![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 possible causes of a cleft palate?
|
1. Shelves too narrow and unable to meet (ie insufficient migration of neural crest cells)
2. reduced shelf force - delays movement to the horizontal 3. Interference in the normal displacement of the tongue (ie paralyzed tongue from nerve damage or abnormail muscles) 4. Epithelial cells fail to die/migrate |
|
|
How does the Cervical Sinus form?
|
The second arch will grow down over the 3rd and 4th arches, fusing along the anterior border of the sternomastid. The inside of the pit that get formed is covered in ectoderm that can get infected and swell and have to be removed.
|
|
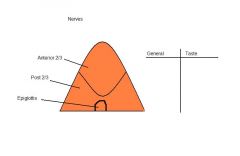
|
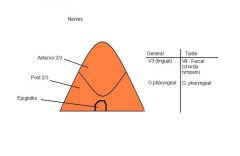
|
|
|
Where does the skin and msk of the tongue come from?
|
The epithelium comes from the arches and the muscles come from the occiput and are thus supplied by Hypoglossal nerve 12.
|
|
|
What is Treacher Collins Syndrome?
- list 5 main symptoms - form of inheritance - Symmetry? - mentation? |
Symptoms:
- anti-mongoloid slant of eyes - small mandible/maxilla - no zygomatic process - abnormal stapedes and malleus (deaf!) - cleft palate - autosomal dominant - Symmetrical and mentally normal |
|
|
What causes lateral facial dysplasia?
- symmetry/mentation? |
In the embryo the blood supply to the face is through the stapedes bone. This changes over to the facial artery and in the process can have bleeding into the facial structures. Blood is fatal to embryological tissue and will thus kill whatever tissue it touches.
Produce asymmetry but normal mentation. May be deaf in ear structures affected. |

