![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hormone |
chemical produced in one tissue that has an effect on other (usually distant) tissues (generally by circulating in the bloodstream) |
|
|
gland |
tissue specialized to secrete substances |
|
|
endocrine gland |
glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream |
|
|
feedback loop |
system by which a process or substance in the body is in the body is initiated, stopped, or produced based on the detected level of another substance or process |
|
|
Peptide |
proteins, polypeptides, amino acids -water-soluble hormones do not enter the cell -blind to cell-surface receptors and initiate cascade of chemical reactions resulting in changes in cell metabolism (something turned on or off, ex. production of enzyme) |
|
|
action of peptide hormones |
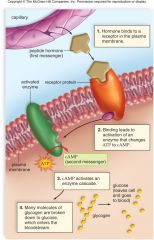
|
|
|
steroid hormones |
-lipids -water-INsoluble hormones diffuse into the cell -binds to receptor in the cytoplasm or nucleus -recepor-hormone complex binds to DNA and initiates transcription followed by translation -new protein(enzymes) are synthesized |
|
|
action of steroid hormones |
made from cholesterol cortisol(synthetic form is cortisone) testosterone estrogen progesterone
steriods act more slowly than peptide hormones |
|
|
organs of the endocrine system |
hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland parathyroid gland thyroid gland thymus liver adrenal gland kidney pancreas ovary placenta testis |
|
|
hypothalamus and pituitary functions |
regulate most other endocrine organs and are sometimes referred to a master gland of the endocrine system |
|
|
negative feedback |
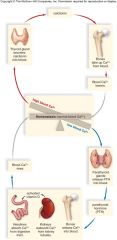
|
|
|
hormonal feedback male |
hormones LH-testoserone FSH-sperm and inhibin |
|
|
male reproduction |
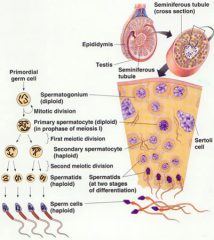
sertoli cells support spermatogenesis and secrete inhibin leydig (interstital) cell secrete testosterone |
|
|
hormal feedback female |
LH- corpus luteum to produce progesterone FSH- stimulates follicles to produce estrogen |
|
|
ovarian cycle |
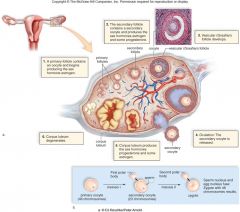
|
|
|
uterine cycle |
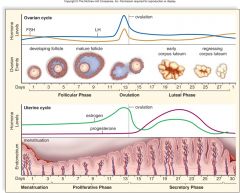
|

