![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Nabta Circle Neolithic "Megalithic Circles" |
|

|
Parietal Art of Wadi Abbad predynastic Pecking |
|

|
Gerzeh Palette predynastic |
|

|
Predynastic Pottery El Amra predynastic terracotta coil made slipped |
|

|
Painted Tomb of Nekhen Naqada II |
|
|
Two Dog Palette Naqada III Serpopards |
|

|
Gebel el-Arak Knife Naqada II Blade is flint Handle is ivory, decorated with scenes Possibly from Abydos |
|

|
Scorpion King Macehead early dynastic 3100-2920 BCE |
|

|
Min Statues of Coptos early dynastic ca. 3150 |
|

|
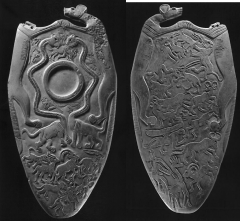
Palette of Narmer 1st dynasty ca. 3000-2920 Hierakonpolis slate low relief carved Says King Narmer’s name between cow-humanhybrids at top (serekh: name of kinginside square, symbol for palace) More commemorative function, showing scene,telling story Smitingpose: motif with hand up in air, about to bash a foe Front side -- wearing crown of Upper Egypt. Backside – wearing crown of lower Egypt organized register people at bottom may be symbolized as cities,king taking over cities serpopards may show upper and lower Egypt –intertwined symbolizes unification |
|
|
Tomb of Queen Merneith
1st dynasty ca 2900 Abydos brick Queen regent – served as queen while son was tooyoung Rounded stelai |
|

|
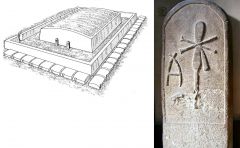
Stele of Peribsen
2nd dynasty Abydos Heresy – descending from normal |
|

|
Seated Statue of Khasekhemwy 2nd dynasty ca 2600 limestone Being seated = symbol for power Crown of upper Egypt Departure from earlier works in that it’s farmore elaborate, larger, well-carved, more naturalistic Bottom has engraved symbols depicting corpses |
|
|
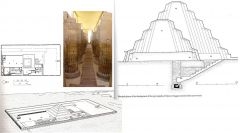
Mortuary Complex of Djoser 3rd dynasty Saqqara ca 2630-2611 Imhotep was architect Architectural innovations – pyramids inspired bythis Retaining wall surrounds – only one entrance,many false entrances Modeled on palace architecture – physical formof serekh Entrance mirrors palace structure – long, dark,narrow corridor – walking towards light Engaged column: column that juts out, notfree-standing; almost like in relief
|
|

|
Seated Statue of Djoser from serdab of Stepped Pyramid of Djoser 3rd dynasty painted limestone Long beard – emblematic of kingship Wrapped in cloak, pulls to chest – Sed Festival: ceremony every 30 yearscelebrating reign Inscription on base mentions Imhotep |
|

|
Limestone Relief of Djoser 3rd dynasty in Mortuary Complex of Djoser Saqqara Was sceptre Engravings of Djoser running |
|

|
Bent Pyramid of Sneferu at Darshur 4th dynasty, Old kingdom ca 2615 Valley temple Relief sculpture – women carrying ankhs, gravegoods, food; names above them – personifications (meant to represent nobilitiesin upper Egypt) Tender moment between lion-headed goddess and ahuman – he has a special relationship with them – to be tender with humanswould show weakness and show he is not a god |
|

|
Pyramids of Giza Menkaure, Khafre, and Khufu 4th Dynasty, Old Kingdom |
|

|
Great Sphinx 4th dynasty, Old Kingdom ca 2550 near Khafre's pyramid older than Khafre’s complex Partially carved from bedrock Sphinx – guards, turn away evil, protector Face of a pharaoh |
|

|
Seated Statue of Khafre Valley Temple of Khafre, pillared hall 4th dynasty ca 2550 Imported stone deliberately chosen for color In plain pillared hall Hawk behind him (Horus) sema tawy:hieroglyph of trachea entwined with papyrus and lily – unification with upperand lower Egypt, allusion to Pharaoh’s power over those areas |
|

|
Menkaure and Khamerenebty Valley Temple of Menkaure 4th dynasty, Old Kingdom ca 2520 slate Wife has physical characteristics of goddesses –suggesting she has a divine component like the pharaoh |
|

|
Pyramid Complex of Sahure 5th dynasty, old kingdom ca 2513-2506 Abusir Standardized pyramid More pyramid texts than previous pyramids |
|

|
The Solar Temple of Niuserre Abu Ghurob 5th dynasty, old kingdom ca 2420 Possible funerary purposes – similarities withtombs Built for god altars outdoors |
|

|
Lion-Headed Goddess Suckling Niuserre from sun temple of Niuserre at Abu Ghurob 5th dynasty, old kingdom ca 2420 |
|

|
Seated Statue of Pepy I Calcite 6th dynasty Ca 2300 BCE Sema tawy symbol on throne Symbols of Osiris’s power Horus reinforcing divine right to rule Idealized, static, rigid Crook and flail – agricultural? Pastoral? Beinggood shepherd |
|

|
Bronze Statues of Pepy I in temple of Hierakonpolis 6th dynasty ca 2320 Sphyrelaton:hammering metal around wood cores to make hollow before lost wax casting methodwas found |
|

|
Seated Statue of Pepy II and Mother 6th dynasty ca 2230 Son of Pepy I Nemes headdress with Uraeus coming out of it smaller pharaoh being held by mother because hewas too young possibly Mother was queen regent Tender but not as tender as moments betweenpharaohs and gods/goddesses |
|

|
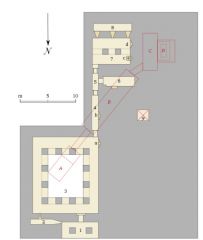
Hippo Hunting, Tomb of Ti 6th dynasty ca 2400 Activity person wanted to participate in –hunting for sport Hippos related to Seth, divine but dark side Ti – wealthy friend of king |
|
|
Tomb of Ti Saqqara 6th dynasty mastaba: Emulation/copying of royalty, flat-roofed, sloping, made of mud brick |
|

|
Seated Scribe 4th dynasty, old kingdom ca 2649-2513 painted limestone Less idealized – more naturalistic – sitting onground |
|

|
Stele of Maaty 11th dynasty Thebes 2051-2030 carved limestone Offering table, detailed collar, some anatomypresent to show fat rolls scribe |
|

|
Stele of Wahankh Inyotef II 11th dynasty Thebes funerary complex of king 2108-2059 presents beer and milk to Ra-Atum and Hathor with song Narrative, recording of how ceremony was done Deep relief, emphasis of outline Old kingdom rigidity, stance |
|

|
Stele of Tjetji 11th dynasty Thebes 2112-2055 BCE Folds in body to show weight or old age |
|

|
Woman from Tomb of Tjetji 11th dynasty Thebes 2112-2055 BCE |
|
|
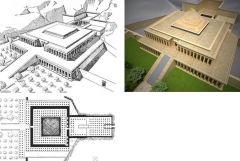
Mortuary Temple of Nebhepetre Mentuhotep 11th Dynasty, Middle Kingdom Deir el-Bahri Hypostyle halls: super column halls, tons ofcolumns Rock cut tomb – cut into bedrock of mountain Functioning like old kingdom tombs but looksdifferent Above ground but feels like its underground |
|

|
Sandstone Statues of Mentuhotep from Ambulatory of Mortuary Temple 11th Dynasty, Middle Kingdom Deir el-Bahri post-reunification style: Stocky Smaller, de-emphasized eyes Long beard Simple clothing Old Kingdom carryovers |
|

|
Paintings from Inner Area of Mortuary Templeof Mentuhotep 11th dynasty, middle kingdom Deir el-Bahri God Montu embracing King Montuhotep I Red crown of lower Egypt Transitional style, moving away frompre-unification Theban style God Montu: falcon god personification of desert,war, devastation from Ra Aten: disk symbol of Ra |
|
|
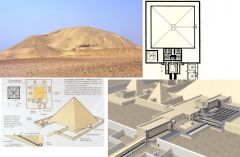
Funerary Complex of Senwosret I Lisht 12th dynasty, Middle Kingdom Looks like pyramids of 6th dynasty |
|

|
Chapel of Senwosret at Karnak 12th dynasty ca 1950 blocks reused in new kingdom buildings carved limestone mostly raised relief but similar style to other relief decoration from the period of Senwosret |
|

|
Stele of Userwer 12th dynasty Grid system, unfinished |

