![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
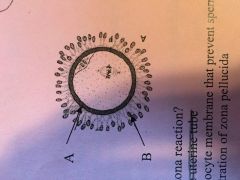
|
A: Zona Pellucida
B: Corona Radiata |
|
|
A: Amniotic Cavity
B: Cytotrophoblasts C: Chorionic Cavity D: Extraembryonic Somatic Mesoderm |
|
|
Describe the Zona reaction
|
Release of products from the occyte membrane that prevents sperm attachment
|
|
|
When does the oocyte complete the second meiotic division?
|
Once fertilization occurs
|
|
|
Epiblast and hypoblast of the bilaminar disc develop from the _______ of the blastocyst
|
Embryoblast
|
|
|
In Gastrulation, all 3 germ laters differentiate from ____________
|
The epiblast
|
|
|
Neurulation, the development of the neural tube, is induced by the __________
|
Notochord
|
|
|
Organogenesis and morphogenesis take place during the __________ period
|
Embryonic
|
|
|
The decidual reaction in the endometrium is an exaggerated secretory phase and is stimulated by high levels of __________
|
Progesterone
|
|
|
In the definitive umbilical cord, what specific structures are embedded in Wharton's jelly?
|
Two Arteries and one Vein
|
|
|
What is the maternal contribution to the definitive placenta?
|
Decidua Basalis
|
|
|
What is the fetal contribution to the definitive placenta?
|
1. Chorion Frondosum
2. Chorionic plate |
|
|
Which is true of the first pharyngeal arch?
|
1. Mesoderm is in part derived from neural crest
2. Gives rise to the mandible by intramembranous bone formation |
|
|
Which of the following bones of the skull are ossified by endochondral bone formation?
|
1. Petrous portion of the temporal bone
2. Body of the sphenoid 3. Basilar portion of occipital |
|
|
The nucleus pulposis of the IVD is formed by the ________
|
Notochord
|
|
|
The myotome develops from the somite and divides into the
A: ________ which forms the intrinsic muscles of the back B: _______ which forms the muscles of the limb and body wall |
A: Epimere
B: Hypomere |
|
|
Where are the locations of the primary ossification centers on a typical vertebra?
|
One on the vertebral body and one on either side of the posterior arch. 3 total.
|
|
|
Limb development is induced by _________
|
Apical ridge ectoderm
|
|
|
What is true of limb development?
|
1. Upper limb paddle rotates 90 decrees laterally to the definitive position
2. Ossification of tarsal and carpals begins only postnatally |
|
|
What is true of Somites?
|
1. Develop from paraxial mesoderm
2. Occipital somites contribute to the skull 3. Give rise to the sclerotome which forms the vertebra |
|
|
Descrive why each of the following conditions is a serious problem.
1. Placenta Previa 2. Cranial synostosis 3. Inadequate amounts of progesterone in 5th month |
1. Placenta is covering the cervix and could cause serious bleeding during birth.
2. Sutures in skull close before the brain is fully formed, so head becomes misshapen 3. Causes an end to the secretory period and the endometrium sloughs off and fetus goes with it. |

