![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A negatively charged rod is brought near a neutral metal sphere. What is the force between the rod and sphere? |
There is an attractive force between the rod and sphere. |
|
|
The field inside a charged parallel-plate capacitor is ____? |
Uniform |
|
|
The electric field inside a metallic conductor is ___? |
Zero |
|
|
A hollow sphere made out of electrically insulating material is electrically neutral (no excess charge). A small amount of negative charge is suddenly placed at point P on the outside of this sphere. If we check on this excess negative charge a few seconds later we will find _____. |
All of the excess charge remains around P. An insulating material does not allow electrons to move around. |
|
|
A hollow metal sphere is electrically neutral (no excess charge). A small amount of negative charge is suddenly placed at one point P on this metal sphere. If we check on this excess negative charge a few seconds later we will find _____. |
The excess charge has distributed itself evenly over the outside surface of the sphere. Charges on a conductor adjust until there is no net force on any charge. This is called electrostatic equilibrium. |
|
|
The electric field _____. |
Is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface. |
|
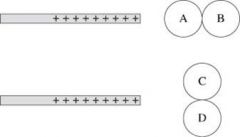
Two spheres are touching each other. A charged rod is brought near. The spheres are then separated, and the rod is taken away. In the first place, the spheres are aligned with the rod, in the second case, they are perpendicular. After the charged rod is removed, which of the spheres is
1) Positive
|
1) B 2) A |
|
|
The statement "A plastic ball can carry a static charge with the amount of 1004.5 x e" (where e is the unit of charge, 1.60 x 10^-19 C) is ______. |
False |
|
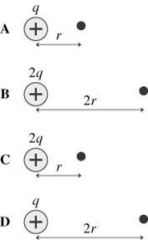
A small, positive charge is placed at the black dot. In which case is the force on the small, positive charge the largest? |
C |
|
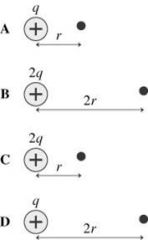
A small, positive charge is placed at the black dot. In which case is the force on the small, positive charge the smallest? |
D |
|
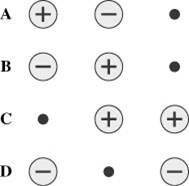
All charges in the diagrams below are of equal magnitude. In each case, small, positive charge is placed at the black dot. In which case is the force on the small, positive charge the smallest? |
D |
|
|
Coulomb's Law |
F(1 on 2) = F(2 on 1) = [K|q1||q2|]/r^2 |
|
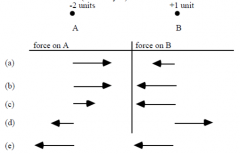
The picture shows a particle (labeled B) which has a net charge of +1 unit. Several cm to the left is another particle (labeled A) which has a net negative charge of -2 units. Choose the pair of force vectors (the arrows) that correctly compare the electric force on A (caused by B) with the electric force on B (caused by A). |
C |
|
|
Two small objects each with a net charge of +Q exert a force of magnitude F on each other. We replace one of the objects with another whose net charge is +4Q. The original magnitude of the force on the +Q charge was F; what is the magnitude of the force on the +Q now? |
4F |
|
|
Two small objects each with a net charge of +Q exert a force of magnitude F on each other. We replace one of the objects with another whose net charge is +4Q. The original magnitude of the force on the +Q charge was F; what is the magnitude of the force on the +4Q now? |
4F |
|
|
Two small objects each with a net charge of +Q exert a force of magnitude F on each other. We replace one of the objects with another whose net charge is +4Q. Now we move the +Q and +4Q charges to be 3 times as far apart as they were. The original magnitude of the force on the +Q charge was F; now what is the magnitude of the force on the +4Q charge? |
4F/9 |
|
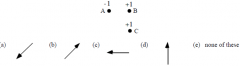
Which of the arrows is in the direction of the net force on charge B? |
A |
|

In the figure, positive charges q2 and q3 exert on charge q1 a net electric force that points along the +x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (b,0), what now will happen to the force on q1? (All charges are fixed at their locations.) |
The size of the net force will change but not the direction. |
|
|
Electric field of point charge q at distance r |
E Vector = [K|q|]/r^2 |
|
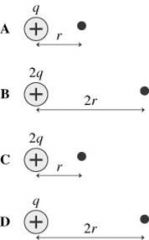
Positive charges create an electric field in the space around them. In which case is the field at the black dot the largest? |
C |
|
|
E capacitor = Q/epsilon0*A |
Electric field in a parallel-plate capacitor with plate area A and charge Q |
|
|
The field inside a parallel-plate capacitor is _____. |
Uniform |
|
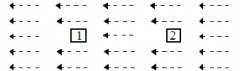
A positive charge might be placed at one of the two different locations in a region where there is a uniform electric field. How do the electric forces on the charge at positions 1 and 2 compare?
|
Force on the charge is greater at 2. |
|
|
A positive charge is placed at rest at the center of a region of space in which there is a uniform, three-dimensional electric field. When the positive charge is released from rest in the uniform electric field, what will its subsequent motion be? |
It will move at a constant acceleration. |
|
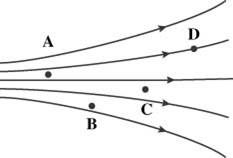
A set of electric field lines is directed as shown. At which of the noted points is the magnitude of the field the greatest? |
A |
|

Two parallel plates have charges of equal magnitude but opposite signs. What changes could be made to increase the field strength between the plates? |
Increase the magnitude of the charge on both plates. |
|
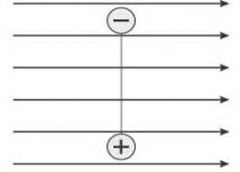
A dipole is held motionless in a uniform electric field. When the dipole is released, what is the subsequent motion? |
The dipole rotates counterclockwise. |
|
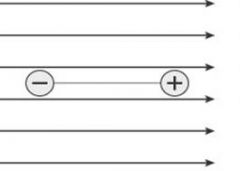
A dipole is held motionless in a uniform electric field. When the dipole is released, what is the subsequent motion? |
The dipole moves to the right. |
|
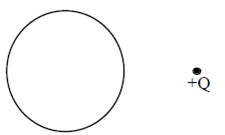
The figure shows a hollow conducting metal sphere which was given initially an evenly distributed positive charge on its surface. Then a positive charge +Q was brought up near the sphere. What is the direction of the electric field at the center of the sphere after the positive charge +Q is brought up near the sphere? |
Zero field |
|
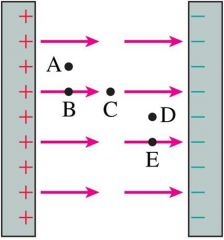
A proton would experience a force if placed at points A to E in this parallel-plate capacitor. Which statement about the force Fa to Fe is correct? |
All the same. |
|
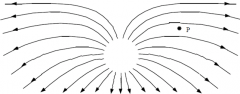
What is the direction of the electric force on a negative charge at point P in the diagram? |
To the left. |
|
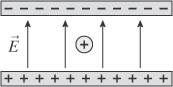
A positively charged particle is motionless in the center of a capacitor. Describe the subsequent motion of the charged particle. |
It will travel to the negatively charged plate of the capacitor. |
|
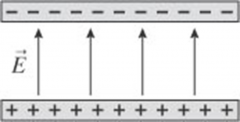
An electron is moving from the left of a capacitor with a speed of V0. Describe the subsequent motion of the charged particle. |
It will travel a distance to the right and then gradually fall to the positively charged plate of the capacitor. |

