![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the main difference in effects between ligand receptors and g protein coupled receptors?
|
Ligand have rapid, short-acting responses while g protein has slow potentials with long-term effects.
|
|
|
What causes excitatory depolarization (ion-wise)?
|
More Na+ in or less K+ out
|
|
|
What causes inhibitory hyperpolarization (ion-wise)?
|
More K+out, more Cl- in or less Na+ in
|
|
|
What are the 4 criteria for being a neurotransmitter?
|
1. Presence (in the presynaptic terminal)
2. Release (in response to depol, Ca2+ dependent) 3. Identity of action (direct application effects = presynap stim) 4. Removal (1+ mechanisms for elimination) |
|
|
What synapses are cholinergic?
|
Neuromuscular, autonomic ganglia, parasymp postgang neuroeffector, sweat glands, between symp pregang and adrenal chromaffin cells, and certain CNS.
|
|
|
What synapses involve norepi (noradrenergic)?
|
Postgang sympathetics and certain CNS.
|
|
|
What synapses involve epinepherine?
|
Certain CNS.
Also a hormone released from chromaffin cells. |
|
|
What synapses involve dopamine?
(dopaminergic) |
Postgan sympathetics in the kidney and certain CNS.
|
|
|
Where is nonadrenergic noncholinergic transmission typically found?
|
Enteric nervous system
|
|
|
What types of transmitters are involved in nonadrenergic noncholinergic transmission and cotransmission?
|
adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP)
vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) neuropeptide Y (NPY) leutinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH) 5-hydroxy tryptamine (5-HT or serotonin) nitric oxide (NO) gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) substance P dopamine |
|
|
Structure of muscarine?
|
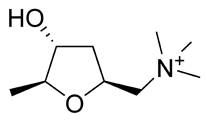
|
|
|
Structure of atropine?
|
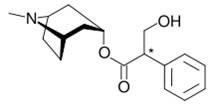
|
|
|
Structure of dopamine?
|
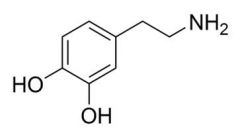
|
|
|
What's cool about NO?
|
Cotransmitter at inhib ENS and neuromuscular junctions (especially important at sphincters). Synthesized by NO Synthase when stimulated by Ca2+, can cross membrane without vesicles.
|
|
|
How's ACh made? What's the rate-limiting step?
|
Synthesized by choline acetyl-transferase in cytosol from acetylCoA and choline. Rate limiting step = choline uptake from ECM via high affinity transporters.
|
|
|
How is ACh broken down?
|
By Acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft
|
|
|
What compound blocks choline uptake? (synthesis)
|
Hemicolinium
|
|
|
What compound inhibits the vesicular ACh transporter? (storage)
|
Vesamicol
|
|
|
What compound blocks exocytosis of ACh by modifying docking proteins and preventing synaptic vesicle fusion with the presynapatic nerve terminal? (release)
|
Botulinum Toxin
|
|
|
What compound is a nicotinic agonist?
|
Nicotine (used in Alzheimer's tx)
|
|
|
What compound is a muscarinic agonist?
|
Bethanacol
|
|
|
What compound is a neuronal nicotinic antagonist?
|
Trimethaphan (blocks ganglionic transmission - major effect = vasodilation)
|
|
|
What compound is a muscular nicotinic antagonist?
|
d-tubocurarine (paralyzes somatic muscle)
|
|
|
What compound is a muscarinic antagonist?
|
Atropine (used locally to dilate the eye and systemically to increase HR and cardiac output)
|
|
|
What compound inhibits acetycholinesterase? (disposition)
|
physostigmine (used to tx myasthenia graves and glacoma)
|
|
|
In the synthesis of norepi, what is tyrosine converted to? What is the enzyme involved?
|
Tyrosine is converted to DOPA via Tyrosine Hydroxylase in the cytosol (*rate-limiting step*)
|
|
|
In the synthesis of norepi, what's DOPA converted to? What's the enzyme involved?
|
DOPA's converted to Dopamime via DOPA decarboxylase in the cytosol
|
|
|
What's dopamine converted to? What's the enzyme involved?
|
Dopamine's converted to norepi via Dopamine Beta-hydroxylase in the vesicle (*released into cleft when the neurotransmitter is*)
|
|
|
What's alpha2 receptor's major function?
|
Located at the presynaptic terminal, provides negative feedback to the presynaptic neuron to stop the release of neurotransmitter.
|
|
|
Which of the beta receptors has the highest affinity for norepi?
|
Beta1
|
|
|
What enzymes metabolize epi and norepi? What are they metabolized into?
|
MAO and COMT metabolize them to vanillylmandelic acid. (dopamine's metabolized to homovanillic acid)
|

