![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Front (Term) |
Electric motor |
|
|
Conventional current |
Positive -> negative |
|
|
Electron flow |
Negative -> positive |
|
|
Insulators |
Electrons are bound to atoms and able to move. No current can pass through material, no charge carriers. |
|
|
Conductors |
Most electrons bound to mets atoms, some delocalised. Delocalised electrons attracted towards positive terminal when pd applied. |
|
|
Semi-conductors |
Bound to atoms but have ability to be liberated. Number of charge carriers increases with increased temperature. |
|
|
Difference between potential difference and voltage |
Voltage is the absolute energy per coulomb of charge in a fixed place. Potentia difference is the difference in energy per coulomb of charge between 2 point. |
|
|
Difference between potential difference and voltage |
Voltage is the absolute energy per coulomb of charge in a fixed place. Potentia difference is the difference in energy per coulomb of charge between 2 point. |
|
|
EMF |
Electromotive force , energy transferred to charge carriers per coulomb of charge, by electrical energy source. |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Resistance |
Measure of how much component opposes the flow of charge carriers/current. |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Resistance |
Measure of how much component opposes the flow of charge carriers/current. |
|
|
The higher the resistance... |
Smaller the potential difference and current. |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Resistance |
Measure of how much component opposes the flow of charge carriers/current. |
|
|
The higher the resistance... |
Smaller the potential difference and current. |
|
|
Resistance arises from... |
Repeated collisions of charge carriers with eachother and ions in material. |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Resistance |
Measure of how much component opposes the flow of charge carriers/current. |
|
|
The higher the resistance... |
Smaller the potential difference and current. |
|
|
Resistance arises from... |
Repeated collisions of charge carriers with eachother and ions in material. |
|
|
Resistor |
Designed to have fixed resistance |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Resistance |
Measure of how much component opposes the flow of charge carriers/current. |
|
|
The higher the resistance... |
Smaller the potential difference and current. |
|
|
Resistance arises from... |
Repeated collisions of charge carriers with eachother and ions in material. |
|
|
Resistor |
Designed to have fixed resistance |
|
|
Resistance of resistor can be measured by... |
Varying current and measuring potential difference across it. |
|
|
Power |
Rate of energy transfer |
|
|
Resistance |
Measure of how much component opposes the flow of charge carriers/current. |
|
|
The higher the resistance... |
Smaller the potential difference and current. |
|
|
Resistance arises from... |
Repeated collisions of charge carriers with eachother and ions in material. |
|
|
Resistor |
Designed to have fixed resistance |
|
|
Resistance of resistor can be measured by... |
Varying current and measuring potential difference across it. |
|
|
Ohm's Law |
Potential difference across conductor is directly proportional to the current through it, provided physical conditions do not change (temperature) |
|
|
Superconductor |
Material that has 0 resistivity, below a critical temperature that depends upon the material. |
|
|
Superconductor |
Material that has 0 resistivity, below a critical temperature that depends upon the material. |
|
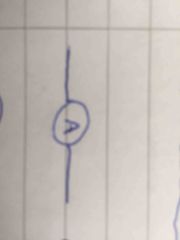
Front (Term) |
Ammeter |
|
|
Superconductor |
Material that has 0 resistivity, below a critical temperature that depends upon the material. |
|
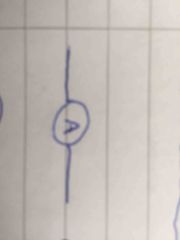
|
Ammeter |
|
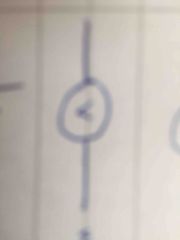
Front (Term) |
Voltmeter |
|
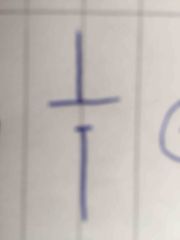
|
Cell |
|
|
Potential difference-current graph's gradient shows... |
R |
|
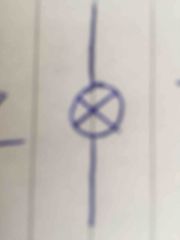
Front (Term) |
Light source/indicator |
|

Front (Term) |
Diode |
|
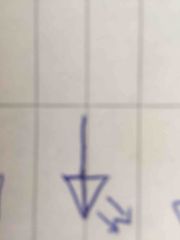
Front (Term) |
Light-emitting diode |
|
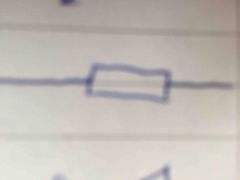
Front (Term) |
Resistor |
|
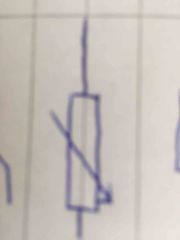
Front (Term) |
Variable resistor |
|
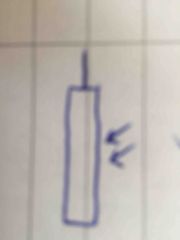
|
Light-dependent resistor |
|

H |
Heater |
|
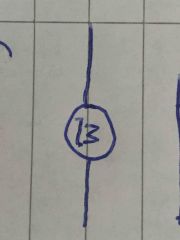
|
Electric motor |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Electric motor |
|
|
Resistors in parallel |
1/R1+1/R2 |
|
|
Resistor in series... |
R1+R2+R3 |
|
|
Internal resistance |
Loss in potential difference per unit current, as current passes through source |
|
|
Voltmeter should have a ... Resistance |
Infinitely high |
|
|
Ammeter should have ... Resistance |
No |
|
|
Potential divider |
2 or more resistors in series with fixed potential difference source |

