![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Short run |
Period in which at least 1 F.O.P. is fixed |
|
|
Long run |
Period in which all F.O.Ps are variable |
|
|
Production takes place in |
Short run |
|
|
Planning takes place in |
Long run |
|
|
TP |
Total product - output with fixed/variable factors in time period |
|
|
AP |
Average product = TP/V - production per variable F.O.P. unit |
|
|
MP |
Marginal Product = change in TP/change in variable factor |
|
|
Diminishing marginal returns |
As extra variable F.O.P. factors are added, MP eventually diminishes |
|
|
Diminishing average returns |
As extra variable F.O.P. factors are added, AP eventually diminishes |
|
|
Economic Cost |
Explicit costs (F.O.P. purchased for production) + Implicit cost (opportunity cost of using F.O.P. in production) |
|
|
Short Run Costs |
TC = TFC + TVC |
|
|
AFC and relation to q |
AFC = TFC/q Falls with increasing q as it is constant in short run |
|
|
AVC and relation to q |
AVC = TVC/q Falls to a point, then rises As MP decreases, cost per unit rises |
|
|
ATC and relation to q |
ATC = ATC + AVC ATC = TC/q Falls and eventually rises |
|
|
MC and relation to q |
MC = change in TC/change in q Falls and eventually rises Hypothesis of eventually finishing marginal returns - marginal returns (change in q) eventually falls |
|
|
Profit (accounting and economic) |
Accounting - Profit = TR-TC Economic - Profit = TR-economic cost |
|
|
Normal profit |
TR = TC (economic) 0 economic profit |
|
|
Abnormal profit |
TR > TC (economic) Economic profit |
|
|
Loss |
TR < TC (economic) Negative economic profit |
|
|
Shut down price |
Where TR < TVC Or P < AVC As ceasing production incurs variable costs, when revenue is less, loss is minimised by not producing in short run |
|
|
Break even price |
Where P = ATC Or TR = TC (Economic costs) |
|
|
Profit maximising output |
Where MR > MC |
|
|
Assumptions of Perfect Competition |
1. Large number of firms 2. Small firms can't effect industry 3. Homogenous goods (all the same) 4. No barriers to entry/exit 5. Perfect knowledge of producers/consumers (prices, costs, etc.) |
|
|
Perfect competition supply/demand curves |
Industry - normal Firms - perfectly elastic at industry price (price takers) |
|
|
Quantity in perfect competition |
Where MC curve cuts MR (demand curve) |
|
|
PC Short run abnormal profit |
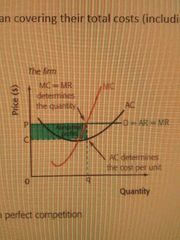
|
|
|
PC short run losses |
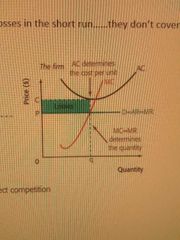
|
|
|
PC short to Long Run - profits |
More firms enter industry (supply curve shifts out) Equilibrium price decreases MR/D increases till MR = AC |
|
|
PC short to Long Run - losses |
Firms exit market Supply curve shift in, industry price increases till MR = AC |
|
|
Productive efficiency |
Resources used is least costly manner Where P=minimum ATC PC long run equilibrium - prices forced down to minimum ATC Firms not productively efficient - lower ATC (improve efficiency) - experience loss and shut down |
|
|
Allocative efficiency |
Where P (value to consumers) = MC (cost to producers) Best allocation of resources for producers and consumers In PC - allocative equilibrium achieved through profit maximization |
|
|
Monopoly Characteristics |
1. Single seller 2. No close substitutes 3. Price maker 4. High barriers to entry |
|
|
Sources of monopoly |
1. Economies of scale - Bulk buying - Specialisation - Financial economies 2. Natural monopolies - large fixed costs 3. Legal barriers - parents 4. Brand loyalty 5. Anti competitive behaviour - Large firm sustains short period losses in price war |
|
|
Monopoly profit maximisation |
MR=MC for quantity, price at AR Can control price or quantity |
|
|
Monopoly abnormal profits |
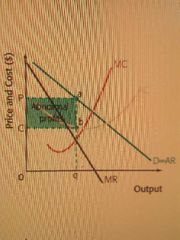
|
|
|
Monopoly losses |
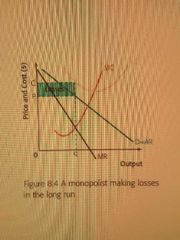
|
|
|
Oligpoply |
Dominated by a few firms (can be other smaller) |
|
|
Oligopoly assumptions |
1. Few large firms 2. Barriers to entry 3. Differentiation can vary 4. Interdependence (reaction to other firms) 5. Strategic thinking (collusion vs. competition) |
|
|
Collusive oligopoly acts like |
Monopoly |
|
|
Non price competiton |
- undercutting generally lowers all profits - brand names, packaging, sponsorship etc increase brand loyalty |
|
|
Disceconomies of scale |
Control/communication problems, alienation/loss of id |
|
|
Natural monopoly curve |
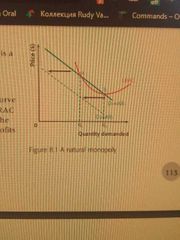
|

