![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|
|
When doing an EOG, do you get the light peak first or the dark trough?
|
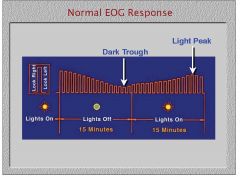
|
|
|
While many diseases of the RPE manifest an abnormal EOG, what is the only disease that manifests an abnormal EOG but a normal ERG?
|
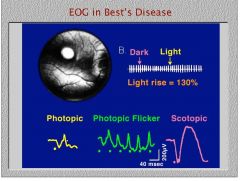
Best's disease
|
|
|
1. Where do you place the active electrode during an ERG?
2. Where do you place the reference electrode? 3. Where do you place the ground electode? |

1. contact lens in the eye with a wire in the contact lens
2. the forehead (doesn't respond to light so it just completes the circuit) 3. the ear (ground is just for safety purposes) |
|

|

|
|
|
Is the ERG response bigger in the dark or in the light? Why?
|

Dark, There are 6 times as many rods as cones.
|
|
|
Is the scotopic ERG faster or slower than the photopic ERG?
|
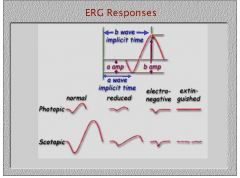
The scotopic ERG is slower because rods respond slower than cones. But M cells we know are faster cause the nerve is wider, go figure.
|
|
|
What type of ERG would show that the photoreceptors are working but the signal is not making it through to the bipolar cells?
|

an electronegative ERG cause the B wave due to bipolar and Mueller cells is absent but the a wave due to photoreceptors is still there.
|
|
|
What do you call an ERG in which photoreceptors and bipolar/Mueller cells are not working?
|

an extinguished ERG
|
|
|
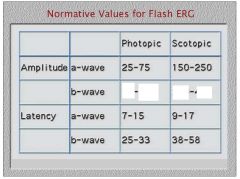
What do you call an ERG in which the amplitude of the waves is lower than normal but the waves are still distinguishable?
|
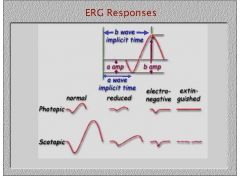
a reduced ERG
|
|
|

|
|
|
What type of ERG would you predict for a patient with RP?
|

1) an extinguished ERG is common in more pronounced RP (X-linked and autosomal)and night blinding diseases
2) Just a reduced ERG in less pronounced cases of RP |
|
|
What type of ERG would you expect for a patient with ophthalmic artery occlusion?
|
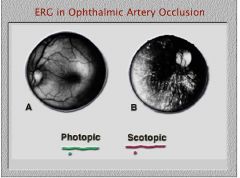
extinguished ERG
|
|
|
In what retinal disease is the a wave of the ERG present but the B wave is absent?
|

any disease that disrupts the synapse,
1. Oguchi's 2. Retinoschisis cause there is a separation of photoreceptors and bipolar cells 3. any disease that disrupts CRA blood flow |
|

What disease might you guess this to be?
|

Hereditary cone disease because the photopic ERG is effected but not the scotopic ERG
|
|
|
If you were to high pass filter an ERG and find oscillatory potentials would you suspect the patient has a vascular retinal disease like hypertensive retinopaty or diabetic retinopathy?
|

No, oscillatory potentials are not present in vascular diseases and the ERG simply looks smooth no matter how closely you inspect.
|
|
|
What ERG uses an opthalmoscope?
|

focal ERG
|
|
|
What type of ERG requires a special electrode that won't disrupt the optics of the eye?
|

PERG gold foil electrode
|
|
|
What type of ERG would be sensitive to ganglion cell death caused by ocular hypertension?
|
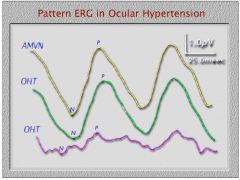
PERG
|
|

1. How much smaller is the PERG response than a normal flash ERG response?
2. Which color OHT curve represents the ocular hypertensive patient who probably develop glaucoma? |
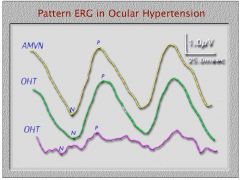
1. A normal ERG is in 100s of microvolts while PERG is 10 times less around 1 or 2 microvolts.
2. The purple curve represents the patient more likely to develop glaucoma. |
|
|
What type of ERG allows you to use just one electrode and get responses from multiple specific retinal areas?
|

multifocal ERG
|
|
|
Name two reasons VEP response is due more to central retina.
|

1. cortical magnification
2. the VEP electrode is place on the scalp and the part of cortex responsible for central retinal vision is located outer to the others and hence closer to the electrode. |
|
|
What ocular condition would reduce the ampplitude of a VEP?
|

cataract
|
|
|
What type of VEP would be best for measuring acuity?
|
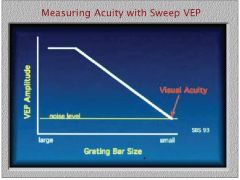
sweep VEP
|
|
|
How do you measure the degree of amblyopia with a VEP?
|

the degree of amblyopia is measured by the ability to see contrast
|
|
|
How do you measure the refractive error with a VEP?
|

measure the latency and correlate it to refractive error.
|
|

|

|

