![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Signs of STEMI on EKG
|
* ST Elevation in 2 consecutive leads &
* New onset LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK |
|
|
What do Q waves signify?
|
Q waves can signify an OLD INFARCT!
|
|
|
What does cardiac ischemia or non-STEMI look like on EKG?
|
Inverted T-waves & ST depression.
|
|
|
Explain PEA and what we should always do when we see or suspect it.
|
PEA can be ANY EKG rhythm as long as there is NOT an associated pulse. When we see PEA, we should always confirm it in a 2nd lead (i.e., leads 1 or 3 is good BUT not lead 2 b/c the pads serve as lead 2)
|
|
|
How often should we check for pulses in ACLS?
|
Check for pulses Q 2 min or when there's a change in rhythm?
|
|
|
What are potential causes for pulses arrest?
|
Search for Tx possible contributing factors:
Remember H's & T's - Hypovolemia - Hypoxia - Hydrogen ions (acidosis) - Hypo/Hyperkalemia (Tx = BCIG ? I think) - Hypoglycemia - Hypothermia - Toxins - Tamponade, cardiac - TENSION PNEUMOtx - Thrombosis (coronary or pulmonary) - Trauma |
|
|
What rhythms are shockable?
|
THE ONLY SHOCKABLE RHYTHMS = VFIB & VTACH (i.e., pulseless Vtach)
|
|
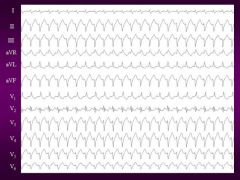
What rhythm is shown and is it a shockable rhythm?
|
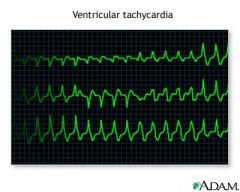
V-tach and YES you better shock it (i.e., defibrillation at 300 joules for monophasic or 200 joules if you don't know if the machine is monophasic or biphasic)
|
|
|
What rhythm is this and can it be shocked?
|
V-fib and you better shock it!
|
|
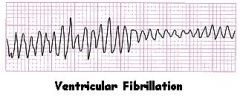
What rhythm is this and can it be shocked?
|
V-fib and you better shock it!
|
|
|
When should we give epi and how much should we give?
|
Give Epinephrine when the Pt is pulseless (Vfib, pulseless Vtach, AND Asystole or PEA).
IF the pt is in Vfib or Vtach, then give it after the shock BUT if the pt is in asystole or PEA then JUST GIVE IT b/c remember we do NOT shock asystole & PEA. Give 1 mg IV/IO ( 1/10,000) Q 3 to 5 mins ad infinitum or until the code has ceased. |
|
|
What can be given, and at what dose, instead of Epi in PEA (i.e., Vfib, Vtach, Asystole & PEA)?
|
Vasopressin 40 U IV/IO X 1 (i.e., ONLY ONCE) IOW, Vasopressin can ONLY be given ONE TIME!!!
As a REPLACEMENT for EITHER the 1ST OR the 2ND dose (i.e., either b4 the first dose of epi or right after the first dose of epi). Also Atropine, 1mg IV/IO Q 3 to 5 mins UP TO 3 DOSES MAX (i.e., MAXIMUM 3 mg), can be given but only in asystole & slow PEA. Atropine is NOT given in Vfib & Vtach!!! (And Atropine is usually given after epi is tried 1st) |
|
|
What is the breaths/ventilation rate in CPR for a Pt with no airway device versus a Pt with an advanced airway device?
|
5 to 6 breaths per minute for a pt with no airway VERSUS 6 to 8 breaths per minute for a Pt with an advanced airway inserted.
|
|
|
What is the neumonic that explains the patency or lack thereof of ones airway.
|
"DOPE"
D-isplacement of the airway O-bstruction (via mucous plug or what not) P-neumothorax E-quipment failure |

