![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
242 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define embryology
|
the science of the origin and development of the organism from the fertilization of the ovum to the period of extrauterine life.
|
|
|
Define differentiation
|
the process by which cells acquire their specialized characeristics
|
|
|
Define differential gene activity. What process is this the basis for?
|
the turning on and off of specific gene sets. Differentiation
|
|
|
Are genes turned off during differentiation turned off permenantely?
|
No, under certain conditions genes turned off during differentiation can be turned back on.
|
|
|
How do you prove that genes are not turned off irreversibly during differentiation.
|
Take the nucleus, put it into an enucleated egg and see which genes are expressed.
|
|
|
Describe pattern formation.
|
Environmental conditions cue cells during differentiation to express different genes based on their location
|
|
|
What are the two aging systems used to stage an embryo? Which is used clinically?
|
Gestational - time from last period. Fertilization - from time of fertilization. Gestational stage is used in clinic.
|
|
|
The embryo begins implantation at the end of which week?
|
first
|
|
|
The extraembryonic membranes are formed during which week?
|
second
|
|
|
Gastrulation occurs during which week?
|
third
|
|
|
Neurulation occurs during which week?
|
fourth
|
|
|
By the end of the 8th week of development, what is the size of the developing embryo?
|
3 cm
|
|
|
The fetal period begins with which week?
|
9th
|
|
|
Which stage ( embryo or fetal ) is characterized by rapid growth?
|
Fetal
|
|
|
At what age can a premature infant be delivered with a good chance of survival?
|
24-28 weeks
|
|
|
What space does the uterine tube open into?
|
Peritoneal cavity (abdomen)
|
|
|
Where does fertilization occur
|
In the oviduct of the uterine tube (distal).
|
|
|
What specialized structure in the uterine tube collects the ovulated secondary oocyte?
|
fimbria
|
|
|
Describe a secondary oocyte?
|
Ovulated egg that has not completed the second meiotic division.
|
|
|
Why are polar bodies beneath the zona pellucida a good indicator of fertilization?
|
One polar body is released with each meiotic division. If there are two, the egg has been fertilized.
|
|
|
Are the male and female pronuclei haploid or diploid?
|
haploid
|
|
|
Define cleavage
|
rapid cell division during the first week without growth
|
|
|
What is the diameter of an ovulated egg? How does this compare to a typical somatic cell?
|
100 microns, 10 microns
|
|
|
Define blastomeres
|
cells produced as a result of cleavage
|
|
|
Blastomeres are totipotential. What does this mean?
|
Each cell can give rise to an entire embryo and extraembryonic tissues.
|
|
|
Define compaction
|
formation of tight junctions between peripheral blastomeres. creates a gradient.
|
|
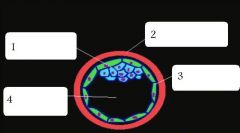
name these embryonic structures
|
inner cell mass, zona pellucida, trophoblast, blastocyst cavity
|
|
|
Extraembryonic membranes are derivitives of what early structure?
|
trophoblast
|
|
|
The embryo is the derivitive of what early structure?
|
inner cell mass
|
|
|
Inner cell mass cells are (totipotent, pluripotent)?
|
pluripotent
|
|
|
Describe hatching?
|
the blastocyst cavity swells, the trophoblast cells produce an enzyme to degrade the zp and the blastocyst emerges.
|
|
|
The blastocyst hatches on what day?
|
6
|
|
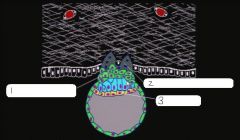
|
1. cytotrophoblast
2. syncytiotrophoblast 3. hypoblast |
|
|
What type of cell produces hcG? What does this hormone do?
|
syncytiotrophoblast cells, hCG stops the menstrual cycle.
|
|
|
What percent of fertilizations result in a spontaneous abortion?
|
60
|
|
|
Describe placenta previa.
|
When implantation occurs over the oz of the cervix. Can lead to rupture of placenta during birth.
|
|
|
Describe ectopic pregnancy
|
When conceptus implants outside the uterus.
|
|
|
Name the four primary events durign the second week of fertilization?
|
1. implantation ends 2. primitive uteroplacental circulation 3. bilaminar embryo 4. extraemebryonic membranes and cavities
|
|
|
Where do lacunar networks form?
|
syncytiotrophoblasts
|
|
|
What type of blood travels through the lacunar networks?
|
maternal
|
|
|
What are the two layers of the bilaminar disk? Which gives rise to the embryo?
|
epiblast, hypoblast
epiblast |
|
|
Which layer of the bilaminar disk faces the inner cavity?
|
hypoblast
|
|
|
What specialized strucutre gives rise to the cranial end of the embryo?
|
prochordal plate
|
|
|
What cavity forms facing the epiblast?
|
amniotic cavity
|
|
|
What does the blastocyst cavity give rise to
|
primary yolk sac
|
|
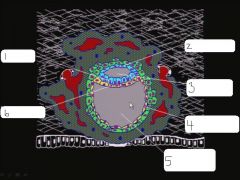
|
epiblast, amniocytes, amniotic cavity, exocoelomic membrane, primary yolk sac, hypoblast
|
|
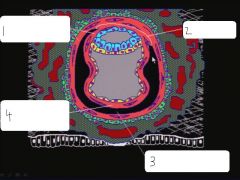
|
somatic extraembryonic mesoderm, connecting stalk, extraembryonic coelom, splanchnic extraembryonic mesoderm
|
|
|
The chorion is composed of what three layers?
|
syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, somatic extraembryonic mesoderm
|
|

|
amniotic cavity, allantois, secondary yolk sac, splanchnic extraembryonic mesoderm, bilaminar embryonic disk
|
|
|
T/F In humans, the allantois is vestigal?
|
True
|
|
|
Extraembryonic mesoderm forms between what layers?
|
between cytotrophoblasts and amniocytes and cytotrophoblasts and exoceolomic membrane
|
|
|
The region of extraembryonic mesoderm that doesn't divide into somatic and splanchnic forms the _____________?
|
connecting stalk
|
|
|
Distinguish betweeen epithelial and mesenchymal cells.
|
polarization, epithelial cells have apical and basal surface, mesenchymal cells migrate through ECM.
|
|

Describe (left to right) these divisions.
|
midsagittal (middle), transverse, coronal
|
|
|
Define gastrulation
|
process by which three germ layers are formed
|
|
|
All three germ layers are formed from what structure?
|
epiblast
|
|
|
gastrulation occurs in a (cranial to caudal / caudal to cranial) direction.
|
cranial to caudal
|
|
|
What structure raises and gives rise to the primitive streak?
|
epiblast
|
|
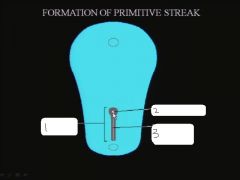
|
primitive streak, primitive pit (Henson's node), primitive groove
|
|
|
The epiblast and hypoblast layers stick together to form what two structures?
|
oropharyngeal membrane and cloacal membrane
|
|
|
As epithelial cells migrate through the primitive streak, them become __________
|
mesenchymal cells
|
|
|
Cells that migrate through the primitive streak and displace the hypoblast give rise to which germ layer?
|
endoderm
|
|
|
Epiblast cells that remain on the surface and don't participate in gastrulation become which germ layer?
|
ectoderm
|
|
|
Which process gives rise to the nervous system?
|
neurulation
|
|
|
Which layer thickens and rolls up to form the neural tube?
|
ectoderm
|
|
|
Which structure beneath the ectoderm induces the formation of the neural tube?
|
notochord
|
|
|
Where does the neural tube first close?
|
in the cervical region
|
|
|
What are the cranial and caudal openings of the nerual tube called?
|
neuropores
|
|
|
What neural tube defects are caused by failure of the caudal neuropore to close?
|
spina bifida
|
|
|
What neural tube defects are caused by failure of the cranial neuropore to close?
|
anencephaly
|
|
|
At what point in development does the neural tube completely close?
|
end of fourth week
|
|
|
Which part of the nervous system (central / peripheral) is formed by the neural tube?
|
Central
|
|
|
What composes the central nervous system?
|
Brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What forms the peripheral nervous system?
|
neural crest cells
|
|
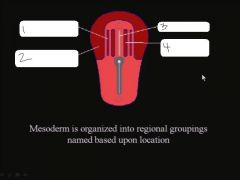
|
intermediate mesoderm, lateral plate mesoderm, notochord, paraxial mesoderm
|
|
|
What develops above the oropharyngeal membrane where the lateral plate mesoderms come together?
|
cardiogenic region (heart)
|
|
|
The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to _____________
|
skeletal muscle
|
|
|
The adult skeleton is divided into which two parts
|
axial and appendicular
|
|
|
The appendicular skeleton arises from _____________
|
lateral plate mesoderm
|
|
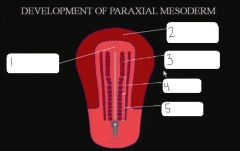
|
oropharyngeal membrane, cardiogenic region, cephalic somitomeres, occipital somites, trunk somites
|
|
|
As somites begin to migrate, they give rise to two populations of cells. What are they?
|
Dermamyotome and sclerotome
|
|
|
Dermamyotome are somitic cells that migrate dorso-laterally and give rise to the ____________
|
dermis and axial skeleton
|
|
|
Chondrogenesis is the formation of __________-
|
cartilage
|
|
|
mesenchymal cells give rise to ________________ which are precartilage cells
|
chondroblasts
|
|
|
What gives cartilage tissue its flexible characteristic?
|
The extracellular matrix between adjacent chondrocytes
|
|
|
name and describe the two growth methods of cartilage
|
appositional - growth from the outside perichondrium. interstitial - growth from the inside - chondrocytes
|
|
|
What is the process of bone formation
|
osteogenesis
|
|
|
What are the two types of bone formation? Which is most common?
|
intramembranous ossification, endochondral ossification. endochondral is the most common
|
|
|
intramembraneous ossification has what type of growth?
|
appositional growth only
|
|
|
T/F primary and secondary ossification systems form during the seventh week of development.
|
false, only primary form then, secondary don't form until after birth
|
|
|
the mesenchyme derived from paraxial mesoderm between bones forms interzonal mesenchyme. What 3 types can it form?
|
snynovial joint, cartilagenous joint, fibrous joint
|
|
|
The joint cavity of interzonal mesenchyme is formed when certain mesenchymal cells undergo what process?
|
apoptosis
|
|
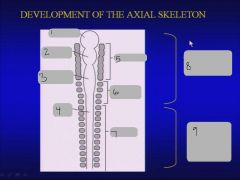
|
prosencephalon, rhombencephalon, spinal cord, somitomeres, occipital somites, somites, neurocranium of skull, vertebrae ribs & sternum.
|
|
|
What are the categories and number of vertebrae?
|
7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 4 coccygeal
|
|
|
The intervertebral discs form from which two parts
|
annulus fibrosis forms from paraxial mesoderm, nucleus pulposis forms from notochord
|
|
|
What is the only adult structure the notochord gives rise to?
|
nucleus pulposis
|
|
|
Describe the formation of the vertebral arch
|
secondary sclerotome circle the neural tube and migrate behind it and close
|
|
|
If the vertebral arch does not close, what neural tube defect do you get?
|
spina bifida occulta
|
|
|
T/F Preductal coarctation is usually associated with a patent ductus arteriosus.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F Preductal coarctation is usually detected at or shortly after birth.
|
True
|
|
|
T/ F Preductal coarctation usually has a poor prognosis without surgical intervention.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F Collateral circulation may allow postductal coarctation to go undetected for years.
|
True
|
|
|
The aortic arches which disappear without making significant contributions to the adult vasculature are:
|
one, two and five
|
|
|
The ductus arteriosus is formed by a portion of aortic arch:
|
six on the left side
|
|
|
Developmental defects of the diaphragm are usually:
|
unilateral (left) and dorsal
|
|
|
A clue to the earliest position of the developing diaphragm is provided by its:
|
innervation by spinal nerves originating from cervical levels
|
|
|
Developmental defects involving the pleuropericardial membrane are rare but, when they occur, the developmental basis is a failure of the pleuropericardial membrane to fuse with the:
|
ventral part of the primitive mediastinum (esophageal portion)
|
|
|
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia involving a posterolateral defect in the diaphragm usually results from a failure of the left pleuroperitoneal membrane to fuse with the:
|
dorsal mesentery of the esophagus
|
|
|
T/F After formation of the head fold, the pericardial cavity is located ventral to the foregut
|
True
|
|
|
T/ F After formation of the head fold, the pericardial cavity is limited caudally by the septum transversum
|
True
|
|
|
T/F After formation of the head fold, the heart is suspended from the floor of the foregut by the mesocardium
|
True
|
|
|
T/F After formation of the head fold, the original polarity of the heart tube has been reversed
|
True
|
|
|
The definitive diaphragm receives contributions from:
|
pleuroperitoneal membranes
septum transversum body wall primitive mediastinum (esophagus and mesoesophagus) |
|
|
T/ F In a congenital diaphragmatic hernia The lungs may be hypoplastic secondary to herniation of abdominal viscera into the thorax.
|
True
|
|
|
T/ F In a congenital diaphragmatic hernia The pleuroperitoneal membranes fail to close the dorsolateral portion of the diaphragm.
|
True
|
|
|
T/ F In a congenital diaphragmatic hernia The defect is 5 times more likely to occur on the left side.
|
True
|
|
|
T/ F In a congenital diaphragmatic hernia The developing lung herniates into the abdominal cavity.
|
False
|
|
|
Which bones originate by endochondral ossification of a branchial arch skeletal element?
|
malleus
incus stapes hyoid |
|
|
The palatine tonsil is usually considered to develop in association with the ___________pharyngeal pouch
|
2nd
|
|
|
The thymic lymphocytes originate from:
|
look it up???
|
|
|
The parenchymal cells of the superior and inferior parathyroid glands originate from the endodermal cells of pharyngeal pouches:
|
3 & 4
|
|
|
The nerve innervating the branchiomeric musculature derived from the first branchial arch is the:
|
mandibular division of the trigeminal
|
|
|
Cervical cysts are thought to originate from epithelialized remnants of the:
|
cervical sinus
|
|
|
First arch syndrome is believed to result from insufficient migration of neural crest cells into the first branchial arch. Name the malformations this could arise from this syndrome:
|
cleft palate
low set ears a small mandible |
|
|
An infant who is hypocalcemic because of a failure in the embryogenesis of the parathyroid glands also commonly shows faulty development of the:
|
thymus
|
|
|
The depression which separates the first and second branchial arches EXTERNALLY is the:
|
first branchial groove
|
|
|
The cranial nerve associated with the third branchial arch is the
|
glossopharyngeal (IX)
|
|
|
Because the skeletal muscle of the larynx is derived from the branchiomeric mesoderm of the fourth and sixth branchial arches, the innervation would be expected to be supplied by the:
|
vagus nerve (X)
|
|
|
The external auditory canal of the adult is considered to be derived from the:
|
first branchial groove
|
|
|
In unilateral clefts of the lip and palate, the course of the cleft passes through the dental (alveolar) arch between:
|
lateral incisors and canines
|
|
|
Failure of the lateral palatine processes to fuse in the midline produces:
|
a simple cleft of the secondary palate
|
|
|
A cleft involving the lip and dental arch (alveolar ridge) is produced by fusion failure between the:
|
medial nasal and maxillary prominences
|
|
|
The sensory innervation of the frontonasal prominence is provided by the:
|
ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve
|
|
|
The viscerocranium is derived from:
|
neural crest cells.
|
|
|
A typical branchial arch contains:
|
a cranial nerve
branchiomeric mesenchyme an aortic arch a skeletal element |
|
|
When considering the developmental origin of the lateral palatine processes, the definitive palate would be expected to receive all or almost all of its afferent innervation via the:
|
maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve
|
|
|
The medial nasal prominence (intermaxillary segment) will form the:
|
medial portion of the maxilla (premaxilla)
|
|
|
Which prominences contribute to the formation of the upper lip?
|
medial nasal and maxillary prominences
|
|
|
What is the process by which the early cells of an embryo acquire their structural and environmental characteristics?
|
Differentiation
|
|
|
Give an example of the consequence of a loss in pattern formation?
|
Teratoma tumor
|
|
|
Do teratoma's retain differentiation.
|
yes
|
|
|
When is normal human partruition?
|
38 weeks
|
|
|
What is the final crucial development that must occur for an embryo to survive outside the uterus?
|
lung development
|
|
|
Which end of the embryonic disk (caudal / cranial) points toward the connecting stalk?
|
caudal
|
|
|
Give some examples of mesenchymal cells?
|
fibroblasts, neural crest cells, chondrocytes, osteocytes
|
|
|
T/F All mesoerm cells are mesenchymal cells?
|
False
|
|
|
What does ectoderm give rise to?
|
Nervous system and epidermis
|
|
|
What does mesoderm give rise to?
|
Most skeletal structures, muscle, blood vessels
|
|
|
What does the endoderm give rise to?
|
gut tube structures, respiratory structures, secretory cells
|
|
|
All three germ layers arise from the ___________
|
epiblast
|
|
|
What structure forms on the embryonic disk to allow for the formation of the germ layers?
|
primitive streak
|
|
|
Where in the embryo does the primitive streak form?
|
caudal, median
|
|
|
epiblast cells that migrate through the cranial most region of the primitive pit and migrate up to the oropharyngeal membrance form what?
|
notochord
|
|
|
At what point in development does the primitive streak regress?
|
end of fourth week
|
|
|
What happens when the primitive streak fails to regress?
|
sacrococcygela teratoma
|
|
|
How do you detect neural tube defects?
|
AFP and ultrasound
|
|
|
Does AFP in the amniotic fluid mean you have a neural tube defect?
|
No, any break in the ectoderm can result in AFP in the amniotic fluid.
|
|
|
Name one way to reduce the occurance of neural tube defects?
|
Maternal ingestion of folic acid.
|
|
|
Describe spina bifida occulta?
|
Neural tube in completely in tact, but the sclerotome has failed to migrate dorsally around the neural tube?
|
|
|
Describe a menigoceole?
|
Only the meninges protrude out
|
|
|
Describe a menigomyloceole?
|
you have meninges and spinal tissue protruding out
|
|
|
Describe rachischia?
|
neural pore fails to close completely, neural tube is split
|
|
|
What is the mesoderm that runs up and down the midline of the embryo called?
|
notochord
|
|
|
What mesoderm is lateral to the notochord? Which is lateral to that? Which grouping is the most lateral?
|
paraxial, intermediate, lateral plate mesoderm
|
|
|
What does the paraxial mesoderm form cranially?
|
somitomeres
|
|
|
What does the paraxial mesoderm form caudally?
|
somites
|
|
|
What cell type is a somite?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What happens to lateral plate mesoderm?
|
Splits to form embryonic coelom
|
|
|
The lateral plate mesoderm associated with the ectoderm is called ____________ and gives rise to the __________.
|
somatic mesoderm, body wall
|
|
|
The lateral plate mesoderm associated with the endoderm is called ___________ and gives rise to the ___________
|
splachnic mesoderm, visceral smooth muscle
|
|
|
Communication between the extraembryonic coelom and embryonic coelom occurs where in the embryo?
|
caudally
|
|
|
What types of folding take a lateral embryonic disk and make it cylindrical?
|
head and tail folding
|
|
|
Head folding moves cranial structures:
|
ventrally and caudally
|
|
|
Tail folindg moves caudal structures:
|
ventrally and cranially
|
|
|
lateral body folding moves lateral structures:
|
ventrally and medialy around the umbilicus
|
|
|
What is critical to the formation of the primary body axis?
|
The cells that move through the primitive pit.
|
|
|
How does left/right axis formation occur:
|
Cilia at henson's node beat and move factors off to the side.
|
|
|
What is the condition where the left/right axis formation is reversed?
|
citus inversus
|
|
|
All skeletal muscles arises from?
|
paraxial mesoderm
|
|
|
The skull bones form from:
|
paraxial mesoderm and neural crest cells
|
|
|
Do precartilage condensations resemble the adult structures they are going to form?
|
yes
|
|
|
Precartilage condesnations are composed of?
|
chondroblasts
|
|
|
Where does intramembranous ossification primarily occur?
|
calvaria of the skull
|
|
|
Describe the process of intramembraneous ossification?
|
mesenchyme --> osteoblast --> osteocyte
|
|
|
When do you start to see primary centers of ossification?
|
8th week
|
|
|
How many trunk somites are there? How many vertebrae? What does this mean?
|
38-40, 33, 5-7 caudal somites must degenerate or form tail
|
|
|
What happens to primary sclerotomes?
|
The split. The caudal portion of one fuses with the cranial portion of another.
|
|
|
Dermatome is going to split dorsally and ventral parts. What are the muscles that go dorsally?
|
epaxial musculature
|
|
|
Dermatome is going to split dorsally and ventral parts. What are the muscles that go ventrally?
|
hypaxial musculature
|
|
|
What is caused by a failure of somitic mesoderm (hypaxial) to complete migration into somatic mesoderm?
|
gastroschisis
|
|
|
What genes, expressed in a specific pattern define the segmental pattern of the paraxial mesoderm into somites
|
Hox genes
|
|
|
What cell type makes up the neural tube?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
In the adult, what is found in the center of the neural tube?
|
cerebral spinal fluid
|
|
|
In the neural tube, epithelial proliferation occurs in which direction?
|
toward the lumen
|
|
|
The proliferation of neuroblasts expand the neural tube to create three layers:
|
marginal (basal)
Intermediate (middle) Ventricular (apical) |
|
|
What do you find in the marginal zone of the neural tube?
|
axons
|
|
|
The neural tube separates itself out into two functional components:
|
Alar plate (dorsal)
Basal plate (ventral) |
|
|
What is the function of the alar plate?
|
sensory
|
|
|
What is the function of the basal plate?
|
motor
|
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells that remain the apical regions form what cell type?
|
ependymal cells that line the neural canal
|
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells that migrate into the intermediate area become:
|
neuroblasts
glial cells |
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells that form neuroblasts and then neurons send out their cell processes in which direction?
|
to the basal surface
|
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells that migrate to form glial cells that remain the intermediate area, give rise to...
|
supporting cells for the neurons (astrocytes)
|
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells that migrate to form glial cells that migrate into the marginal zone, give rise to....
|
cells that form myelin to support the axons (oligodendrocytes)
|
|
|
T/F Microglia come from neuroectoderm?
|
False, they invade into the neural tube but arise from mesenchymal cells
|
|
|
neural crest cells give rise to...
|
peripheral ganglia, schwann cells, chain ganglia (sympathetic, parasympathetic), chromaffin cells, melanocytes, components of pia and arachnoid
|
|
|
Where do you find the cell bodies for all the fibers of the central root of a spinal nerve?
|
central nervous system
|
|
|
Where do you find the cell bodies associated with the sensory part of a spinal nerve?
|
peripheral NS
|
|
|
Where do cell bodies associated with motor in a spinal nerve come from?
|
central NS, neural tube
|
|
|
What causes an aganglionic megacolon (Barium enema)
|
lack of formation of post ganglionic parasympatheic cell bodies in the colon region which means smooth muscle cells can't contract. This is caused by a failure of neural crest cells to migrate into this regions.
|
|
|
Where does the spinal cord terminate in the neonate? Where in the adult? Why is it not the same?
|
L3, L1-2
Vertebral column grows faster than the spinal cord. |
|
|
Dorsal and ventral roots coming off the spinal cord are stretched to form the:
|
cauda equina
|
|
|
What do you call the portion of the spinal cord that connects to the vertebral column?
|
filum terminale internum
|
|
|
What happens if a teathered spinal cord fails to sever?
|
it can pull the cerebellum down through the foramen magnum.
|
|
|
Where does the parietal layer of serous membrane (mesothelium) come from?
|
somatic mesoderm
|
|
|
Where does the visceral layer of serous memrane (mesothelium) come from?
|
splachnic mesoderm
|
|
|
What larger structure forms in the cranial most region of the embryo where the lateral plate mesoderm thickens? What does this give rise to?
|
septum transversum,
diaphragm |
|
|
The heart forms in (somatic / splachnic) mesoderm?
|
splachnic
|
|
|
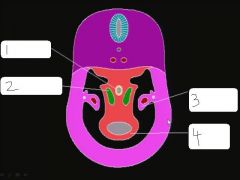
esophagus, bronchial bud, pleuropericardial fold, heart
|
|
|
What separates pericardial cavity from pericardial peritoneal canals?
|
pleural pericardial membranes
|
|
|
What type of mesoderm (somatic / splachnic) composes pleural pericardial membranes?
|
somatic, comes from lateral body walls
|
|
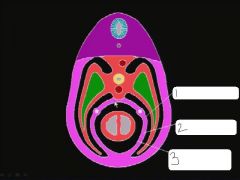
|
parietal pleura, fibrous pericardium, parietal pericardium
|
|
|
When does the heart begin to form? When does it begin to beat? When can it be seen by ulatrasound?
|
3rd week
4th week 5th week |
|
|
Name the primitive heart chambers from cranial to caudal:
|
truncus arteriosus, bulbus corids, primitive ventricle, primitive atrium, sinus venosus
|
|
|
In the primitive heart, blood flows from __________ to ___________.
|
caudal to cranial
sinus venosus to truncus arteriosus |
|
|
What happens when the heart tube fails to loop properly?
|
dextrocardia
|
|
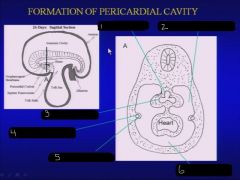
|
foregut, pericardioperitoneal cavity, lung bud, common cardinal vein, pleuropericardial fold, pericardial cavity
|
|
|
Describe the flow of oxygenated blood in the fetal heart.
|
Oxygenated blood enteres the right atrium from the placenta and is carried to the left atrium via a shunt which will will later be closed.
|
|
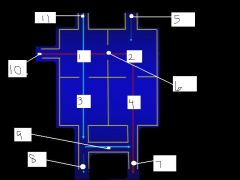
label the parts of the fetal heart
|
RA, LA, RV, LV, pulmonary veins, septum transversum, aorta, pulmonary artery, ductus arteriosus, inferior vena cava, superior vena cava
|
|
|
Once the foramen ovale in the fetal heart is closed it is referred to as the:
|
fossa ovalus
|
|
|
Once the ductus arteriorsus in the fetal heart is closed it is referred to as the:
|
ligamentum arteriosum
|
|
|
In the primary heart tube the cardiogenic region is (caudal/cranial) to the septum transversum and (caudual/cranial) to the oropharyngeal membrane.
|
Caudal, Cranial
|
|
|
What comprises the endothelial tubes of the primary fetal heart?
|
angioblasts arising from splanchnic mesoderm
|
|
|
In the primary fetal heart, the (venous/arterial) ends of the tubes are cranial and the (venous/arterial) ends are caudal.
|
venous, arterial
|
|
|
Head folding bends the dorsal aortae of the primary heart to form the:
|
1st aortic arch
|
|
|
What is the myocardium
|
the cardiac muscle
|
|
|
What is the epicardium?
|
the visceral pericardium
|
|
|
What are the two components of the myoepicardial mantle?
|
myocardium and epicardium
|
|
|
What divides the common atrioventricular canal?
|
endocardial cushions
|
|
|
What is a common cardiac defect in Down's Syndrome?
|
failure of endocardial cushion to fuse. atrioventricular defects.
|
|
|
The primitive atrium is divided by:
|
septum primum and secundum
|
|
|
T/F although right and left atria become separated, right-to-left shunting of blood persists til birth.
|
True
|

