![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Current |
Flow of charge |
|
|
Charge (Q coulombs ) |
Current x time taken |
|
|
Diode |
Allows current in one direction only |
|
|
Voltmeter |
Always connected in parallel to measure volts |
|
|
Ammeter |
Connected in series to measure current |
|
|
Potential difference = |
Energy transferred / charge Q |
|
|
Resistance (ohms) |
Voltage / current |
|
|
Ohms law |
The current and potential difference across a resistor is directly proportional so long as temperature is constant |
|
|
Current Pd graph for filament lamp |
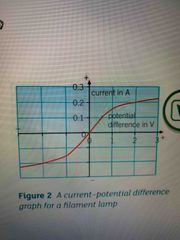
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Current pd graph for a diode |
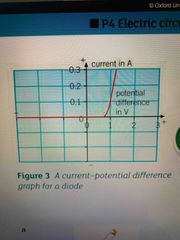
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Thermistor |
When the temperature increases the resistance decreases |
|
|
Light dependent resistor |
When the light intensity increases the resistance decreases |
|
|
In a series circuit what happened to the current |
It is the same everywhere through each component |
|
|
What happens to the voltage in a series circuit |
It is split, sum of the pd of cells = sum of all components |
|
|
What happens to the voltage in a series circuit |
It is split, sum of the pd of cells = sum of all components |
|
|
In a series how do you work out the total resistance |
Add up all the resistances of the different components |
|
|
What happens to the current in a parallel circuit |
Sum of the currents through the separate branches |
|
|
What happens to the voltage in a series circuit |
It is split, sum of the pd of cells = sum of all components |
|
|
In a series how do you work out the total resistance |
Add up all the resistances of the different components |
|
|
What happens to the current in a parallel circuit |
Sum of the currents through the separate branches |
|
|
What happens to the voltage in a parallel circuit |
The potential difference across each component is the same |
|
|
Total resistance in a parallel circuit |
1/ R total = 1/ R1 + 1/R2 |
|
|
The more resistors there are in a parallel circuit |
The smaller the total resistance |
|
|
In a series circuit adding more resistors |
Increases the total resistance |
|
|
The total of two/more components in parallel |
Is less than the resistance of the resistor with the least resistance |
|
|
Power = |
Energy transferred / time |
|
|
Power supplied = |
Current x voltage |
|
|
Power to resistor = |
Current squared x resistance |
|
|
Charge flow = |
Current x time |
|
|
Energy transferred = |
Charge flow x potential difference |

