![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define electronegativity |
Electronegativity is the power of an atom to attract the electron density in a covalent bond towards itself. It is measured using the Pauling scale which runs from 0-4 the greater the number the more electronegative it is. Noble gases no number as they generally do not form covalent bonds. |
|
|
What does electronegativity depend on? |
1) Nuclear charge 2) Distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons 3) The shielding of the nuclear charge by electrons in inner shells The smaller the atom, the closer the nucleus is to the shared outer main level electrons and the greater it's electronegativity. The larger the nuclear charge ( for a given shielding effect), the greater the electronegativity. |
|
|
Describe Trends in electronegativity |
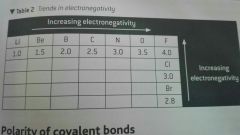
Going up a group in periodic table, electronegativity increases ( the atom gets smaller) and there is less shielding by electrons in inner shells. Going across the periodic table electronegativity increases. The electronegativity increases as the number of inner main levels remain the same and the atoms become smaller Most electronegative atoms found at top right corner of table excluding noble gases |
|
|
Describe polarity of covalent bonds |
Polarity is about the unequal sharing of the electrons between atoms that are bonded together covalently. It is a property of the bond. |
|
|
Describe the effect of polarity between 2 atoms of the same or similar.ilar electronegativity? |

When both atoms are the same e.g. f2 the electrons in the bond must be shared equally between atoms- both atoms have exactly same / similar electronegativity and the bond is completely non - polar. |
|
|
Describe covalent bonds between two atoms with different electronegativity? |
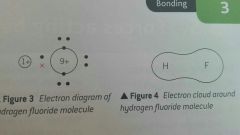
In a covalent bond between two atoms with different electronegativity the electrons in the bonds will not be shared equally between the two atoms. E.g. Hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen = 2.1 Fluorine = 4.0 This means electrons in covalent bond will be attracted to Fluorine more than hydrogen. The Fluorine molecule will therefore have a relatively negative end Hydrogen will have a relatively positive end This will make the covalent bond polar the greater the difference in electronegativity the more polar the bond is. |

