![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ectoparasite
|
Class Insecta: Flies, Fleas, Lice
Class Arachnida: Ticks, Mites |
|

Order: Siphonaptera
FLEAS |
Wingless
Laterally: Flattened Head, Thorax, Abdomen 3 Paris of Legs +/- combs: Pronotal,Genal) |
|
|
Ctenocephalides spp
|
Host Spectrum: Canids, Felids, Humans, Cattle, Etc
-Host preferential rather than host specific Ctenocephalides felis: Is the most prevalent of all flea species Ctenocephalides canis: Not as common as the cat flea |
|
|
What does the adult look like?
|
The Adult:
Dark brown with a rounded head Piercing-sucking mouthparts Genal and pronotal combs -Combs look like a mustache! -Genal: on the cheek -Pronotal: on the posterior border of first segment |
|
|
What is its life cycle?
|
1) Eggs are laid on the host and fall off to enter the host's bed, favorite sleeping spot, etc: They are called "environmental hot spots"!
2) Larvae feed on dry blood, feces and other organic materials and may remain in this stage for as long as 200 days! 3) Pupal stage is the most tolerant stage and can last from 3-50 weeks as pre emergent adult, depending on the environmental conditions. 4) Pre emergent adults are stimulated to emerge by heat, carbon dioxide and movement 5) Life cycle takes an average of 18-21 days, but may take 20 months or more |
|
|
What is its pathogenesis?
|
1) Irritation: Restlessness, Biting, Scratching, Poor Hair Coat
2) Heavy infestations: Anemia 3) Flea allergy dermatitis: FAD, Flea bite hypersensitivity 4) Pruritic reaction locations: Lumbar-sacral area, abdomen, neck, inside of hind legs 5) Transmit: Acanthocheilonema reconditum and Dipylidium caninum***** |
|
|
Choices for Treatment?
|
1) Advantage: Spot on
2) Frontline: Spot on and Spray 3) Program: Tablet and Injectable 4) Vectra: Spot on 5)Biospot: OTC spot on Advantix: Spot on, ONLY IN DOGS Nex Guard: Beef flavored chewables: ONLY IN DOGS Note: Resistance is on the rise If you use "spot on" method, then the drug must GET DOWN TO THE SKIN otherwise it will not work. Treat the Host(s): All animals in the house, even if you don't think they have fleas Treat the Enviornment: Shampoo carpets, Vacuum the house, Room foggers or Exterminator, Wash pets bed frequently, Flea Traps |
|
|
Is this species a Public Health Risk?
|
This species will bite humans: Some people can be very sensitive to a flea bite
|
|

Xenopsylla cheopis
|
Host Spectrum: Rats, Humans, Squirrels, Other Mammals
Combs are absent Head is smoothly rounded Pigmented spermatheca |
|
|
What is its life cycle?
|
1) Female lays eggs on host: Eggs then drop off
2) Larvae hatch within 2-21 days 3) Three instars over 9-15 days 4) Pupate for a minimum of 1 week 5) Adults emerge and jump on host |
|
|
What is its pahthogenesis?
|
1) Annoyance
2) Vector of Yersinia pestis AKA Bubonic Plague |
|
|
Choices for Treatment?
|
Flea Control
|
|
|
Is this species a Public Health Risk?
|
SERIOUS: Still a significant problem in Asia, Africa, and South America
Endemic: Africa, India, and SW states of U.S. 3 Forms: Bubonic, Septicemic and pneumonic forms -All transferred by flea bites -Bubonic can progress to septicemic, or 30% lead directly to septicemic form -Pneumonic forms is most feared because it can be spread from person to person |
|

Order Anoplura
"Sucking Lice" |
Adults: Slate gray and wingless, Dorso-ventrally flattened, Head narrower than the thorax, Piercing sucking mouth parts
Eggs(nits): Whitish, Operculated, Attached to hairs Nymphs: Tiny replicas of the adults |
|

Haematopinus spp.
|
Hosts: H. asini: Equids
H. suis: Swine H. eurtsternus: Cattle **Are host specific Infestations Site: Skin, Hair Adults: All tarsal claws are of equal size Lateral margins of the abdomen are heavily sclerotized (Armored) |
|
|
What is its Life Cycle?
|
1) Eggs are attached to hairs, where they hatch
2) Goes through 3 nymphal stages 3) Entire life cycle is spent on the host 4) Transmission is by direct contact or by blankets, brushes, etc 5) Life cycle takes 3 -4 weeks to complete 6) LIFE STAGES: NIT --> NYMPH --> ADULT |
|
|
What is its Pathogenesis?
|
1) Often a winter time problem
2) Irritation: Scratching, Licking, Restlessness 3) Suck Blood: Loos may be mild to severe 4) Decreased weight gain, Poor hair coat 5) H. suis: May serve as vector of swine pox 6) "Louse Breeders": Some animals in a herd carry a very high population of lice -Weakened, may perish during winter |
|
|
Choices for Treatment?
|
Cattle: Organophosphates, Ivermectcin
Pigs: Organophosphates(Permerthrin, Ivermectin Horses: Ivermectin **Repeat treatment in 2-3 weeks |
|
|
Is there a Public Health Risk?
|
Some bite humans but will not complete their life cycle
|
|
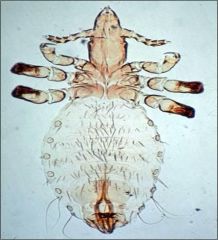
Linognathus spp
|
DH Spectrum: **L. setosus: Canids
**L. pedalis (Foot louse): Sheep L. vituli(Long Nosed Cattle Louse): Cattle L stenopsis: Goats Infestation Sites: Skin, Hair L. pedalis: Legs, Feet of sheep, where there is no wool 1st pair of tarsal claws smaller than second and third pairs Lateral margins of the abdomen NOT heavily sclerotized |
|
|
What is its Pathogenesis?
|
A winter time problem
Irritation Suck blood Severe infestations in sheep can cause lameness ****L. setosus: May serve as vector for Acanthocheilonema reconditum |
|
|
Any choices for Treatment?
|
Sheep: Organophosphates, Synthetic pyrehoids
Dogs: Organophosphates, Carbaryl |
|
|
What are Control Measures?
|
Dogs and Cats: Good nutrition with adequate Vitamin B12
Large Animals: Cull "louse breeders", Adequate nutrition, Avoid overcrowding, Avoid stress |
|
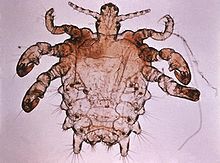
Pthirus pubis
(CRAB LOUSE) |
Hosts: Human, Occasionally dogs
Infestation Site: Coarse body hairs Pubic, perianal, armpit, mustache, beard Eyebrows and Eyelashes in Children Large tarsal claws, shorter body Looks like a crab |
|
|
What is its Life Cycle?
|
1) Life cycle requires about one month from egg to egg
2) Usually sexually transmitted, but can be transmitted by fomites( Ex: blankets, towels, bedding) |
|
|
What is its Pathogenesis?
|
Intense puritis
Papular dermatitis, with discoloration of the skin Once feeding they may stay in one spot for days |
|
|
Any choices for treatment?
|
Lindane: Cream, lotion, and shampoo
Treatment may need to be repeated in heavy infestation Launder clothes in hot water 50 degrees for 30 min |
|
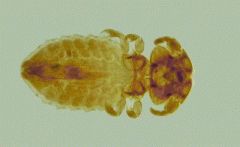
Order Mallophaga
"Chewing Lice" |
Infect birds and mammals
Sandy brown, wingless, dorsoventrally flattened Head as broad or as broader than the thorax Chewing mouthparts |
|
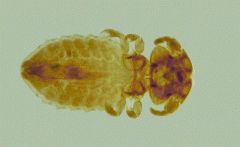
Trichodectes canis
|
Host: Dogs
Adults: Minute tarsal claws Nymphs: Are similar to adults Infestation Site: Skin, Hair |
|
|
What is its Life Cycle?
|
Same Life Cycle for Sucking Lice
|
|
|
What is its Pathogenesis?
|
A winter time problem
Scratching, licking, biting, and alopecia Blood loss Poor hair coat, loss of condition, lower milk production May be a vector for Diplydium caninum **** |
|
|
Any choices for treatment?
|
Organophosphates
Eprinomectin or Invermectin Repeat Treatment: 2-3 weeks |
|

Felicola subrostratus
|
Host: Only Louse found in Cats
Infestation Site: Skin, Hair Same as Trichodectes expect for the head -The head is shaped like a house** |
|
|
What is its Pathogenesis?
|
Winter time problem
Scratching, itching, biting, alopecia Blood loss Poor hair coat, loss of condition, lower milk production May be a vector for Dipylidium caninum *** |
|
|
Any choices for Treatment?
|
Organophosphates
Carbaryl containing shampoos Repeat treatment in 2-3 weeks |

