![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is osteoarthitis |
Heterogenous group of disorders with similar pathological and radiological features Characterised by loss of articular cartilage but affects all joint tissues |
|
|
How do you classify osteoarthritis |
Primary = localised and generalised (often postmenopausal women w/ Heberden's nodes) Secondary = congenital disorders, trauma, Paget's disease, inflammatory joint disease, avascular necrosis |
|
|
Symptoms and signs of OA |
Pain - worse on use of joint Stiffness - mild in morning, severe after immobility Loss of movement Pain on movement / restricted range Tenderness (articular or periarticular) Bony swelling Soft tissue swelling Joint crepitus |
|
|
Normal bone vs osteoarthritic bone |
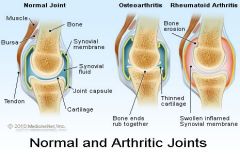
Thickened capsule Cyst formation and sclerosis in subchondral bone Shelving fibrillated cartilage osteopytic lipping synovial hypertrophy altered contour of bone |
|
|
Radiological features of OA |
Narrowing of joint space Osteophytosis Altered bone contour Bone sclerosis and cysts Periarticular calcification Soft tissue swelling |
|
|
Compare distribution of OA and RA |
OA = DIP and PIP RA = MCP, PIP, carpal bones, spares DIP |
|
|
Compare swelling of OA and RA |
Bony swelling (OA) vs soft tissue swelling (RA) |
|
|
Compare stiffness of OA and RA |
Limited stiffness (OA) and stiffness prominent (RA) |
|
|
Epidemiology of osteoarthritis |
Spine > DIPJ > knee > hip prevalance of OA increases w/ age at all sites majority of people with OA related disability are middle aged or young elderly |
|
|
Risk factors for knee osteoarthritis |
Age Gender Genetics Obesity Knee injury Occupational Heavy physical exercise Previous RA Chondrocalcinosis |
|
|
What is the vicious cycle of OA |
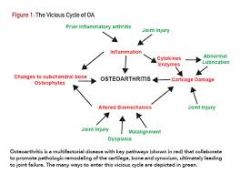
|
|
|
Name some age related changes in matrix molecule metabolism |
Decrease in type II collagen turnover and aggrecan turnover Accumulation of glycation end products, cleavage products of matrix molecules eg fibronectin ,decrease in antioxidant defences |
|
|
Chondrocyte cellular senescence |
Mitotic activity decreases Increase in B galactosidase Increase in epigenetic hypermethylation Decrease in telomere length |
|
|
Treatment of OA |
treat symptoms Reduce pain and stiffness, maintain joint mobility, reduce handicap, improve HRQL, limit progression of joint damage, educate patients about nature of OA and its management |
|
|
Definition of osteoporosis |
A systemic skeletal disease, characterised by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase in bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture |
|
|
name three common sites for osteoporotic fractures |
wrist fracture spine fracture hip fracture |
|
|
Presentation of osteoporosis |
Back pain Thoracic kyphosis Loss of height
|
|
|
Causes of age related bone loss |
Decrease in bone formation Increase in bone resorption Increase in sensitivity to PTH and hydroxy vitamin D in absence of oestrogens |

