![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is economics |
The study of people and the choices they make in a world of scarcity |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Understanding economics requires? what is objective thinking? |
Objective thinking. Not influenced by personal feelings, interpretations, or prejudice |
|
|
|
Feelings and emotions are generally...? and have no...? |
irrational and have no intelligence |
|
|
|
many of our preconceptions about things are wrong true or false? |
True |
|
|
|
We tend to think we know more than we actually know true of false? |
True |
|
|
|
We are all ignorant. it's simply a matter of ...? |
degree |
|
|
|
What does the work "scarce" mean? |
Anything that has a positive price is scarce. A thing is said to be "scarce" if, at a zero price, less is available than is desired - thus the positive price |
|
|
|
Economists classify resources into 4 basic groups name all 4 and what they entail and give an example for each |
Land: All natural resources, or gifts of nature Labor: The physical and mental effort of workers Capital: Physical Capital - the man-made things that are used to product other things (tools, machinery, instruments, buildings) Human Capital - the know how Entrepreneurial Abilities: The human resource that organizes labor, land, and capital |
There is actually 5 |
|
|
what does an entrepreneur do? |
1)Entrepreneurs come up with new ideas about what and how to produce. 2) Entrepreneurs come up with new ways to run businesses. 3) Entrepreneurs are the risk takers - they try new things |
|
|
|
Scarcity produces what four economic problems? |
What's to be produced? How will it be produced? When will it be produced? Who's going to get it? |
|
|
|
How to resolve scarcity produces economic problems? |
1)The market mechanism 2)Government dictates what,how,when,and for whom 3)Violence - let people get weapons and physically fight it out |
|
|
|
Give the definition of Rational self interest |
People will make the choices that, at the time and with the information they have at their disposal, will give then the greatest amount of satisfaction for the effort or money they spend |
|
|
|
Fallacy of composition is? |
The False assumption that what is best for one would be best for the group as a whole |
|
|
|
what is microeconomics? |
the study of individual economic units-the behavior of buyers, sellers, product markets, resource markets |
|
|
|
what is macroeconomics? |
the study of aggregates in the economy |
|
|
|
What is the difference between normative economic statements and Positive economic statements |
normative deals with "what ought to be" positive deals with "what is" |
|
|
|
What is mutually beneficial voluntary exchange |
|
|
|
|
Name the first Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economics and give its definition |
1) Understanding the Notion of opportunity Cost The opportunity cost of a thing is the highest valued forgone "opportunity" |
|
|
|
Name the Second Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economics and give its definition |
2) Recognizing that people Economize to economize means to get the mose for the least |
|
|
|
Name the third Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economics and give its definition |
3) The basic POSTULATE of economics is that people respond to incentives |
|
|
|
Name the fourth Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economics and give its definition |
4) Realize that decisions are made at the "margin" In economics, marginal means incremental or change-in or additional |
|
|
|
Name the fifth Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economics |
5) Realize that information and time are essential in making choices, but both are expensive |
|
|
|
Name the sixth Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economicsand give its definition |
The failure to consider secondary effects is the most common source of economic error. Secondary effects are often thought of as “unintended consequences.” |
|
|
|
Name the seventh Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economicsand give its definition |
Q: What is the value of a fresh tomato? It depends! It depends on who you are asking.
|
|
|
|
Name the eighth Guidepost to Objective thinking in Economicsand give its definition |
A good economic model is one that predicts well |
|
|
|
What are the two main sources of a higher standard of living? |
Productivity and economic freedom |
|
|
|
What are some of the things that have led to greater productivity? |
Technology is a main source of increased productivity. Investment in human and physical capital is another. |
|
|
|
What is the ultimate source of inflation? |
Circulating too much money |
|
|
|
What is the fundamental economic problem? |
Resources are scarce |
|
|
|
What are the four resource categories? |
1. Natural resources
2. Labor 3. Capital a) Physical capital b) Human capital 4. Entrepreneurial activities |
|
|
|
What does it mean for a thing to be scarce? |
At a zero price more is wanted than is available, thus there is a positive price |
|
|
|
What is the big trade-off in economics? |
Efficiency versus equality The cost of forcing outcomes to be more equal is that we get less from the resources we use |
|
|
|
What is opportunity costs? |
Whatever must be given up or foregone when a decision is made or a thing is obtained.
The cost of something is what you give up to get it. We’re not just talking about money. There is no such thing as a free lunch! There is an opportunity cost associated with every action/decision. |
|
|
|
What is a market economy? |
A market economy is an economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many firms and many households as they interact in markets for goods and services.
It’s really a system where the dollar votes of consumers drives production. |
|
|
|
What is the invisible hand? |
When people (households and firms) do what is best for themselves, they generally end up doing what is best for society, as if guided by market forces—or an “invisible hand.” The invisible hand will only work if the government protects/enforces property rights.
|
|
|
|
What do you think is the most important property right of all? |
In my view, the most important property right of all is self ownership. “I own myself.” |
|
|
|
What are the four basic participants in the economy. |
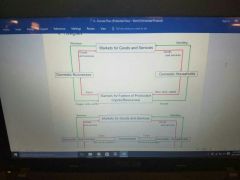
1. Domestic households 2. Domestic businesses 3. The government 4. Foreigners |
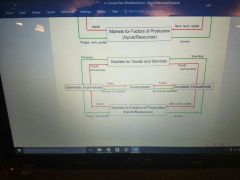
|
|
|
What is a production possibility curve and what does it show? |
reflects all combinations of two goods that can be produced given the availability and quality of resources and given the level of technology.
|
|
|
|
What do all of the combinations on a produciton possibility curve represent? |
1. full employment of available resources 2. full utilization of existing technology |
|
|
|
What are all the combinations inside a PPC represent |
1. unemployment 2. underemployment 3. underutilization of existing technology 4. some combination of all three |
|
|
|
What happens to the opportunity cost of beans as more beans are produced? |
The opportunity cost of beans increases.That is, as more beans are produced, an increasing number of CDs must be foregone. |
|
|
|
What then happens to the opportunity cost of CDs as more CDs are produced? |
The opportunity cost of CDs increases. That is, as more CDs are produced, an increasing amount of beans must be foregone. |
|
|
|
What is it that explains increasing opportunity costs? |
resources and technology |
|
|
|
What are some things that would increase a nation’s production possibilities (shift the curve outward)? |
1. An increase in the availability of resources. 2. Technological advancement. 3. An improvement in the rules under which the economy functions can increase output. |
|
|
|
Why do individuals trade with each other? |
Trade among individuals results in gains that are not possible without trade. Trade, in and of itself, creates value. When individuals engage in voluntary exchange with one another, both parties are made better off, regardless of where they reside. By directing goods and resources to those who value them most, trade creates value and increases the wealth created by society’s resources. |
|

