![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
136 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are five rhythms that originate on the SA node?
|
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia Sinus Dysrhythmia Sinus Arrest |
|
|
What are two characteristics of sinus node rhythms/dysrhythmias?
|
Normal P waves preceding each QRS
Each PR interval WNL (0.12-0.20 sec) |
|
|
This rhythm to which all other rhythms are compared to, this is the normal standard. The heart rate is 60-100 bpm, regular rhythm, normal P wave preceding each normal QRS, PR interval with normal duration and constant. Each QRS is followed by normal T wave.
|
Normal Sinus Rhythm
|
|
|
This is characterized by a HR < 60 bpm, this leads to longer R-R and P-P.
|
Sinus Bradycardia
|
|
|
What are two basic causes of Sinus bradycardia?
|
1. May occur naturally, i.e. at rest (2/2 increased vagal stimulation and decreased sympathetic stimulation)
2. In conditioned athletes |
|
|
What cardiac d/o cause sinus bradycardia?
|
Cardiac d/o: SA node dz, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, ischemia, infarction, heart block
|
|
|
What drugs can cause sinus bradycardia?
|
Drugs - BB, Digoxin, CCB, Lithium, Amiodarone
|
|
|
The following can cause what type of dysrythmia? Increased Vagal tone and decreased sympathetic stimulation - Carotid sinus massage, valsalva maneuver, deep relaxation, sleep
|
Sinus Bradycardia
|
|
|
What non cardiac d/o can cause sinus bradycardia?
|
Non cardiac d/o: Hypothermia, hypoxia, increased potassium, increased intracranial pressure, hypothyroidism, glaucoma.
|
|
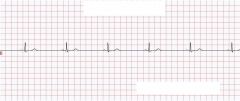
What type of rhythm is this?
|
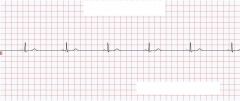
Sinus Bradycardia
|
|
|
This is a HR > 100 BPM with a shorter R-R and P-P intervals.
|
Sinus Tachycardia
|
|
|
This may occur naturally with exercise, pain, fear, anxiety secondary to increased sympathetic stimulation in response to need of increased 02 and nutrients.
|
Sinus Tachycardia
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause sinus tachycardia?
|
CHF, Cardiogenic shock, pericarditis
|
|
|
What are the drugs that can cause sinus tachycardia?
|
Epinephrine, isoproterenol, dopamine, dobutamine, atropine, EtOH, Caffieine, nicotine, amphetamines
|
|
|
What can cause an increase in sympathetic stimulation, resulting in sinus tachycardia?
|
Exercise, pain, stress, fever, fear, anxiety, respiratory distress, hypoxia, PE, anemia, sepsis, hyperthyroidism
|
|
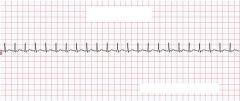
What type of rhythm is this?
|
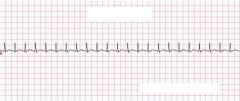
Sinus Tachycardia
|
|
|
Sinus dysrhythmia is characterized by irregularly firing SA node which causes slowing, then speeding up, then slowing again, this is in response to what?
|
In response to the respiratory cycle.
The HR increases during inspiration and decreases during expiration. |
|
|
In what instances can sinus dysrhythmia occur naturally?
|
In athletes, children and older adults.
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that can cause sinus dysrhythmia?
|
Heart dz, inferior wall MI
|
|
|
What are the drugs that can cause sinus dysrhythmia?
|
Digoxin, Morphine
|
|
|
What are the non-cardiac d/o that can cause sinus dysrhythmia?
|
Increase in intercranial pressure
|
|
|
Usually no intervention is needed, but these may be associated with palpitations, dizziness, or syncope?
|
Sinus dysrhythmia
|
|
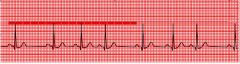
What type of rhythm is this?
|
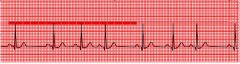
Sinus Dysrhythmia, AKA sinus arrhythmia.
|
|
|
This is characterized by the SA node transiently not firing which leads to a pause until a lower level pacemaker initiates impulse or SA node resumes normal function.
|
Sinus Arrest
|
|
|
What are the causes of sinus arrest?
|
Increased parasympathetic tone on SA node, hypoxia, ischemia
|
|
|
These two things are classified as SA node diseases that cause sinus arrest?
|
Fibrosis, idiopathic degeneration
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause sinus arrest?
|
Chronic CAD, MI, acute myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, HTN
|
|
|
What drugs cause sinus arrest?
|
Digoxin, procainamide, quinidine, salicylates, excessive BB, CCB
|
|
|
These three things cause sinus arrest and are causes for increased vagal tone.
|
Valsalva maneuver, carotid sinus massage, vomiting.
|
|
|
Increased potassium and hypoxia can cause what?
|
Sinus arrest
|
|
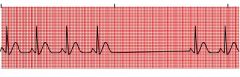
What type of rhythm is this?
|
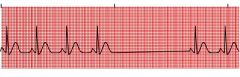
Sinus Arrest
|
|
|
These origionate outside the SA node in atrial tissue or in internodal pathway?
|
Atrial Dysrhythmias
|
|
|
This is a part of the atrial dysrhythmia mechanism, it is when the atrial cells spontaneously depolarize and initiate impulses before SA node generates impulse.
|
Increased Automaticity
|
|
|
What causes increased automaticity in atrial dysrhythmia mechanism?
|
Secondary to ischemia, hypoxia, atrial dilation due to CHF, mitral valve dz.
|
|
|
This is a part of the atrial dysrhythmia mechanism, it is when the injured cells only partially repolarize leading to repetitive ectopic firing also secondary to digoxin toxicity.
|
Triggered activity after depolariztion
|
|
|
This is a part of the atrial dysrhythmia mechanism, it is a slow pathway, secondary to CAD, cardiomyopathy or MI.
|
Reentry
|
|
|
This is when a premature SA impulse reaches AV node, and the fast pathway is refractory, the impulse goes down slow pathway, when it reaches Bundle of HIS, fast pathway is open, retrograde conduction back up to the atria and then back down slow pathway leading to continuous rapid flow of electrical impulses causing tachycardia.
|
Reentry mechanism
|
|
|
P waves look different from normal P waves and there is an abnormal PR interval, but the QRS is unchanged. These are characteristics of what?
|
Atrial Dysrhythmias
|
|
|
What are the 6 Atrial dysrhythmias?
|
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
Premature Atrial Complex (PAC) Atrial Tachycardia Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) Atrial Flutter Atrial Fibrillations |
|
|
This is characterized by a 3 P wave morphology, with variable PR intervals.
|
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
|
|
|
When are wandering atrial pacemakers normal?
|
In children, elderly or athletes.
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause wandering atrial pacemaker?
|
Coronary or valvular heart disease.
|
|
|
What are the drugs that can cause wandering atrial pacemaker?
|
Digitalis toxicity
|
|
|
What is the Tx for wandering atrial pacemaker?
|
Resolve/eliminate underlying trigger
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
Wandering atrial pacemaker
|
|
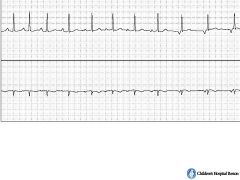
What type of rhythm is this?
|
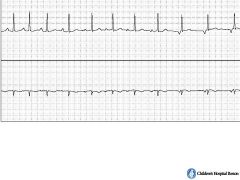
Wandering atrial pacemaker
|
|
|
The key characteristics of this are early ectopic beat originating outside of SA node, and it can originate from one or several ectopic sites.
|
Premature Atrial Complexes
|
|
|
What are the cardiac causes of PAC?
|
Coronary or valvular heart dz, pulmonary dz.
|
|
|
What drugs cause PAC?
|
digitalis
|
|
|
Respiratory failure, hypoxia, electrolyte imbalances, infection, caffeine, tobacco or alcohol use, anxiety, fatigue or fever all can cause what dysrhythmia?
|
PAC
|
|
|
What is the tx for PAC?
|
Resolve/eliminate underlying trigger
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
PAC
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
PAC
|
|
|
This is characterized by regular rhythm, arises from one atrial pacemaker site, faster than SA node, P can be hard to see, HR 150-250.
|
Atrial tachycardia
|
|
|
Atrial tachycardia can occur at what age?
|
It can occur at any age.
|
|
|
What sinus node disease can cause atrial tachycardia?
|
Sick sinus syndrome
|
|
|
What cardiac d/o can cause atrial tachycardia?
|
MI, cardiomyopathy, congenital anomalies, Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, valvular heart dz, HTN, cor pulmonale
|
|
|
What drugs can cause atrial tachycardia?
|
Digitalis toxicity
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of atrial tachycardia?
|
Digitalis toxicity
|
|
|
This is another cause other than cardiac d/o or drugs that can cause atrial tachycardia?
|
Hyperthyroidism
|
|
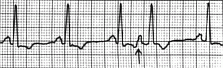
What type of rhythm is this?
|
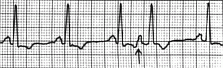
PAC
|
|
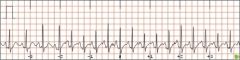
What type of rhythm is this?
|
Atrial tachycardia
|
|
|
This is characterized by irregular rhythm, at least 3 different P wave configurations origionating from the SA node, atria and/or AV junction (can be as often as ever beat), HR 120-150.
|
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
|
|
|
What are the causes of multifocal atrial tachycardia?
|
Advanced COPD, CHF, acute mitral regurgitation.
Advanced COPD = 99% of cases |
|
|
If HR is normal, and you see MAT, what does this mean?
|
Wandering Pacemaker
|
|
|
What is MAT sometimes mistaken as?
|
Atrial Fib.
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
|
|
|
The key characteristics for this are an atrial rate 250-350, P waves blend together into saw tooth or picket fence pattern. Not every atrial impulse is conducted to ventricles.
|
Atrial Flutter
|
|
|
What is the mechanism for atrial flutter?
|
Reentry and increased automaticity
|
|
|
Enlarged atria, elevated atrial pressure post cardiac surgery, severe mitral valve dz, cardiomyopathy, pericarditis, myocarditis, CHF and AMI are all cardiac d/o that cause?
|
Atrial Flutter
|
|
|
COPD, hypoxia, digitalis toxicity, hyperthyroidism, infection, catecholamine release during exercise, in healthy person with excessive coffee, EtOH, tobacco use or person fatigued or under stress are all causes for what?
|
Atrial Flutter
|
|
|
This is characterized by atrial rate of over 350, chaotic asynchronous impulses from multiple areas in atria, atria quiver instead of contract, AV conducts impulses only sporadic and irregularly.
|
Atrial Fibrillations
|
|
|
Atrial quiver increases the risk of what?
|
Thrombi
|
|
|
This can lead to heart failure, angina or syncope.
|
Increased ventricular rate
|
|
|
This is the most common atrial tachycardia?
|
Atrial fibrillations
|
|
|
What cardiac d/o cause atrial fibrillations?
|
CHF, CAD, AMI, pericarditis
|
|
|
What are the non cardiac causes of atrial fibrillations?
|
RA, chest trauma
|
|
|
This can occur after exercise, excessive caffeine, EtOH or tobacco, fatigue, stress, digitalis toxicity.
|
Atrial fibrillations
|
|
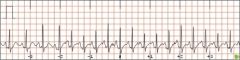
What type of rhythm is this?
|
Atrial Fibrillation
|
|
|
These are rhythms that originate around the AV node and bundle of HIS. This is when an impuse is generated due to the SA node failing.
|
Junctional dysrhythmias
|
|
|
What are the common causes of junctional dysrhythmia?
|
Hypoxia, ischemia, MI and drug toxicity
|
|
|
Impulses from AV junction create retrograde depolarization of atria because of its location due to what three things?
|
P wave is inverted with short PR interval
P wave not seen (buried in QRS) Follows QRS complex |
|
|
In junctional dysrhythmias ventricles depolarize normally. QRS complexes are?
|
Within normal limits .06-.12 seconds
|
|
|
What are the four junctional dysrhythmias?
|
Premature Junctional Complex
Junctional Escape Rhythm Accelerated Junctional Rhythm Junctional Tachycardia |
|
|
This is characterized by single early electrical impulse origionating in the AV junction, occurs before next AV impulse is fired.
|
Premature Junctional Complex
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of PJC?
|
Enhanced automaticity and reentry
|
|
|
These, digoxin toxicity, excessive caffeine, inferior MI, rheumatic heart dz, AV junction swelling post cardiac surgery, are causes of what?
|
PJC's
|
|
|
More than how many PJCs per minute indicate pending trouble?
|
4-6
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
PJC
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
PJC
|
|
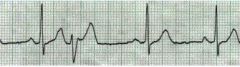
What type of rhythm is this?
|
PJC
|
|
|
These are characterized by a slow HR 40-60, inverted P that precede, are lost or follow QRS; PR interval is shorter than 0.12 seconds.
|
Junctional Escape Rhythms
|
|
|
This is a protective mechanism when higher centers in the conduction system fail to fire.
|
Escape rhythm
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause junctional escape rhythm?
|
Increased vagal tone on SA node, sick sinus syndrome, inferior MI, rheumatic heart dz
|
|
|
What drugs cause junctional escape rhythm?
|
Digitalis, Quinidine, BB, CCB
|
|
|
Post cardiac surgery and hypoxia cause what?
|
Junctional Escape Rhythm
|
|
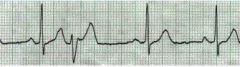
What type of rhythm is this?
|
Junctional Escape Rhythm
|
|
|
This is characterized by HR 60-100, inverted P that precede, are lost or follow QRS; PR interval shorter than <0.12 seconds.
|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause accelerated junctional rhythm?
|
Inferior or posterior MI, rheumatic fever, post open heart surgery.
|
|
|
What drugs cause accelerated junctional rhythm?
|
Digoxin
|
|
|
Decreased K and COPD can cause what?
|
Accelerated junctional rhythm
|
|
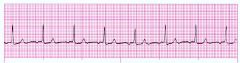
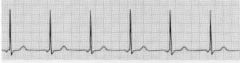
What type of rhythm is this?
|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
|
|
|
This is characterized by HR 100-180, inverted P that precede, are lost or follow QRS, PR Interval shorter than <0.12 seconds.
|
Junctional Tachycardia
|
|
|
With HR > 150 it is hard to distinguish junctional tachycardia from what?
|
atrial tachycardia
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o causes of junctional tachycardia?
|
Inferior or posterior MI, rheumatic fever, post open heart surgery
|
|
|
What drugs cause junctional tachycardia?
|
Digoxin, particularly in presence of decreased K.
|
|
|
Excessive catecholamine administration, anxiety, hypoxia, electrolyte imbalance, espescially decreased Potassium, are causes of what?
|
Junctional Tachycardia
|
|
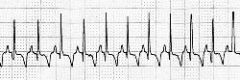
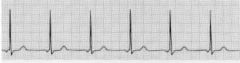
What type of rhythm is this?
|
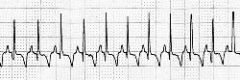
Junctional Tachycardia
|
|
|
These originate in the ventricle below the bundle of HIS. It may be benign or life threatening. Occurs when both the atria and AV junctional pacemakers are unable to initiate an electrical impulse.
|
Ventricular Dysrhythmias
|
|
|
What are the four types of ventricular dysrhythmias?
|
Premature ventricular complexes
Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation Asystole |
|
|
This is characterized by early ectopic beat originating from an irritable focus in ventricle, usually benign.
|
Premature Ventricular Complexes
|
|
|
What is the mechanism for PVC?
|
Enhanced automaticity or reentry
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause PVC?
|
MI, enlarged ventricles, CHF, myocarditis
|
|
|
Cocaine, amphetamines, tricyclic antidepressants, EtOH, caffeine, tobacco, PCP, epinephrine, isoproterenol cause what?
|
Drugs that can cause PVC
|
|
|
Hypoxia, electrolyte imbalance (decreased K, increased K, decreased Mg, decreased Ca), metabolic acidosis, increased sympathetic stimulation all cause what?
|
PVC
|
|
|
When is Tx needed for PVC?
|
Intervention needed if >3 consecutive PVCs
|
|
|
What type of rhythm is this?
|
PVC
|
|
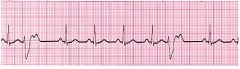
What type of rhythm is this?
|
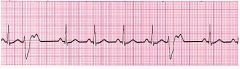
PVC
|
|
|
This is the distance between the normal beats before and after the premature ventricular contraction is equal to twice the normal cycle length.
|
Full compensatory pause.
|
|
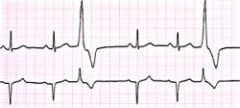
What is this?
|
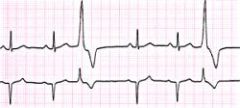
Full compensatory pause
|
|
|
The characteristics of this are HR 100-250, made up of more than 3 PVCs, often precedes ventricular fibrillation and sudden death.
|
Ventricular Tachycardia
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause V tach?
|
MI, CAD, valvular heart dz, CHF, cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
Digitalis, triglyceride antidepressants, cocaine amphetamines cause what?
|
V tach
|
|
|
Electrolyte imbalance (decreased K), acid base imbalance, trauma, EtOH, caffeine and tobacco can cause what?
|
V tach
|
|
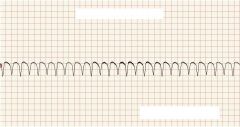
What type of rhythm is this?
|
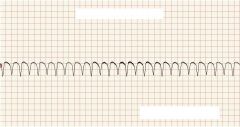
V Tach
|
|
|
This is known as "twisting of the points", it is a unique variant of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. The QRS complexes gradually alternate between upright and downward deflection.
|
Torsades de pointes
|
|
|
What is the Tx for Torsades de pointes?
|
Magnesium Sulfate, if pt is in cardiac arrest the pt needs immediate defibrillation.
|
|
|
Torsades de pointes is considered a _____ rhythm?
|
regular
|
|

What type of rhythm is this?
|

Torsades de pointes
|
|
|
This is characterized by HR 300-500, chaotic firing in ventricles, ventricles quiver (bag of worms), no effective muscular contraction, no cardiac output leads to death if not defibrillation.
|
V Fib
|
|
|
What are the cardiac d/o that cause V fib?
|
MI, untreated ventricular tachycardia, underlying heart dz
|
|
|
Acid base imbalance, electric shock, severe hypothermia, electrolyte imbalance (decrease K, increase K, increase Ca) can cause what?
|
V Fib
|
|
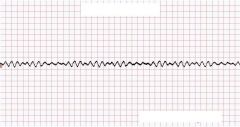
What is this?
|
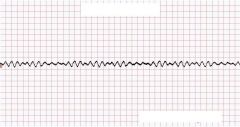
V Fib
|
|
|
This is characterized by an absence of cardiac activity, no cardiac output.
|
Asystole
|
|
|
This can be caused by MI, underlying heart dz.
|
Asystole
|
|
|
Severe uncontrolled acid base imbalance, electrical shock, electrolyte imbalance esp increased K, massive PE, prolonged hypoxemia, drug intoxication (ie cocaine overdose) can cause?
|
Asystole
|

