![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
During the 4'h week of embryonic development the tongue appears in the form oftwo lateral lingual swellings and one medial swelling, the so-called______: • foramen cecum • sulcus terminalis • tuberculum impar • epiglottic |
tuberculum impar |
|
|
The posterior third of the tongue originates from the ___________ pharyngeal arche(s).
|
The posterior third of the tongue originates from the second, third and fourth pharyngeal arches
|
|
|
The extreme posterior part of the tongue is derived from the ____pharyngeal arch(s).
|
The extremeposterior part of the tongue Is derived from the fourth pharyngeal arch.
|
|
|
The anterior two-thirds of the tongueare separated from the posterior third by ___________.
|
The anterior two-thirds of the tongueare separated from the posterior third by a V-shaped groove called the terminal sulcus.
|
|
|
The foramen cecum,the remnant of the proximal end of the ______ duct is located at the apex of the terminal sulcus.
|
The foramen cecum,the remnant of the proximal end of the thyroglossal duct is located at the apex of the terminal sulcus.
|
|
|
The______ are stacked bilateral swellings of tissue that appear inferior to thestomodeum (primitive mouth) during the ______ of embryonic development.
|
The branchial arches are stacked bilateral swellings of tissue that appear inferior to the stomodeum (primitive mouth) during the fourth week of embryonic development.
|
|
|
The branchial arches are covered externally by ectodermal lined___________.
|
The branchial arches are covered externally by ectodermal lined branchial clefts.
|
|
|
Branchial arches are lined by endodermal lined __________.
|
They are internally lined by endodermal lined branchial pouches.
|
|
|
Branchial arches support the lateral walls of the __________. |
Branchial arches support the lateral walls of the primitive pharynx. |
|
|
______ is the result of lack of fusion of the distal tongue buds (or lateral swellings). This seems to be common in _________ infants. |
Bifid tongue is the result of lack of fusion of the distal tongue buds (or lateral swellings). This seems to be common in South American infants. |
|
|
Most tongue muscles develop from _______originating in the _______ somites. Therefore, thetongue musculature is innervated by the ________ nerve.
|
Most tongue muscles develop from myoblasts originating in the occipital somites. Therefore, the tongue musculature is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve.
|
|
|
The ______branchial arch is so rudimentary that they are absent in humans or are included with the_____ branchial arches.
|
The fifth branchial arch is so rudimentary that they are absent in humans or are included with the fourth branchial arches.
|
|
|
Parotid gland is derived from ____.
|
Parotid gland is derived from ectoderm. |
|
|
The ______ glands appear early in the sixth week and are the first toform.
|
The parotid glands appear early in the sixth week and are the first toform.
|
|
|
The _________ glands appear late in the sixth week, and the_______l glands appear in the eighthweek.
|
The submandibular glands appear late in the sixth week, and the sublingual glands appear in the eighthweek.
|
|
|
Sublingual and submandibular salivary glands are derived from _____.
|
Sublingual and submandibular salivary glands are derived from endoderm
|
|
|
Development of the Tongue
(Ref diagram) |
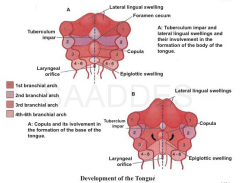
|
|
|
The cartilages of first and second branchial arches are derived from _____.
|
The cartilages of first and second branchial arches are derived from neural crest cells.
|
|
|
The cartilages of the fourth-sixth branchial arches are derived from _______.
|
Whilethe cartilages of the fourth-sixth branchial arches are derived from mesoderm.
|
|
|
Cartilage of 1st branchial arch
|
Meckel's cartilage
and Quadrate. |
|
|
Failure of fusion of which of the following will lead to cleft lip?
• frontonasal process; lateral nasal process • maxillary process; medial nasal process •lateral nasal process; medial nasal process •maxillary process; lateral nasal process |
[MnM] • Medial nasal process• Maxillary process; |
|
|
What is the 1st branchial arch also called? |
1st branchial arch is also known as the Mandibular arch. |
|
|
Cartilage derivatives of 1st branchial arch . |
Cartilage derivatives of 1st branchial arch : [IG MASS] I=Incus G=Genial tubercle of mandible M=Malleus A=Anterior ligament of malleus S=Spine of Sphenoid S=Sphenomandibular ligament |
|
|
Muscle derivatives of 1st branchial arch |
Muscle derivatives of 1st branchial arch:[My MATT]
Mylohyoid Muscles of mastication Anterior belly of digastric Tensor tympani Tensor veli palatini |
|
|
Nerve derived from 1st branchial arch |
Trigeminal nerve mandibular division |
|
|
What is the 2nd pharyngeal arch also called? |
Hyoid arch |
|
|
Embryonic cartilage of 2nd arch? |
Reichert's cartilage |
|
|
Cartilage derivatives of 2nd brachial arch |
Cartilage derivatives of 2nd brachial arch: [Let's buy her a Staples & Stupid Stylus] i)Lesser horn and upper part of body of Hyoid ii) Stapes iii) Styloid process of Temporal bone iv) Stylohyoid ligament |

