![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Ecosytem |
All the organisms living in a community plus all the non-living (abiotic) conditions in the area in which they live |
|

Community |
A group of interacting populations of different species living in the same place at the same time |
|

Population |
A group of organisms from the same species found in the same area at the same time and potentially able to interbreed |
|

Habitat |
The environment in which an organism or population of organisms usually lives |
|
Biotic |
The living features of an ecosystem for example the presence of predators or food |
|
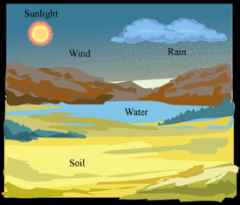
Abiotic |
The non-living features of an ecosytem |
|

Niche |
The role of a species within its habitat. e.g what it eats, where it feeds, when it feeds |
|
Adaptation |
The feature that members of a species have that increases their chance of survival and reproduction |
|
Describe the process of natural selcetion |
Organisms with better adaptations are more likely to survive and pass on the advantageous alleles to the next generation. Over many generations the advantageous allele increases in frequency in a population and the adaptation becomes more common |
|
|
What factors are organisms adapted to in their environment? |
Abiotic and biotic factors |
|

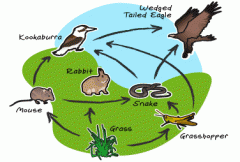
Give examples of biotic factors |
presence of predators, competition (interspecific and intraspecific), presence of food |
|
|
Why might it look like two organisms are occupying the same niche? |
two species could be eaten by the same predator but eat a variety of different organisms, one of the species could be nocturnal |
|
What are the biotic interactions of an organism? |
living interactions, what an organism eats, what it is eaten by, disease, competition |
|

What are the abiotic interactions of an organism? |
The non-living interactions, the temperature range that an organism can live in or the time of day when an organism is active |
|

What is competitive exclusion? |
If two species try to occupy the same niche they will be in competition with one another. One species will eventually be more successful than the other and only one species will be left. |
|
|
Population Size |
the total number of organisms of one species in a habitat |
|

Carrying capacity |
The maximum population size that can remain sustainable in an ecosystem |
|
|
As a result of what does the carrying capacity vary? |
abiotic and biotic factors |
|

What happens to population size if abiotic factors such as temperature, water availability, space availability, light intensity and chemical composition of their surroundings are unfavourable? |
The organisms will grow more slowly and in some scenarios the population size can decrease |
|

What is interspecific competition? |
Competition that occurs between different species |
|
|
What does the competitive exclusion principle state? |
No two species can occupy the same ecological niche |
|
|
Why will the population size decrease if there is interspecific competition for same food/ habitat resource? |
The species have to share the fame food so there will be less available for both species so there will be less energy available for growth and reproduction |
|

Why is the fluctuations in population size around the carrying capacity? |
Intraspecific competition, when there are more food resources available the population size grows as more energy for growth and reproduction. However large population means resources are used up quickly and less energy for growth and reproduction, population size decreases. |
|
|
What is the carrying capacity always between? |
The lowest population size and the largest population size |
|
|
What is intraspecific competition? |
Competition occurring between members of the same species |
|

What is Predation? |
Where an organism kills and eats another organism |
|

Why are the population sizes of predator and prey interlinked? |
As the population of one changes it causes a changes the change in the other. If the population of the prey increases there is more food available to the predator, however if the population of predator increases population of prey decreases, so population of predator will also decrease |
|
|
What does the predator -prey relationship create? |
Selection pressure |
|

What is selection pressure? |
Those members of the species who are better adapted to escape or hide from predators are more likely to be able to survive and reproduce. It is a factor in an ecosystem that limits the population size. |
|
|
Why is selection pressure useful? |
This ensures each new population is better adapted for survival |
|
|
If a population decrease in an organism is due to decreased food availability, what could the decrease in population be accelerated by? |
Predation |
|
How can the fact that microoragainsms will grow at a steady rate with enough food and space be investigated? |
Growing bacteria a liquid broth and measuring light absorbency at regular time intervals |
|
|
What is a broth culture? |
a liquid containing bacteria |
|
|
What machine can measure light passing through a sample of culture and produce an absorbance value? |

Spectrophotometer (colorimeter) |
|
|
What does a high absorbance value suggest? |
A high number of bacteria as the more bacteria presence the more light absorbed |
|
|
What is a liquid broth? |
a liquid containing nutrients the bacteria need to grow |
|
|
Why is light scattered when it passes through a broth culture? |
Because bacteria are present |
|
|
What graph is produced when looking at the steady growth rate of bacteria and why? |
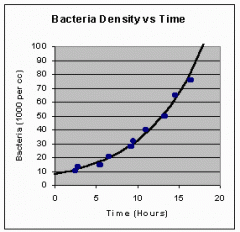
exponential, as the bacteria double over certain time intervals |
|
|
On a log graph if the y axis reads 3.02 how do you calculate how many bacteria are present? |
=log³·º² |
|

What are McCartney bottles? |
Strong clear glass bottle with wide mouth and aluminium screw cap with rubber liner. Bacteria. |
|
|
Why is the neck of the McCartney bottle flamed with a bunsen burner? |
To prevent contamination and infection |
|

How can abundance be measured? |
Frequency-the number of samples a species is recorded in or percentage cover- how much of the area you are investigating is covered by the species |
|
|
Which species can percentage cover only be used for? |

Non motile or slow moving species |
|
|
How can populations be investigated? |
By looking at abundance and distribution of populations |
|
|
What is abundance? |
The number of individuals of one species in a particular area |
|

What is distribution? |
How a species is spread across a habitat. A species could be evenly spread throughout the whole habitat, they could favour a specific area within an ecosystem or they could be randomly spread. |
|
|
Why is randomly sampling useful? |
It is representative data (not biased) that can be calculated in a reasonable time scale |
|
|
How does reliability increase with sample size |
The larger the sample size the more reliable the data |
|

Describe 5 steps in random sampling. |
1. Split an area into coordinates 2. Use a random number generator to generate coordinates on a grid 3.Use appropriate sampling technique 4. Take as many samples as possible (minimum 15) 5. Carry out statistical analysis on data collected for example percentage cover or mean |
|

What can a quadrat be used to find? |
Species frequency Number of individuals (in each quadrat) Percentage cover |
|
|
What is species frequency? |
The likelihood of a particular species occuring within a quadrat |
|
|
What is percentage cover? |
count the number of square in the quadrat covered by a species (include if a square is covered more than half) |
|
|
How is a quadrat useful for analysis over a long period? |
They can be left in the same place to analyse repeatedly |
|
|
Describe a quadrat |
A square frame divided into to smaller square using strings attached to outer frame |
|
|
What methods can be used investigate non-motile/ slow moving populations? |
quadrats, transects |
|
|
When are transects more useful than quadrats? |
When there are changes in abiotic factors across an area |
|
|
What is a belt transect? |
quadrats placed next to each other along a linhe of study |
|
|
What can belt transects be used to investigate? |
species frequency and percentage cover |
|
|
What is an interrupted belt transect? |
Place quadrats at regular intervals along line of study, for example 1m apart |
|
|
Give examples of investigating motile species |
nets, traps, sweep nets, pitfall traps |
|
|
Describe mark release recapture method |
Capturing an individual of a species, harmlessly marking them so they can be easily identified again and then releasing them again. A second sample can be taken when it is certain the first has had time to mix with non -marked population |
|
|
What assumptions does mark-release-recapture method make? |
1. The marked sample has had enough time and opportunity to mix with non marked population 2. The marking hasnt affected the individuals chance of survival 3. The mark is still visible 4. There are no changes in population size |
|
|
Why may there be changes in population size |
births,deaths, migration |
|
|
What are disadvantages of mark release recapture |
ethical issues, stress after recapture, might be more likely to be caught again |
|
|
What is the equation to wotk out population size from mark release recapture method |
= No. in first sample x no. in second sample/ no. marked in 2nd sample |

