![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
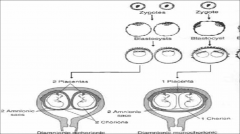
chorion is the portion of
|
fetal membrane that eventually forms the fetal side of the placenta.
|
|
|
|
Chorion is formed by
|
extraembryonic mesoderm
and the two layers of trophoblast |

It is formed by extraembryonic mesoderm(visceral) and the two layers of trophoblast and surrounds the embryo and other membranes.
|
|
|
The chorion is divided into the smooth chorion and the villous chorion. The villous chorion forms the ___________ =
|
placenta
|
|
|
|
The chorionic villi emerge from the chorion, invade the
|
endometrium
|
|
|
|
The chorion undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic villi, which invade the+
|
uterine decidua.
|
|
|
|
The chorion contains _____ ______
|
chorionic villi,
These villi are snipped or suctioned off for study in the procedure. Since the chorionic villi are of ______ ________ |
fetal origin,
examining samples of them can provide the genetic makeup of the fetus. |
|
|
CVS (chorionic villus sampling)
The test can be done before amniocentesis, about __ - __ = wks |
6-11 weeks
10-12th week, after a missed period. |
|
|
|
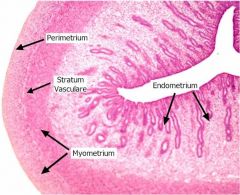
- the functional layer of the endometrium in a pregnant woman. is aka =
|
Decidua
refers to the gravid endometrium |
|
|
|
________ is the term for the endometrium during a pregnancy
|
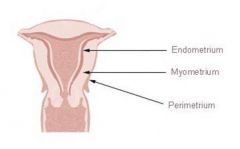
Decidua
, which forms the maternal part of the ____________ = |
placenta
|
|
|
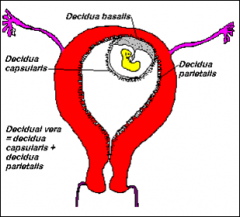
The three regions of the decidua are named according to their relation to the implantation site
|
decidua basalis
decidua capsularis decidua parietalis info |
The decidua basalis is the part of the decidua deep to the conceptus that forms the maternal part of the placenta
The decidua capsularis is the superficial part of the decidua overlying the conceptus The decidua parietalis is all the remaining parts of the decidua |
|
|
the part of the decidua deep to the conceptus that forms the maternal part of the placenta
|
decidua basalis
|
|
|
|
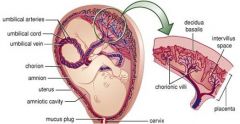
umbilical cord comes from the same zygote as the fetus
Umbilical Cord normally contains = |
two arteries
one vein |
|
|
|
umbilical cord develops from and contains remnants of the
|
yolk sac and allantois
info |
and is therefore derived from the same zygote as the fetus).
|
|
|
umbilical cord
forms by the ______ week of fetal development, |
5th wk
replacing the yolk sac as the source of nutrients for the fetus.The |
|
|
|
, the umbilical vein continues towards the transverse fissure of the
|
liver
One of these branches joins with the The second branch (known as the |
hepatic portal vein (connecting to its left branch
ductus venosus |
|
|
the majority of the incoming blood (approximately 80%) to bypass the liver and flow via the
|
left hepatic vein
into the inferior vena cava, which carries blood towards the heart. |
|
|
|
The two umbilical arteries branch from the
|
the internal iliac arteries, and pass on either side of the urinary bladder before joining the umbilical cord.
|
|
|
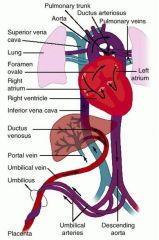
, the umbilical vein and ductus venosus close up, and degenerate into fibrous remnants known as the
= 2ct |
round ligament of the liver
the ligamentum venosum |
|
|
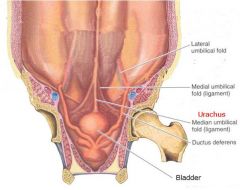
WHAT IS THE MEDIAL LIGAMENT CALLED =
DESCRIBE IT = |
.Urachus
fetal canal connecting the bladder with the allantois, persisting throughout life as a cord (median umbilical ligament). |
|
|
|
Development of Placenta
By the end of the __ wk = |
, the anatomical arrangements necessary for physiological exchanges between the mother and embryo are established.
|
|
|
|
Development of Placenta
A complex vascular network is established in the placenta by the end of the which facilitates maternal-embryonic exchanges of gases, nutrients, and metabolic waste products. |
4th wk
|
|
|
|
Chorionic villi
cover the entire chorionic sac until the beginning of the __ wk = |
8th
As this sac grows, the villi associated with the decidua capsularis are compressed, reducing the blood supply to them. These villi soon degenerate, producing a relatively avascular bare area, the ______ ________ = |
smooth chorion.
|
|
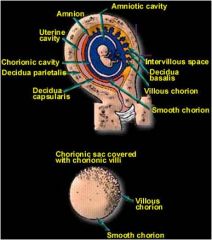
This bushy part of the chorionic sac is the ______ ________ =
|
villous chorion.
|
|
|
|
The fully developed placenta covers ____ to _____ % of the decidua
|
15 to 30%
of the decidua |
|
|
|
The placenta has two parts
|
The fetal part of the placenta :
The maternal part of the placenta : |
|
|
|
The fetal part of the placenta :
Formed by the = |
villous chorion
The chorionic villi that arise from it project into the intervillous space containing maternal blood |
|
|
|
The maternal part of the placenta :
Formed by the = |
Formed by the decidua basalis,
the part of the decidua related to the fetal component of the placenta By the end of the fourth month, the decidua basalis is almost entirely replaced by the fetal part of the placenta. |
|
|
|
Info
Endometrial arteries and veins pass freely through gaps in the cytotrophoblastic shell and open into the intervillous space. ( The intervillis space is where maternal blood goes and diffusion occurs there in the shell.) |
.
|
|
|
|
It is through the numerous _______ ______ which arise from stem villi, that the main exchange of material between mother and fetus takes place.
|
branch villi,
|
|
|
|
Placental circulation
2ct |
Fetal Placental Circulation
Maternal placental circulation |
|
|
|
Poorly oxygenated blood leaves the fetus and passes through the
|
umbilical arteries
|
|
|
|
chorionic arteries that branch freely in the _______ _______ to the placenta.
|
umbilical arteries
|
|
|
|
At the site of attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta, these arteries divide into several radially disposed ________ _______
|
chorionic arteries
|
|
|
|
The blood vessels form an extensive arterio-capillary-venous system within the _____ ________ , which brings the fetal blood extremely close to the maternal blood.
|
within the chorionic villi,
|
|
|
|
T/F
There is normally intermingling of fetal and maternal blood. |
F
|
|
|
|
Maternal placental circulation
These vessels discharge into the intervillous space through gaps in the |
cytotrophoblastic shell.
|
|
|
|
Info
Reductions of uteroplacental circulation result in fetal hypoxia and IUGR. Severe reductions of uteroplacental circulation may result in fetal death. |
.
|
|
|
|
The intervillous space of the mature placenta contains about 150 ml of blood that is replenished ____ ____ ____ ______ per minute.
|
maternal blood from fetal blood.
info |
The composition of the placental membrane changes during pregnancy.
|
|
|
A. In early pregnancy, the placental membrane has 4 layers:
|
Syncytiotrophoblast
Cytotrophoblast Connective tissue, Endothelium of fetal capillaries |
|
|
|
_______ _______(large, sometimes pigmented, elliptical cells found in connective tissue) are most numerous in early pregnancy and have characteristics similar to those of macrophages
|
Hofbauer cells
|
|
|
|
The placenta has three main functions
3ct |
Metabolism
Transport of gases and nutrients Endocrine secretion |
|

