![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The period of time from fertilization to death is called |
Ontogeny( life cycle) |
|
|
|
Ontogeny is divided into two namely |
1. Prenatal period/development 2. Postnatal period/development |
|
|
|
The study of Embryology is focused on the prenatal period which studies________? |
The developmental changes that occur in a developing human from fertilization to delivery. |
|
|
|
What is fertilization and where does it occur? |
It is the process of union between the genetic materials of both male and female gametes to form a zygote. It occurs in the ampullae of one of the fallopian tubes. |
|
|
|
Describe the morula |
1.It is a stage of cleavage which occurs from 2-4 days.( Or on day 3) 2.It consist of 16- 32 blastomeres |
|
|
|
Daughter cells of the zygote, within the enclosure of the zona Pellucida are called _______? |
Blastomeres |
|
|
|
What is compaction and when does it occur? |
It a phenomenon whereby blastomeres are held together by tight junctions to form a compact ball of cells.It occurs after the 3rd cleavage( 8 cell stage). |
|
|
|
A morula has both inner cell mass and outer cell mass. T/F |
T |
|
|
|
A blastocyst is formed when fluid penetrates the ___________ into the __________ of the inner cell mass. Forming a fluid filled cavity called ________. At this stage the inner cell mass will now be called_________ while the outer cell mass will be called__________. |
Zona Pellucida Intercellular spaces Blastocele Embryoblast Trophoblast |
|
|
|
Underthe influence of ____________ , early blastocyst stage embryoblast differentiates into_________&__________. |
Fibroblast growth factors( FGF) Epiblast (Dorsally) ED Hypoblast( ventrally) |
|
|
|
Blastula is formed _______ days after fertilization. |
4-6 |
S-U |
|
|
Abnormal gametes are formed due to failure of separation of homologous chromosomes at which stage? |
Anaphase I |
|
|
|
What is crossing over? |
It is the exchange of homologous chromosomes' segments. |
|
|
|
Crossover ensures? |
New combination of genes / redistributes or recombines genes |
|
|
|
Gamete formation in males are____ while they are _____in females |
Continuous Cyclic |
|
|
|
What is the ovarian cycle? |
Regular monthly changes that occurs in the ovary of females. It begins at puberty and ends at menopause. |
|
|
|
The ovulation cycle is in _____ phases, namely: |
3 •Maturation of follicle •Ovulation •Post ovulation follicular changes |
|
|
|
When a follicle becomes atretic, the surrounding follicular cells along with the oocyte degenerates and is replaced by connective tissue called? |
Corpus atreticum |
|
|
|
FSH stimulates maturation of primordial follicle into primary follicle. T/F |
F •FSH +GDF9 rescues only about 15-20 of the already formed primary follicles, allowing them to develop further into secondary follicles while the rest degenerates and becomes atretic. |
|
|
|
In early primary follicles, the follicular cells differentiate into _________? While in late primary follicles the follicular cells becomes______? |
•Unilaminar cuboidal cells •Multilaminar cuboidal cells now called granulosa cells. |
|
|
|
The primary follicular stage is ended with the formation of the _______, a gel like layer of glycoprotein rich in_____. And also the surrounding stroma cells form the _______ |
•Zona Pellucida •GAGs •Theca folliculi( theca interna and externa) |
|
|
|
Primordial follicles have their development arrested at______ stage, by the help of _____ until puberty after the release of____. |
•Meiotic prophase I stage • OMI oocyte maturation inhibitor. •LH. |
|
|
|
In secondary follicular stage, a cavity is formed in between the granulosa cells called _____, also the part of granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte are differentiated to form _______. CR(___________)is also developed. |
•Antrum •cumulus ophorus •corona radiata |
|
|
|
LH has three important effects in ovulation. Mention the 3 important effects |
1. It causes an elevation in the concentration of maturation promoting factors which allows oocytes to complete meiosis I and begin II. 2. Luteinization - which is the production of progesterone from stroma cells in ovaries. 3. Follicular rupture.
|
|
|
|
Describe the mechanism of follicular rupture? |
1. Local bulge appears at an area on the ovary 2. Avascular spot also called stigma appears at the tip of that bulge 3. Collagenase begins to digest the collagen fibers of the surrounding follicle. 4. Prostaglandins causes local muscular contractions in the ovary, forcing out the oocyte. |
|
|
|
Some of the cumulus ophorus rearrange themselves to around the ________ to form_______. |
Zona Pellucida Corona radiata |
|
|
|
Corpus luteum is formed after release of oocytes. If fertilization occur it becomes _________ which continues to secrete________ until end of __ month since the role is taken over by the__________. Whereas, if fertilization doesn't occur it becomes________. |
•Corpus luteum graviditatis •Progesterone •4th •trophoblastic component of the placenta. •Corpus Albicans |
|
|
|
During coitus, spermatozoa is deposited at the ___________ of the vagina. |
•Posterior Fornix |
|
|
|
Only about ____of spermatozoa enters into the cervix. They move as a result of __________________ and very little by their own_______ |
• 1% •Muscular contractions occuring in the uterus and uterine/fallopian tube. •Propulsion |
|
|
|
Spermatozoa are unable to fertilize eggs until after undergoing two processes to ensure their viability. |
• Capacitation • Acrosome reaction |
|
|
|
Oocytes are directed via ________, through the contraction or sweeping action of the _______ into the ______ of the uterine tube. Then gets to the ampulla in ___mins via the _________ of the oviduct wall. |
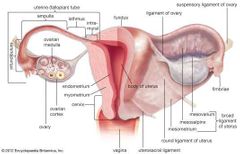
•Follicular fluid •Fibriae •Lumen of the Infundibulum. •25 •waves of peristalsis of muscle cells |
|
|
|
Define capacitation |
It is a conditioning period spanning about 7hrs and involves the removal of •glycoprotein coat •seminal plasma protein. From the plasma membrane that overlies the acrosomal region. It is initiated by substances secreted by uterus and uterine tube. |
|
|
|
Capacitation causes some morphological changes to the spermatozoa. T/F |
F |
|
|
|
Acrosome reaction is a process induced by______? |
•Penetration of the corona radiata |
|
|
|
Acrosome reaction Involves morphological modifications( structural alterations) by ___________of the ___________ with the __________. Followed by the rupture of the fused membranes which produces several/multiple pores through which enzymes such as(_____,_____,_____)(3) from the acrosome can escape. |
•multiple points fusion • plasma membrane • outer membrane of the acrosome •Hyaluronidase, trypsin-like enzymes, acrosin. |
|
|
|
There are five phases of fertilization which includes: |
1. Penetration of corona radiata 2. Penetration of the zona Pellucida 3. Fusion of the male and female gametes 4. Constitution of the male pronuclei 5. Fusion of the nuclei |
|
|
|
Cleavage takes place partly in (location and time) ____&____. |
•Uterine tube ( first 3 days) • Uterus( day 4 -6 ) |
|
|
|
Implantation begins on day_____ and ends on day______ |
7 13 |
|
|
|
On the ___ day fluid passes in from the uterine cavity through the ________ into the cell to form a single fluid filled space called_________. The resulting cell could then be called a _____. |
•4th •Zona Pellucida •Blastocystic cavity/ blastocoele • blastocyst/ blastula.
|
|
|
|
The process of implantation occurs in five stages: |
1. Attachment of the blastocyst (via L-selectin) to the endometrium epithelium which contain receptors. 2. Penetration/ invasion of the endometrium by action of enzymes like Integrin, Laminin, Fibronectin. 3. Reparation of the site of implantation defect at the point of invasion via close plug(operculum) which comprises blood clot and cellular debris 4. Formation of uteroplacental circulation. 5. Manifestation of decidual reaction. Featuring: • accumulation of glycogen and lipids by ESCs - endometrial stromal cells • formation of more capillaries around conceptus • increase in glandular activities of stroma cells- secretion of enzymes • |
|
|
|
The normal site of implantation is the_______? |
Posterior wall of mid portion of the uterus |
|
|
|
Ectopic sites are |
•Ampullary •isthmic • cornual • abdominal or ovarian |
|
|
|
A space develops with accumulation of fluid within the epiblast, which is called _______?
|
Amniotic cavity |
|
|
|
The trophoblast is differentiated into: |
Cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast |
|
|
|
An outer layer of multinucleated cell without distinct cell boundaries |
Syncytiotrophoblast |
|
|
|
Formation of the AVE-_____, establishes the ____________ |
•Anterior visceral endoderm •dorsal-ventral and cranio-caudal axes |
|
|
|
During day 8, fluid accumulates between the epiblast to form_______ |
Amniotic cavity fluid |
|
|
|
At day 9, three things happen |
1. The blastocyst becomes deeply embedded in the endometrium with Closure of implantation defect by fibrin clot 2. Formation of spaces within the syncytiotrophoblast cells called - Lacunae 3. Some of the hypoblast cells migrate to form a membrane called the exocoelomic (Heuser) membrane over the cytotrophoblast. And the cavity created by the boundaries of the Heuser membrane and the hypoblast cells is called the primitive yolk sac/exocoelomic cavity. |
|
|
|
4 things happens btw day 11&12 |
1. The blastocyst becomes completely embedded in the endometrial stroma. 2. The lacunae of the syncytiotrophoblast merges the stromal capillaries to form sinusoids, establishing the uteroplacental circulation. 3. New cells develop between the cytotrophoblast and the Heuser membrane called the extraembryonic mesoderm EEM 4. The EEM bear develops spaces which will layer formyhe chorionic cavity. The EEM closer the cytotrophoblast is splanchnopleuric. While the one adjacent to the primitive yolk sac is somatopleuric. |
|
|
|
On the 13th day, three things happen/ are observed: |
1. The cytotrophoblast begins to grow into the syncytiotrophoblast via finger like projections called primary villi 2. New cells from the hypoblast migrate to the inner part of the Heuser membrane and causes a large pinch off from the primitive yolk sac called the secondary/definitive yolk sac. A smaller exocoelomic cyst is seen embedded in the extraembryonic cavity 3. The embryonic part is then seen to be attached to the cyto trophoblast by just a connecting stalk which would later become the umbilical cord. |
|

