![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Autotroph |
An organism that makes its own food. |
|

Heterotroph |
An organism that depends on something else to get their food. |
|

Photosynthesis |
The process that occurs within autotrophs and converts sunlight into glucose or energy. |
|

Consumers |
They use up glucose when eating plants. They wat other heterotrophs. |
|

Law of Conservation of Energy |
Says that energy is neither created or destroyed. Consumers transfer energy back into the enviornment after cellular respiration as heat. |
|
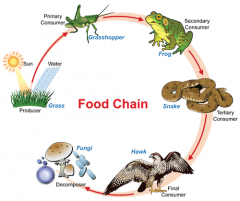
Food Chain |
The simplest path that energy takes through an ecosystem. |
|
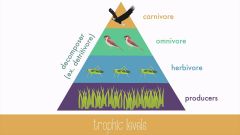
Trophic Level |
An organism's feeding level. |
|

Producers |
(First trophic level) They are autotrophs and contain the most amount of energy in an ecosystem. |
|

Primary Consumers |
(Herbivores) Typically eat plants. |
|

Secondary Consumers |
Kwown as carnivores and omnivores. |
|

Consumers |
(Secondary consumers.) Include carnivores and herbivores. |
|

Carnivores |
(Secondary Consumers) A heterotroph that eats other heterotrophs. |
|

Omnivores |
(Secondary Consumers) A heterotroph that eats both autotrophs and heterotrophs. |
|

Decomposers |
A heterotroph that breaks down material. |
|

Herbivores |
(Primary Consumers) A heterotroph that only eat autotrophs (plants). |
|
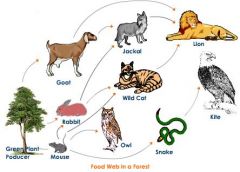
Food Web |
Represents the many interconnected food chains describing the various paths energy takes. |
|
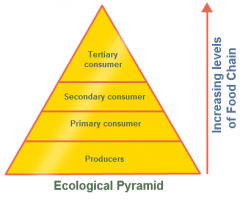
Ecological Pyramid |
Represents how energy is consumed as you go through the fod chain. As you move up, each trophic level can only support so many species in an ecosystem. |
|
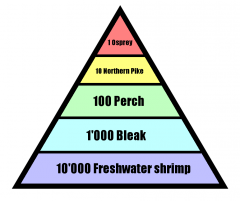
Number Pyramid |
Represents the number of organisms in a trophic level. The autotrophs are at the bottom and the heterotrophs are at the top. |
|
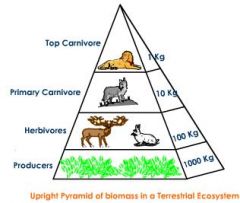
Biomass Pyramid |
Represents the total mass of organisms available at each level. (Not energy, mass.) |
|

Glucose |
Sugars. |

