![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Abiotic |
Non-living things (physical environment) |
|
|
Aeration |
is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or substance. |
|
|
adaptation |
Is any genetic trait that improves an organism’s chance of survival (and to reproduce) Adaptations: Camouflage Mimicry-prey species ( have colourings/markings that look like other predators) Opposable thumbs Sonar |
|
|
biodegration |
the decay process that makes the nutrients contained in waste and dead matter available to producers once again |
|
|
biome |
Distribution of organisms. Basically-the distribution of life in biosphere is largely determined by 2 factors: Average temperature, Average precipitation *called climate. Climate depends on Latitude and elevation |
|
|
biotic |
Living things (organisms |
|
|
community |
all of the different populations in a particular area that interact with one another; the third level of organization |
|
|
carbon cycle |
the cycling of carbon through ecosystems |
|
|
commensalism |
one organism benefits and the other is unaffected. Eg: fish on shark, barnacles on whales |
|
|
denitrification |
the process that converts ammonia and nitrate back to nitrogen gas |
|
|
ecological succession |
a gradual change in the types of plants that represent the structure of a community |
|
|
ecosystem |
includes the living community as well as the physical environment in which the organisms live;the fourth and most complex level of organization |
|
|
food chain |
a representation of the pathway taken by nutrients and energy through the trophic levels of ecosystems |
|
|
food pyramids |
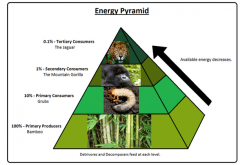
Animals at the top of food chain/web require the least amount of prey because of how energy flows through food chains. *The blocks represent amount of energy available at each level. Often only 10% of energy is transferred from one level to the next. |
|
|
keystone species |
A species whose presence plays a vital role in sustaining the health of an ecosystem. If these keystone species are eliminated the whole ecosystem collapses. |
|
|
mutualism |
both organisms benefit. Eg: bird and hippo, human and bacteria |
|
|
nitrification |
the process that produces nitrate from ammonium |
|
|
natural selection |
Is a process that favours the survival of organisms with traits that make them better adapted to the environment. |
|
|
parasitism |
one organism benefits at the other’s expense: tape worm and animal |
|
|
phosphorus cycle |
the path of phosphorus through ecosystems
|
|
|
photosynthesis |
the process whereby plants use the suns energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen |
|
|
predation |
hunts/captures its food-consumer |
|
|
symbiosis |
a specialized form of integration between 2 different species; often, each species develops very specialized behaviours, life cycles, or structures; includes mutualism, commensalism and parasitism |
|
|
trophic levels |
a category of living things thatt describes the position of and organism in relation to the order of nutrient and energy transfers in an ecosystem; the first trophic level contains autotrophs and each higher level contains heterotrophs. |
|
|
Biodiversity |
The variety of organisms in a given ecosystem. A large biodiversity indicates a healthy ecosystem-complex and diverse. These healthy ecosystems have high primary productivity (amount of available energy by producers) |
|
|
extirpation |
Local extinction of a species in an area. They still exist elsewhere. |
|
|
bioaccumulation |
This is the process in which substances ( toxic,organic chemicals) accumulate (increase in concentration) moving up a food chain.Eg: Organic mercury in Minamata, Japan |
|
|
niche |
an overall role of an organism in a community-taking account of biotic and abiotic factors. Organisms cannot share the same niche. They can be in the same habitat. |
|
|
Competition |
when niches overlap and organisms compete for resources |
|
|
adaptive radiation |
when species adapt differently to changes in the environment. They become ultra specialized, so have a very specific niche. Become ultra-specialized , so they have a very specific niche. Eg: finches in the Galapagos |
|
|
foreign species |
Often out-compete native species. Often they have no natural predators): Eg american bullfrogs, scotch broom. |
|
|
climax community |
final habitat. It is the most complex and stable ecosystem |
|
|
primary succession |
Primary succession starts from barren/bare rock-no soil |
|
|
secondary succession |
starts when a climax community has been devastated (eg volcanic eruptions, forest fires |
|
|
detrivore |
(eg: worms): organisms that feed on waste products/materials (feces, dead plants etc). Aka decomposers because they break complex molecules into more simple molecules. |
|
|
levels of organizations |
1st Level: organism-how does one particular organism survive in its habitat (behaviour, adaptations, functions etc..) 2nd Level: population-how does a group of same organisms survive in a habitat 3rd Level: community- how different populations interact 4th Level- ecosystems- includes living community and physical environment5th Level- biosphere- total area of Earth where living things are found |

