![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
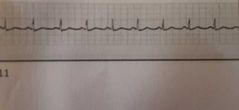
|
NSR= normal sinus rhythm- R to R interval regular rate 60-100 bpm, PR interval consistent 12 & .20 secs, QRS duration consistent .06 & .10 secs |
|
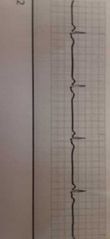
|
Sinus bradycardia- R to R interval regular with less then 60 bpm, PR interval consistent. .12-.20 secs, QRS duration consistent .06-.10 secs |
|
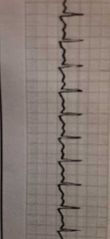
|
Sinus tachycardia- Rhythm more than 100 bpm, PR interval consistent .12-.20 secs, QRS consistent .06-.10 secs |
|
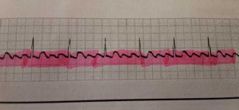
|
Atrial flutter ( A flutter)- R to R regular rhythm rate varies, PR interval not identifiable, QRS interval .06 -.10, (easily identified by P wave saw tooth formation) |
|
|
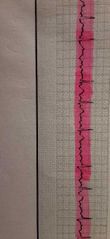
Atrial fibrillation (A fib)- irregular rhythm (notice the R to R interval), P wave configuration cannot be identified, PR interval cannot be identified, New onset of A-Fib can be indicative of a CVA (stroke) or MI (myocardial infarction) immediate notification to Dr is neccessary. |
|

|
Supraventricular Dysrhythmias (SVT)- R to R interval usually regular, P wave if identifiable usually regular, ventricular rate is 150-300 bpm, PR interval usually unable to determine. Similar to sinus tachycardia but PR interval cannot be identified usually. |
|

|
3rd Degree Heart Block (Complete Heart Block)- all electrical impulses originating above the ventricles are blocked, no correlation exists between atria and ventricle depolarization . Easily identified as it is the only one that is upside down on the exam. |
|

|
Ventricular Tachycardia (Vtach)- 3 or more PVCs occur in a row, ventricles are in a continuous state of contraction-relaxation, atrial rate cannot be determined. Ventricular rate is 100-200 bpm |
|

|
Ventricular Fibrillation (Vfib)- rhythm P-P interval cannot be determined, R to R interval if able to determine will be irregular, atrial rate cannot be determined, ventricular rate if identifiable will be greater than 300bpm (AED might needed) |
|

|
Asystole (straight line or flat line)- No electrical activity is present in the myocardium( middle layer of heart responsible for pumping action), No rates, rhythm, waves, or intervals present. |
|
|
AED= Automated external defibrillator |
A device used to shock the heart back to it's normal pumping function. |
|
|
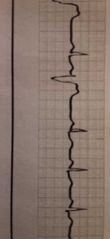
Atrial fibrillation (Afib) |
PT exhibits signs of decreased cardiac output.This condition may have no symptoms, but when symptoms do appear they include palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue, weakness, syncope, fast irregular heartbeats. AED might be needed to shock PT's heart back to normal pumping function. |
|
|
Premature ventricular contractions (PVC) |
|
|
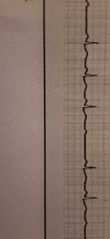
2nd degree AV block, Mobitz ll |

