![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The prenatal manifestations are known as hydrops fetalis; in severe forms this can include what S/S = |
petechiae and purpura.
|
|
|
|
►Blood tests done on the mother
for RH Heme = |
D antigen of the Rhesus blood group system typing
|
|
|
|
Rho (D) immune globulin (RhoGAM, MICRhoGAM) is a human immunoglobulin (IgG) preparation that contains antibodies against Rh factor and prevents a maternal antibody response to Rh-positive cells that may enter the maternal bloodstream of a Rh-negative mother.
|
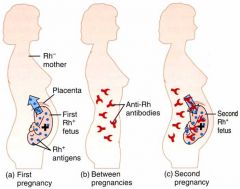
This drug is administered to Rh negative mothers within 72 hours after the birth of an Rh-positive baby
to prevent erythroblastosis fetalis during subsequent pregnancies. |
Rhogam prevents B-cell activation and memory cells formation.
|
|
|
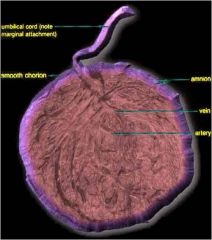
The margins of the placenta are continuous with the
|
amniotic and chorionic sacs.
|
|
|
|
The characteristic cobblestone appearance of the maternal surface is produced by slightly bulging villous areas – .
|
cotyledons
|
|
|
|
The umbilical cord usually attaches to the
|
fetal surface of the placenta.
|
|
|
|
The umbilical vessels branch on the fetal surface to form chorionic vessels, which enter the chorionic villi and form the
|
arteriocapillary-venous system.
|
|
|
|
The attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta is usually near the
|
center of the fetal surface of placenta but it may attach at any point.
|
|
|
If insertion of cord at the placental margin--
|
battledore placenta
|
|
|
a placenta in which the umbilical blood vessels abnormally travel through the amniochorionic membrane before reaching the placenta proper.
|
Velamentous placenta :
|
|
|
If these blood vessels cross the internal os, a serious condition called
|
vasa previa
|
|
|
|
result from deep implantation of the placenta into the decidua.
|
►Circumvallate placenta is
|
|
|
|
occurs when the placenta attaches in the lower part of the uterus, covering the internal os.
|
Placenta previa
|
|
|
|
►The placenta normally implants in the
|
posterior superior wall of the uterus.
|
|
|
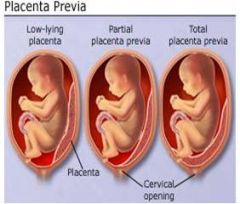
Complications: ?
|
.
|
|
|
|
Placental abruption
|
occurs when a normally implanted placenta prematurely separates from the uterus before delivery of the fetus.
|
|
|
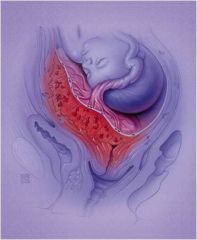
an abnormally deep
attachment of the placenta, through the endometrium and into the myometrium. |
Placental accreta
|
|
|
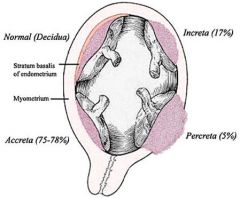
three forms of placenta accreta,
|
75-78% of all cases
invasion of the myometrium which does not penetrate the entire thickness of the muscle. |
Placenta accreta occurs when there is abnormal adherence of the chorionic villi to the uterine wall with partial or complete absence of the decidua basalis.
|
|
|
occurs when the placenta further extends into the myometrium and happens in around 17% of all cases.
|
.
|
|
|
|
villementous
abruption previa know for test |
.
|
|
|
|
is a placenta consisting of small accessory lobes completely separate from the main placenta.
|
Succenturiate placenta
|
|
|
|
►►Care must be taken to assure that the accessory lobes are eliminated afterbirth.
Info |
.
|
|

