![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are balanced three phases and what is the diagram for this |
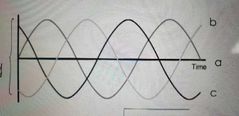
A set of three electrical values that: -Have the same magnitude -Are 120 degrees apart from each other. |
|
|
What is the main advantage of three phases |
All currents are balanced so the return wire can be combined into one common wire. For a balanced system the neutral wire will have no current so it can be eliminated. |
|
|
What are the advantages of three phase |
- More power can be transmitted with less wires - Generators operate with a more constant torque compared to single phase. - It leads to a reduced cost of transformers - Balanced three phases can be represented by a single line diagram |
|
|
Diagram representing a balanced three phase system with a single line diagram |

|
|
|
How are the Phasor for three phase systems |

They rotate at a constant frequency Their projection to the x axis gives their instantaneous value of voltage |
|
|
What does a star connection look like |

|
|
|
What does the delta connection look like |
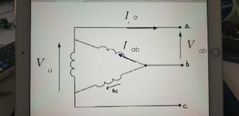
|
|
|
What are the phase voltages and phase currents of a star connection |
Phase I = Line I
Line V = root 3 * Phase V |
|
|
What is the Phasor diagram for a star connection |

|
|
|
What are the phase voltages and phase currents of a delta connection |
Phase V = Line V Phase I = root 3 * Line I |
|
|
What is the Phasor diagram for a delta connection |

|
|
|
How would we find the phase current of an unbalances star connected three phase load |

|
|
|
What is a heavily meshed transmission grid |
When there is more than one route for power to travel. |
|
|
What are the advantages of a heavily meshed transmission grid |
- The grid can tolerate the loss of major components this making the grid more reliable and optimised.
- A meshed grid also allows for the cheapest generation to be utilised. - We can share reserve generation capacities throughout the system. |
|
|
What are the advantages of an interconnected grid |
- It is easier for the generation to meet changing loads because generation reserves from different locations can be shared. - The grid is synchronous to the same common frequency. |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of underground cables to overhead cables |
Advantages: - Less environmental impact - Less prone to animal, human, weather damages Disadvantage: - Cost, it is 10-20x more expensive. |
|
|
Why do we increase the voltage down a transmission line |
We will get a loss of power due to Mould heating in the cable, this is equal to Delta P = I^2 R = I ^2 ((ro x L) / A) Whereas the power available at the input to the cable is: P = I * VT Therefore, percentage power loss is Delta P / P, this leads to power less decreasing with an increasing VT. |
|
|
What is a generator |
A manufacturer of electricity, it is a source of active power and may apply or absorb reactive power. |
|
|
What is a bus |
A very low impedance electrical connection between two or more electrical components. |
|
|
What is a switchgear |
Used to change electrical topology connections within a network when the network is in operation. |
|
|
What is the load factor of a plant |

The higher the load factor of a power plant the better it is being utilised. |
|
|
How would we calculate the energy output of a plant over a year |
Output in MWh = (Max Power) x (Load Factor) x 24 x 365 |
|
|
What is the safety factor |

Extra 'head room built into plants to supply extra load at times of stress. |
|
|
What is the Diversity factor |

A measure of how much the potential maximum load is actually utilised in practice. The higher the DF the more the system is benefiting from the diversity of loads which do not reach the peak simultaneously. |
|
|
Diagramatically what is the market structure of energy in the UK |

|
|
|
What is the gross pool energy market structure |
Any generator can sell energy to any retailer on the wholesale power market. There are bilateral contract for differences that sure-up any mismatches between what a contract was deemed to be worth and what it was actually worth. |
|
|
What does the energy bill consist of |

|
|
|
What are the benefits for a consumer to invest into solar panels |
- Subsidy for each kWh of electricity generated - Subsidy per kWh exported to the grid. - Create less stress on the distribution network. |
|
|
What are transmission lines used for |
To physically transmit power from generators to sub-stations then to loads. |
|
|
What is the diagram and equations of the transmission line model |

|
|
|
What are the complications of the transmission line model |
- A transmission line had both series and shunt impedances the series impedance is inductive and the shunt impedance is capacitive.
- There are three phases and an earth wire in a normal transmission line.
- There is also mutual inductance and capacitance between phases
- Each conductor has self and mutual impedances of these series and shunt parameters.
|
|
|
What is the matrix line model of transmission |

We use inductive impedances to relate voltage drops to current using the complex form of ohms law in a matrix. |
|
|
Learn the lattwr half of lecture 4 |
Do it |
|
|
What does a transformer do |
It steps up and steps down AC voltages so that we can transmit at the highest voltage to minimise power losses. They can also perform galvanic isolation and measure quantities. |
|
|
How are transformers designed |
To maximise inductance and minimise losses. Use an iron gap to capture magnetic flux. Three phases have three limbs in the core. |
|
|
How does current and voltage of a transformer relate to it's turns (formula) |

|
|
|
What is the formula that relates impedance ratio in trends of the turns ratio |

|
|
|
What is the circuit diagram that represents a single phase transformer with no load |

|
|
|
What is the phasor diagram that represents a single phase transformer with no load |
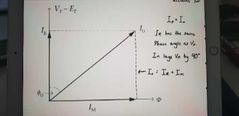
|
|
|
What does Im and Io represent in the transformer circuit diagram. |
Im through the inductor Lo represents the magnetising current in the core which lags the voltage Vp by 90 degrees. Im causes an alternating magnetic flux in the cite resulting in heat loss represented by Ir through resistor Ro. Io is the resultant current in the core of the primary and the Phasor sum of Im and Ir. |
|
|
What change occurs when the transformer becomes on load |
There will be a current in the secondary windings. |
|
|
What is the equation for the secondary current referred to the primary |

|
|
|
What are assumptions made about the on load transformer |
The flux in the core remains constant at all loads. The power factor is dictated by the type of load connected. |
|
|
Formula to refer the load to the primary |

|
|
|
What is the circuit diagram of the full model for a single phase transformer |

|
|
|
What is the formulas for the primary and secondary impedances |

|
|
|
How are 3 phase transformers designed |
With a solid single core with three limbs. Each limb accommodates the high voltage and low voltage winding for each phase. The primary and secondary phases are both 120 degrees apart. Winding configurations may be either delta or star. |
|
|
What are the three objectives of electricity supply: |
Reliability
Affordability Environmental Friendlyness
|
|
|
What is the objective of reliability |
The ability to maintain continuous per supply, avoid power cuts and minimise the damage of power cuts.
|
|
|
What is the objective of affordability |
Minimise fuel costs for generationMinimise energy losses on power lines and transformers.Minimise the cost of power outages. Low costs for building new infrastructure and a low cost of smart grid solutions. |
|
|
What is the objective of environmental friendlyness |
Decarbonise both energy generation and consumption. Replace fossil fuel generation with renewable generation. Replace conventional vehicles and gas heating with electric alternatives. |
|
|
What issues are there with evaluation towards a modern day power system |
Investments to improve reliability adds to customers build thus compromising affordability. LCEs incur costs to the network these costs eventually have to be recovered from costumers energy bills. |
|
|
What are smart grid solutions |
Exploiting the flexibility from the network and/or customers to advance one or more of the three objectives whilst minimally compromising the rest of the objectives. |

