucous Glands D. Oral Cavity Side E. NKSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
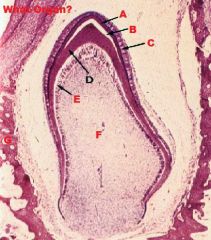
|
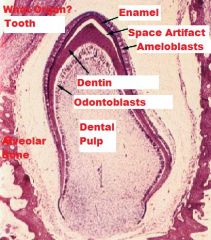
|
|
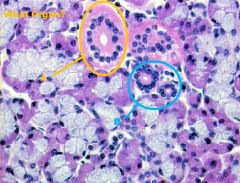
|
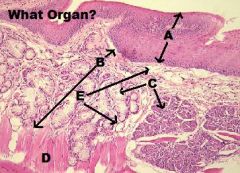
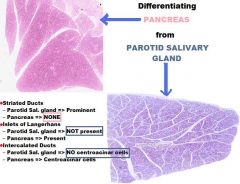
-SALIVARY GLAND
A. Striated Duct B. Intercalated Ducts |
|
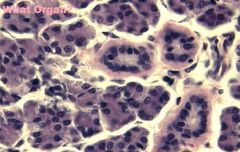
|
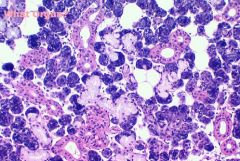
PAROTID SALIVARY GLAND
|
|
|
MIXED SALIVARY GLAND
|
|
|
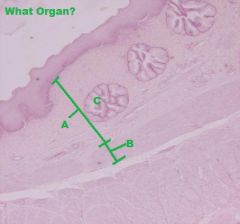
AVIAN ESOPHAGUS
A. Lamina Propria B. Muscularis Mucosa C. Esophageal Glands (Mucous) |
|
|
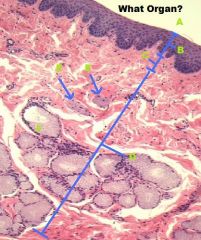
MAMMALIAN ESOPHAGUS
A. Lumen B. KSS C. Lamina Propria D. Submucosa E. Muscularis Mucosae F. Esophageal Gland (Mucous) |
|
|
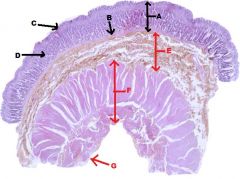
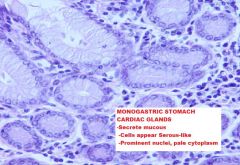
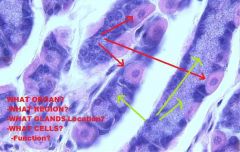
A. Monogastric Stomach
B. Esophagus |
|
|
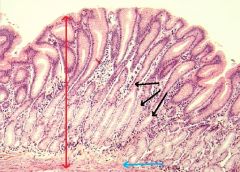
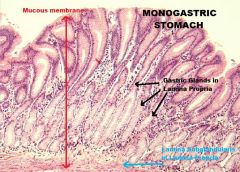
STOMACH
A. Mucous Membrane B. Muscularis Mucosa C. Epithelium D. Lamina Propria E. Submucosa F. Tunica Muscularis G. Serosa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
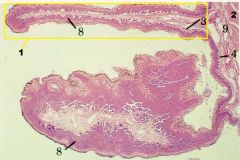
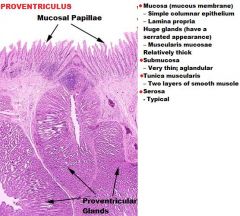
RUMEN
1-Papilla (mucosal projection) 2-Muscularis Externa 3- Connective tissue band 4+9- Submucosa blended w/ LP (aglandular) 8- Stratified Squamous Epithelium, Keratinized (also can be NKSS) -NO MUSCULARIS MUCOSA -Tunica Muscularis=2 Layers of Smooth Muscle -Serosa=Typical |
|
|
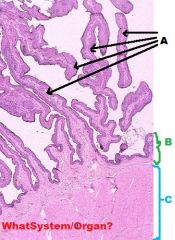
Digestive System/Rumen
A-Papillae B-Mucosa C-Tunica Muscularis |
|
|
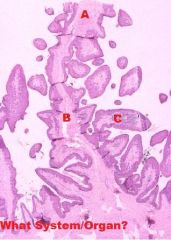
Digestive System/Reticulum
A-Muscularis Mucosa (Incomplete; located only in upper end of reticular crests) B-Primary Fold C-Secondary Fold |
|
|
Digestive System/Reticulum
-Muscularis mucosa In upper part of a reticular crest;appear as bundles of smooth muscle |
|
|
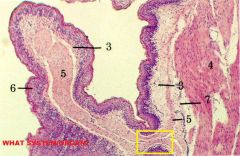
Digestive System/Omasum
3-Lamina Propria 4-Tunica Muscularis 5-Muscularis Mucosae (COMPLETE!=Distinguishing factor!!!) 6-Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium 7-Submucosa |
|
|
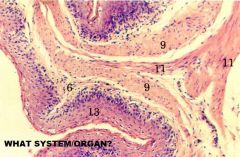
Digestive System/Omasum
6-Lamina Propria 9-Muscularis Mucosae 11-Tunica Muscularis (Smooth Muscle) 13- Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

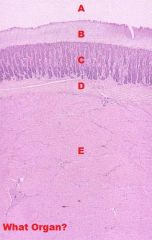
What Tissue?
|
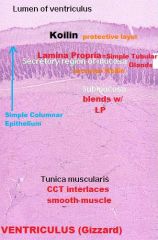
Ventriculus (Gizzard)
-Interlacing CCT within the Tunica Muscularis (special stain) |
|
|
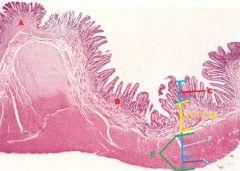
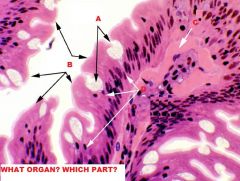
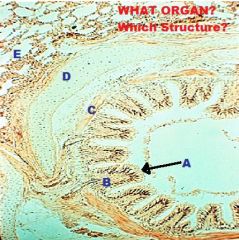
A- Stomach
B- Small Intestine (Duodenum) C- Mucous Membrane D- Submucosa + Glands E- Tunica Muscularis F- Circular Muscle G-Longitudinal Muscle |
|
|
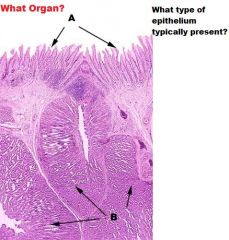
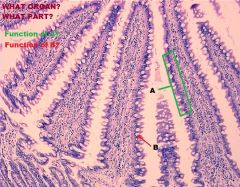
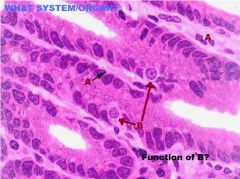
Small Intestine
Mucous Membrane A. Goblet Cells B. Microvilli of Brush Border C. Central Lacteal D. Goblet Cell Nuclei |
|
|
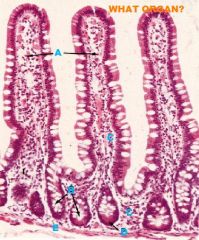
Small Intestine
-Mucous Membrane -Villi (projections of mucous membrane....KEY TO ID SMALL INTESTINE!!) A.-simple columnar epithelium -absorptive cells B.-Goblet cells increase in #s from duodenum to ileum -Secrete mucin (protection/lubication) |
|
|
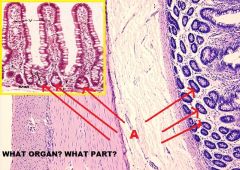
Small Intestine
Mucous Membrane-LP A. Villi (Distinguishing) B. Intestinal Crypt C. Lamina Propria D. Paneth Cell E. Muscularis Mucosae |
|
|
Small Intestine
Mucous Membrane (LP) A. Intestinal Crypts |
|
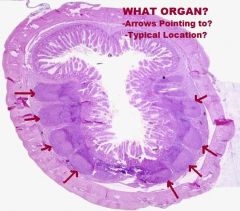
|
Small Intestine - Ileum
Peyer's Patches (Aggregations of Lymph Nodules) -Typically located in submucosa, occasionally found in lamina propria |
|
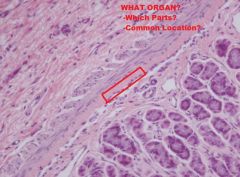
|
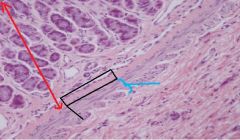
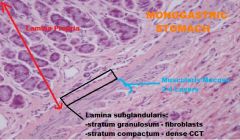
Small Intestine
(THIS PIC is from STOMACH) -Lamina subglandularis -stratum compactum; -stratum granulosum -found in carnivores -located in deepest LP; can be found in proximal jejunum |
|
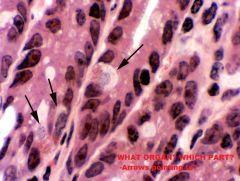
|
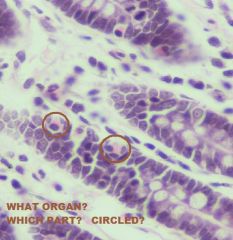
Small Intestine; Deep in intestinal crypts
-Intestinal Enteroendocrine Cells (Acidophilic granules face LP, clear cytoplasm around nucleus) |
|
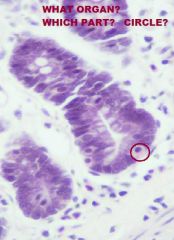
|
Small Intestine; Deep in intestinal crypts
-Intestinal Enteroendocrine Cells (Acidophilic granules face LP, clear cytoplasm around nucleus) |
|
|
Small Intestine; Deep in intestinal crypts
-Intestinal Enteroendocrine Cells (Acidophilic granules face LP, clear cytoplasm around nucleus) |
|
|
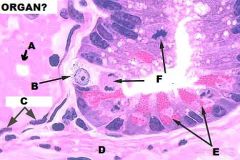
Small Intestine, Intestinal Crypt
A. Blood Vessels B. Enteroendocrine Cell (APUD) C. Endothelial Cell D. Muscularis Mucosae E. Paneth Cells F. Mitotic Figures |
|
|
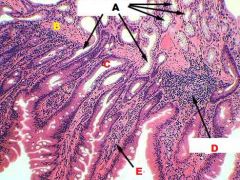
Small Intestine
A. Brunner's Glands (Submucosal Intestinal Glands) B. Muscularis Mucosae C. Intestinal Crypt D. Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue E. Villus |
|
|
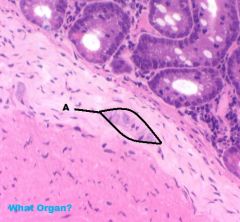
Small Intestine
A. Submucosal Plexus |
|
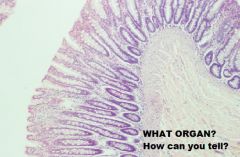
|
Large Intestine
-NO VILLI! |
|
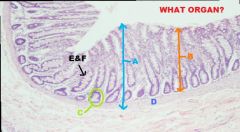
|
Large Intestine
A. Mucous Membrane B. Lamina Propria C. Intestinal Crypts D. Muscularis Mucosae (Usually Thin) E. Simple columnar epithelium with F. Goblet cells & (Microvilli) |
|
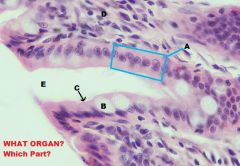
|
Large Intestine; Mucous Membrane
A. Simple Columnar Epithelium with B. Goblet Cell & C. Microvilli D. Lamina Propria E. Intestinal Crypt RELATIVELY FEW ENTEROENDOCRINE CELLS! |
|
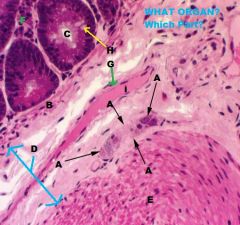
|
Large Intestine
A. Submucosal Plexuses (Aglandular) B. Muscularis Mucosa C. Intestinal Crypt D. Submucosa E. Muscularis Externa, inner circular F. Lamina Propria G. Smooth Muscle H. Goblet Cell i. Vein |
|
|
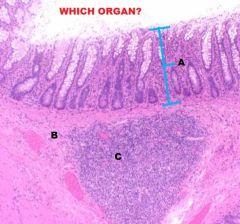
Large Intestine
A. Mucous Membrane B. Submucosa C. Peyer's Patch (Lymph Nodule) |
|
|
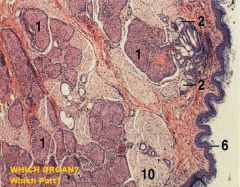
Large Intestine, Anal Canal
1. Circumanal gland, nonsebaceous 2. Circumanal gland, sebaceous 6. Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epidermis 10. Skeletal Muscle (Anal Sphincter) |
|
|
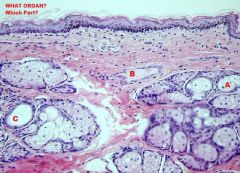
Large Intestine
Anal Canal A. Sebaceous Glands B. Hair Follicle C. Apocrine Tubular Gland |
|
|
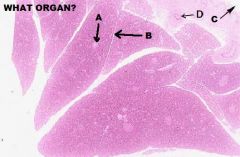
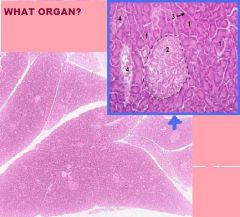
LIVER
A. Islet of Langerhans B. CT, septum of C. Pancreatic Duct D. Intercalated duct (x.s) |
|
|
Liver
1 - acinus 2 - islet of Langerhans 3 - interlobular connective tissue septa 4 - blood vessels |
|
|
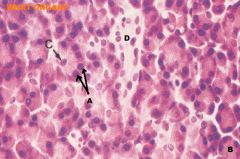
Pancreas
A. Acinar Cells B. Acinus C. Centroacinar Cell D. Intercalated Duct, l.s. |
|
|
|
|
|
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS PARS DISTALIS A. Chromophobe B. Basophil C. Acidophil |
|
|
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
PINEAL GLAND |
|
|
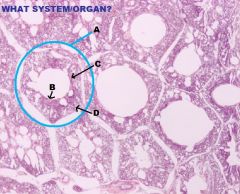
Endocrine System
Thyroid Gland A. Thyroid Follicle B. Follicular Epithelium (Simple Cuboidal) |
|
|
Endocrine System
A. Thyroid Gland B. Parathyroid Gland C. CCT |
|
|
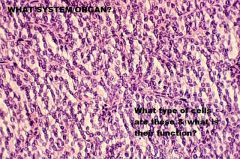
Endocrine System
Parathyroid Gland Principal Cells -Secrete PTH |
|
|
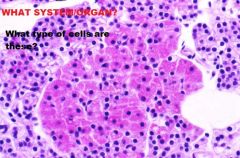
Endocrine System
Parathyroid Gland -Oxyphil Cells |
|
|
|
|
|
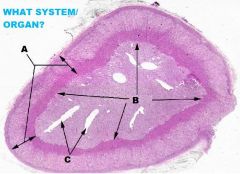
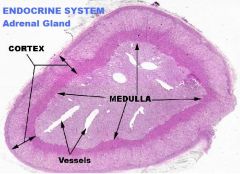
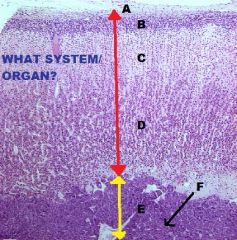
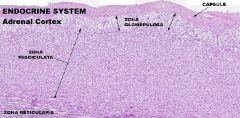
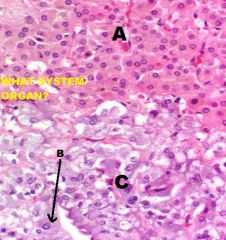
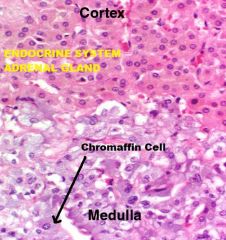
Endocrine System
Adrenal Gland A. Capsule (CCT) B. ZG C. ZF D. ZR E. Medulla F. Chromaffin Cell(s) |
|
|
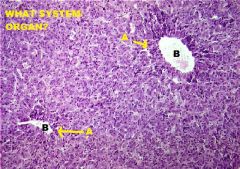
Endocrine System
Adrenal Medulla A. Chromaffin Cells (polarized around) B. Blood Vessels |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
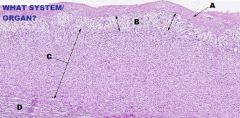
Endocrine System
Adrenal Gland |
|
|
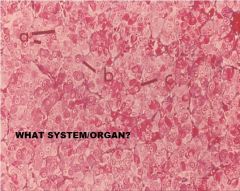
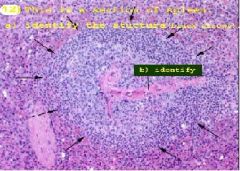
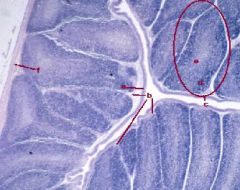
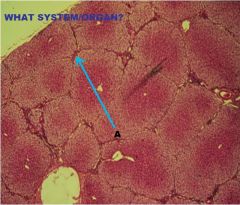
a. splenic nodule
b. nodular arteriole (or central arteriole or paracentral arteriole) |
|
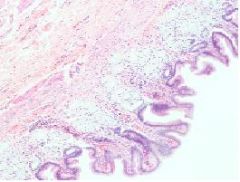
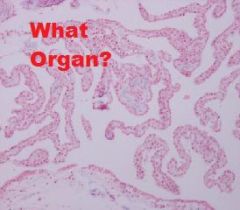
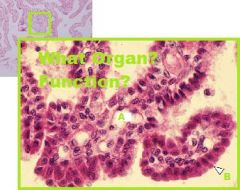
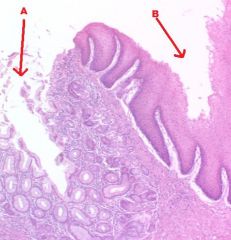
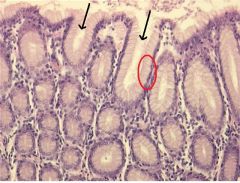
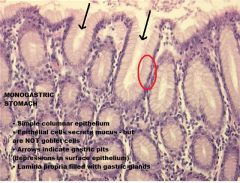
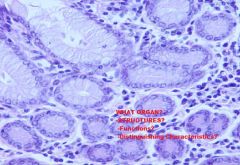
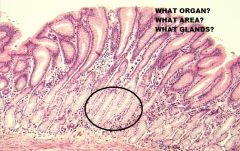
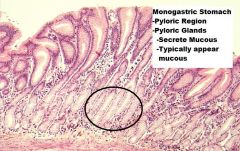
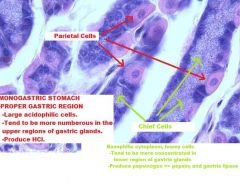
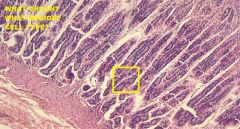
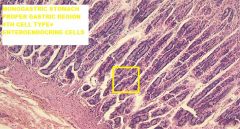
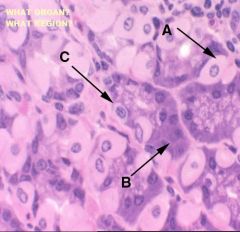
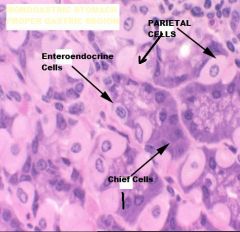
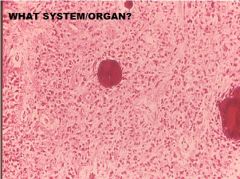
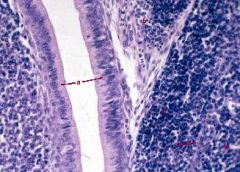
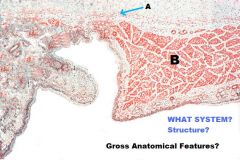
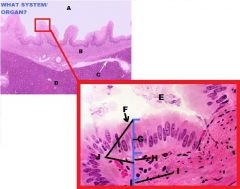
Which region of the monogastric stomach is shown in this photomicrograph?
|
Pyloric gland region
|
|
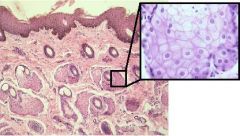
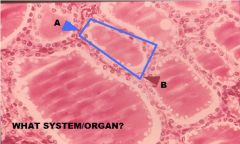
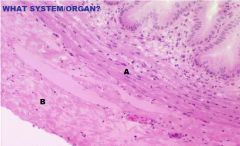
What specific type of gland is shown and in the enlarged region to the right?
|
Sebaceous gland
|
|
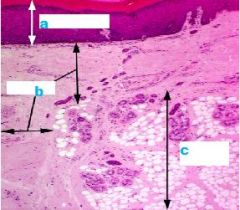
Basic Skin Structure
|
a. Epidermis
b. Dermis c. Hypodermis (NOT part of Skin) |
|
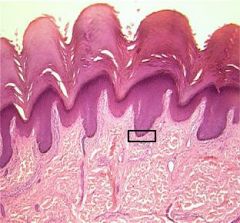
What layer of epidermis is this?
|
Stratum basale (Stratum germinativium) = Deepest layer of skin
|
|
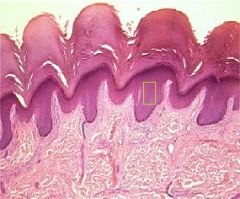
What layer of living epidermis is this?
What cells does it contain & what is their function? |
-Stratum Spinosum (2nd Deepest Layer)
-Keratinocytes (Accumulate Keratin) |
|
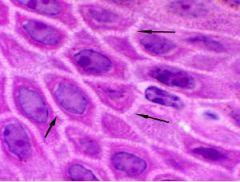
What layer of epidermis is this?
Spiney appearance caused by structures arrows are pointing to? |
-Stratum Spinosum
-Desmosomes |
|
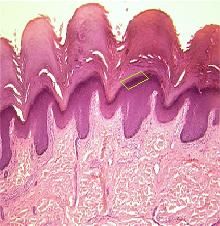
What layer of epidermis is this?
|
Stratum Granulosum (3rd layer starting from deepest)
|
|
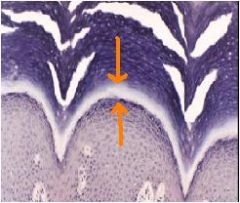
What layer of epidermis is this?
Where is it normally seen? What is its cells filled with? |
-Stratum lucidum
- “optional" epidermal layer -Seen in thick skin, but not in thin skin -Seen in places of very heavy wear, like foot pads. -It does not form in skin that has hair follicles. -Forms clear band above stratum granulosum. -Eleidin, a fibrous protein that maybe an intermediate form of keratin. |
|
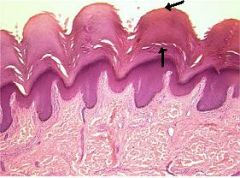
What layer of epidermis is this?
What is it comprised of? |
Stratum corneum=Keratin=a dead layer on surface
|
|
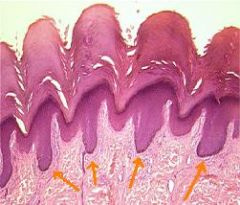
|
Rete pegs or Epidermal ridges/pegs
|
|
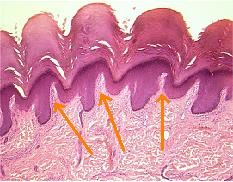
What are the arrows pointing to?
What two layers are within? -Other structures/functions within? |
-Dermal papillae
-CCT Layers = indistinct -Papillary layer = adjacent to epithelium; interdigitates with epithelium (epidermal pegs) Interdigitation provides structural support -Reticular layer = deeper layer -Blood vessels = supply nutrients to epidermis -Nerves -Receptors: Pacinian Corpuscle =pressure Meissner’s Corpuscle = touch |
|
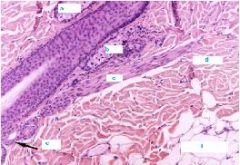
|
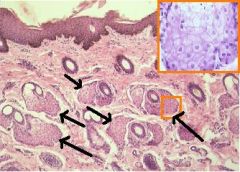
a. Sebaceous Gland
b. Sebaceous Gland c. Arrector Pili m. d. Dermis e. Sweat Gland f. Hypodermis |
|
|
Sebaceous Glands
|
|
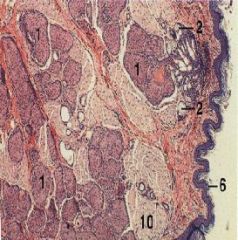
|
1. circumanal gland, nonsebaceous
2.Circumanal gland, sebaceous 6. Keratinized epidermis 10. Skeletal m. |
|
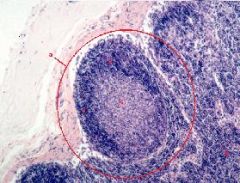
*b forms in response to?
|
a. Secondary Lymph Nodule
b. Germinal Center c. Corona (mantle layer) d. Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue *Antigenic stimulation of B Lymphocytes |
|
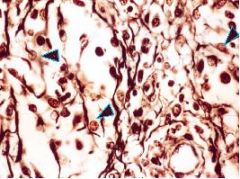
What system is this picture associated with?
|
Reticular Cells
-Lymphatic System (Within the medulla of a lymph node) |
|
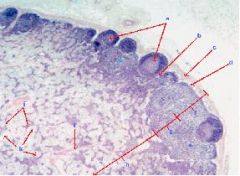
What is this a section of?
|
Lymph node
a. Secondary Lymph Nodule w/ Germinal Center b. Intermediate Sinus c. Capsule d. Subcapular Sinus e. Diffuse Lymphoid Tissue f. Outer Cortex g. Inner Cortex h. Medulla i. Trabecula j. Medullary Sinus k. Medullary Cord |
|
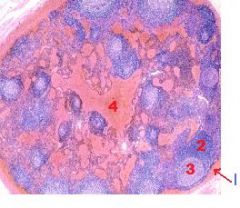
What is this a picture of?
|
Hemal Node (resembles spleen) NO CORTEX/ MEDULLA!!
1. Capsule (Dense CCT) 2. Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue 3. Nodular Lymphatic Tissue 4. Blood Filled Sinuses |
|
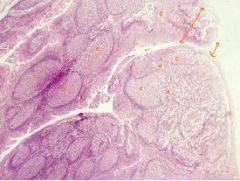
What is this a picture of?
|
Palatine Tonsil
a. Lymph Nodule b. Non-keratinized statified squamous epithelium c. Lamina Propria d. Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue |
|
What is this a picture of?
|
Palatine Tonsil
a. Crypt b. Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium c. Lymph Nodule d. Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue |
|
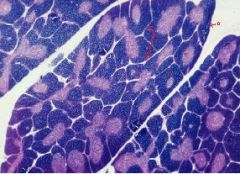
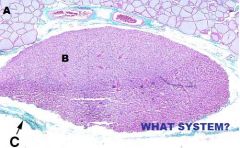
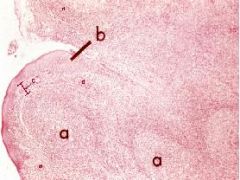
What is this a picture of?
|
Thymus
a. Capsule b. Cortex c. Medulla d. Septum |
|
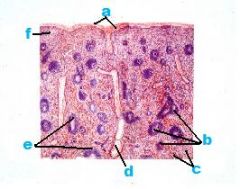
What is this a picture of?
|
Spleen
a. Capsule b. White Pulp c. Red Pulp d. Trabecular Vein e. Central Arteries f. Red Pulp |
|
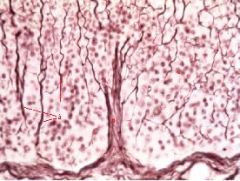
What organ is represented?
|
Spleen
a. Elastic Fibers b. Trabecula c. Red Pulp |
|
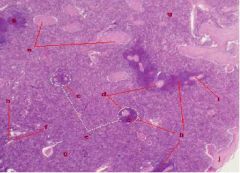
What is this?
|
Spleen
a. Trabeculae b. Splenic Cord c. Splenic Nodules d. Nodular (Central) Arterioles e. White Pulp f. Splenic Sinusoid g. Red Pulp h. PALS (T Cells) i. Sheathed Artery, Lumen j. Capsule |
|
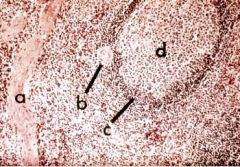
What Organ is represented?
|
Spleen
a. Trabecula b. Nodular Arteriole in White Pulp c. PALS (T Cells) in white pulp d. Splenic Nodule (B Cells) in white pulp |
|
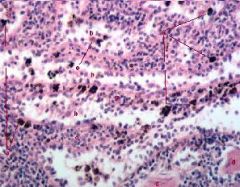
What organ is represented?
|
Spleen, red pulp
a. Macrophages b. Splenic Sinusoids c. Splenic Cords d. Smooth Muscle e. Reticular Cells |
|
What organ is represented?
|
Cloacal Bursa
a. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium b. Lamina Propria c. Lymph Follicles d. Cortex e Medulla f. Muscularis (Smooth m.) |
|

What Organ is Represented?
|
Spleen
a. Trabeculae b. Red Pulp c. White Pulp d. Splenic Nodules e. Nodular Arterioles |
|
What organ is Represented?
|
Cloacal Bursa
a. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium b. Lamina Propria c. Cortex d. Medulla e. Capillary Layer |
|
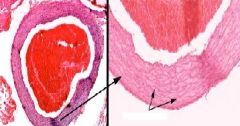
Identify the blood vessel
|
Elastic Artery
|
|
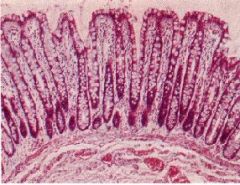
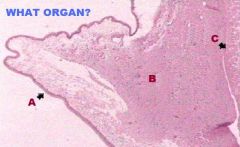
Identify the Organ:
|
Large Intestine
|
|
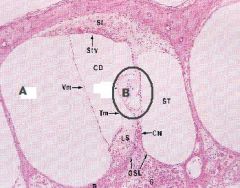
|
Pinna of Ear
A) Scala vestibuli B) Organ of Corti |
|
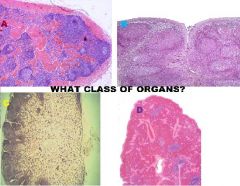
|
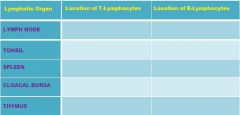
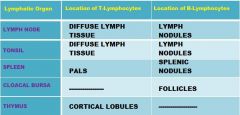
Lymphatic Organs
A. Hemal Node B. Tonsil C. Lymph Node D. Spleen |
|
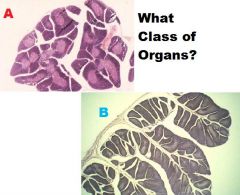
|
Lymphatic Organs
A. Thymus B. Cloacal Bursa |
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
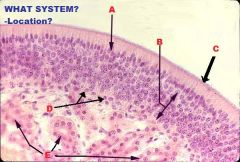
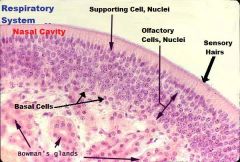
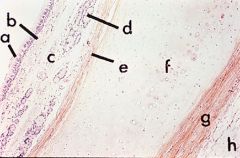
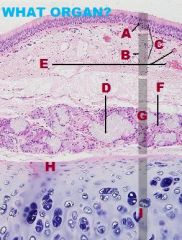
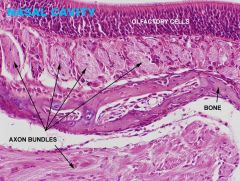
Respiratory, Nasal Cavity
A. Olfactory Epithelium C. Respiratory Epithelium |
|
|
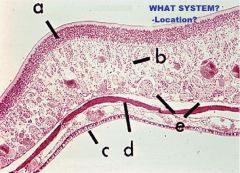
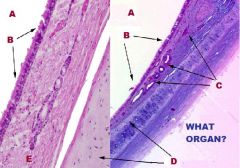
Respiratory System
Larynx -IRREG. TUBULAR ORGAN btw PHARYNX & TRACHEA A. Cartilage B. Skele. M. |
|
|
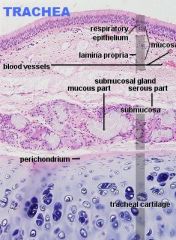
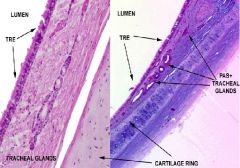
Respiratory System
Trachea/Extrapulmonary Bronchi A. PSSCCil, Gob. B.Lamina Propria C. Submucosa D. Mixed Glands E. Trachialis Muscle F. Hyaline Cartilage G. Fibroelastic membrane H White Fat |
|
|
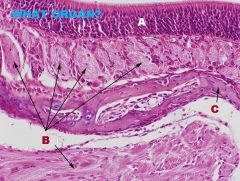
Respiratory System
Trachea/Extrapulmonary Bronchi A. Goblet Cell B. PSCilCol Epithelium and LP C. Submucosa D. Vein E. RBCs in vein F. Serous Gland NO Muscularis Mucosa! |
|
|
Respiratory System
Intrapulmonary Bronchus (IN LUNG!) A. Pulmonary Epithelium B. Lamina Propria C. Muscularis Mucosa Now present! (NO TRACHEALIS M.!!) D. Hyaline Cartilage Plate (NOT RING anymore!) E. Alveolus (In the lung son!) |
|
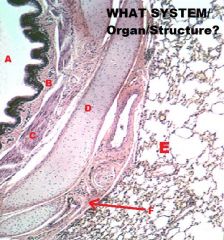
|
Respiratory System
Intrapulmonary Bronchus A. Lumen B. LP C. Muscularis Mucosae D. Cartilage Plate E. LUNG!! F. CT & Vessels |
|

|
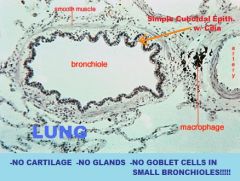
|
|
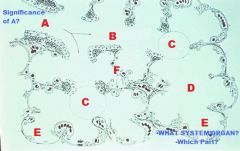
|
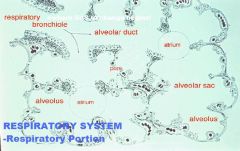
|
|
|
Respiratory System
Larynx A. NKSS B. Vocal Lig. C. Vocal M. (Skeletal) |
|
|
|
|
what are the common sites of atheroma in intracranial vessels?
|
origin of MCA, ends of basilar artery
|
|
|
|
|
|
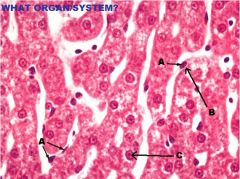
Digestive System
Liver (Stroma) A. Interlobular CT (loose CCT) |
|
|
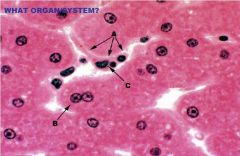
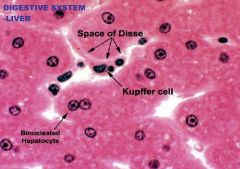
Digestive System
Liver (Parenchyma) A. Endothelial/Kupffer Cell (Hepatic sinuosoids) B. Space of Disse C. Hepatocyte (microvilli present but not visible) |
|
|
|
|
|
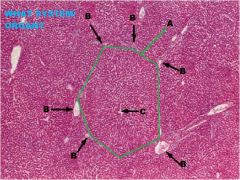
Digestive System
Liver A. Hepatic Lobule B. Portal Triad C. Central Vein |
|
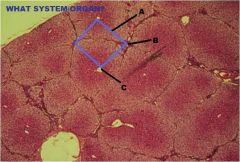
|
Digestive System
Liver A. Hepatic Acinus B. Portal Triad C. Central Vein |
|
|
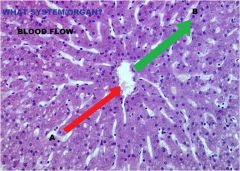
Digestive System
Liver A. Blood Flows from Portal Vein To Central Vein B. From Central Vein to Portal Triad |
|
|
|
|
|
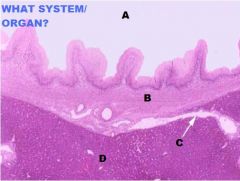
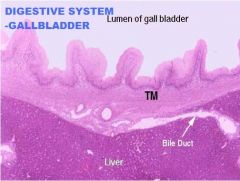
Digestive System
Liver/Gallbladder A. Lumen of GB B. Tunica Muscularis C. Bile Duct D. Liver E. Serosa F. Microvilli G. Simple Columnar Epith. H. LP/Submucosa I. Tunica Muscularis J. Mucosa NO MUSCULARIS MUCOSAE!!!!! |
|
|
Digestive System
Gallbladder A. Tuncia Muscularis B. Perimuscular CT |
|
|
Digestive System
Small Intestine A. Lamina Propria B. Enteroendocrine Cells -Secrete CCK into Gallbladder |
|
|
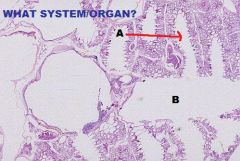
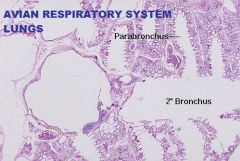
Avian Respiratory System
Lungs A. Tertiary or Parabronchus cross section B. Simple Cuboidal or Simple Squamous Epithelium C. Lamina Propria D. Muscularis Mucosa Arranged in Bundles of Smooth m. |
|
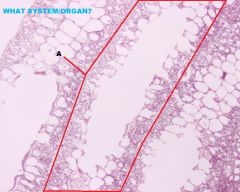
|
Avian Respiratory System
Lungs A. Parabronchus (Tertiary) in Longitudinal Section |
|
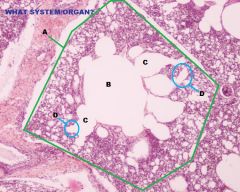
|
Avian Respiratory System
Lung A. Parabronchi B. Lumen C. Air Vesicles D. Air Capillaries |
|
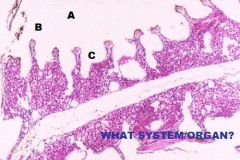
|
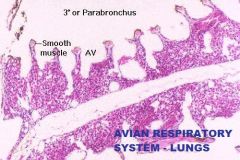
|
|
|
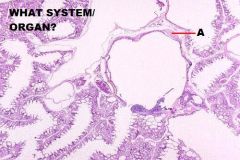
Avian Respiratory System
Lung A. Hyaline Cartilage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is associated with the palatine tonsil?
|
NKSS
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is associated with the cloacal bursa?
|
Simple Columnar
|
|
|
Name 2 lymphatic organs that have an epithelium and underline the one with simple columnar epithelium
|
Tonsils and Cloacal bursa****
|
|
|
Pars Distalis + 1 + 2 = adenohypophysis
|
1= pars tuberalis
2= pars intermedia |
|
|
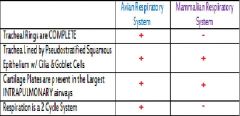
|
|
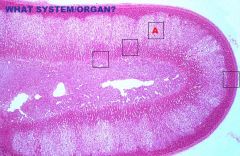
|
Endocrine System
Adrenal Gland A. Zona Fasiculata |
|
|
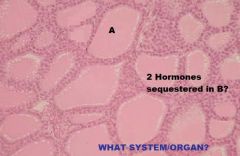
Endocrine System
Thyroid Gland B. T3&T4 |
|
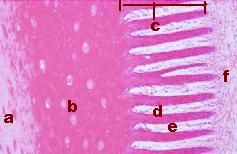
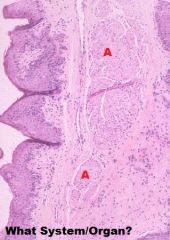
What System/Organ is Represented?
|
Integumentary, Hoof
a. Stratum Externum b. Stratium Medium c. Stratum Internum d. Primary Dermal Papilla e. Primpary Epidermal Papilla f. Dermis |
|
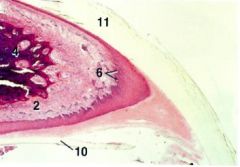
What System/Organ represented?
|
Integumentary, Claw
2. Dermis 4. Distal Phalanx 6. Stratum Basale 10. Sole (Stratum Granulosum & Stratum Lucidum) 11. Wall (Stratum Corneum) |
|
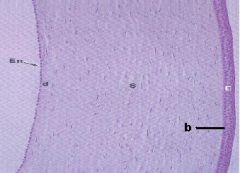
What organ/part is represented?
|
Eye/Cornea
En. Posterior Epithelium (Endothelium) d. Descemet's membrane S. Substantia propria/ Stroma b. Bowman's Membrane E. Anterior Epithelium (NKSS) |
|
|
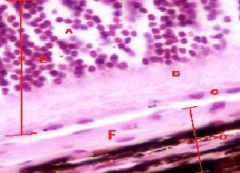
EYE
A- Cell bodies B- Rods&Cones C-Pigmented Epithelium D-Choroid E-Retina F-Tapedum |
|
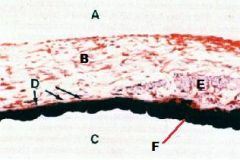
|
EYE
A-Anterior Chamber B-Iris C-Posterior Chamber D-Radial (Dilator) m. E-Circular (Constrictor) m. F-Pigment of Iris |
|
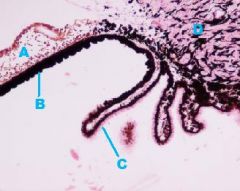
|
A-Iris
B-Insensitive Retina-Iridial Portion (Both layers pigmented) C-Insensitive Retina-Ciliary Portion (Only inner layer pigmented) D-Ciliary Body |
|

|
A-Eye
B-Lens C-Anterior Epithelium (Simple Cuboidal) |
|
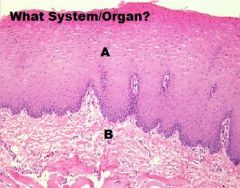
|
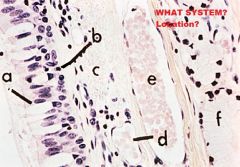
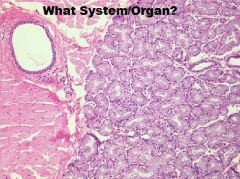
Digestive System-Cheek
A. Mucosa (NKSS) (Usually) B. Lamina Propria/ Submucosa (NO MUSCULARIS MUCOSA! or remaining layers) |
|
|
Digestive System/Cheek
|
|
|
|

