![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the three economic agents? |
Consumers, Producers, government |
|
|
|
What is the economic problem? |
The inability to meet everyone’s needs and what’s |
|
|
|
What are the three key choices that economists make? |
What to produce? How to produce? For whom are we producing? |
|
|
|
Difference between positive and normative statements |
Positive Statements are objective and they can be tested or rejected by referring to evidence or facts, while normative statements express a value or judgement about what ought to be. They are subjective. |
|
|
|
What does Ceteris Paribus mean? |
All other things being equal |
|
|
|
What assumptions do economic models make about humans? |
People are rational and self interested |
|
|
|
What is opportunity cost? |
The benefit lost from the next best alternative foregone. E.g When choosing economics a level over maths a level, maths a level is the opportunity cost |
|
|
|
What are economic goods and free goods |
Economic Goods are resources that are scarce. Free Goods have no opportunity cost. E.g. Breathing air |
|
|
|
What are the factors of production? (Check Hints for acronyms) |
Capital Enterprise Land Labour |
CELL |
|
|
Define Capital |
Goods used to produce consumer goods |
|
|
|
What the Production Possibility Frontier? (Is it similar to anything from Macroeconomics?) |
Represents the maximum productive potential of an economy. Similar to Long Run Aggregate Supply. |
|
|
|
What two types of good will the PPF show? |
Capital Goods(y-axis) and Consumer Goods (x-axis). |
|
|
|
Why is the PPF curved? |
The opportunity cost varies as not all factors of production will be equally suited to both capital goods and consumer goods |
|
|
|
What else can PPF show? |
The opportunity cost of moving from different pints on the curve. It shows what you lose in terms of either consumer or capitalist goods. |
|
|
|
What causes a shift in the PPF? |
The quantity and quality of the factors of production. |
|
|
|
What could be possible reasons for an outward shift in the PPF? (To the right) (5 Reasons) |
Government Investment (Capital) Deregulation (Enterprise) Recovered Land (Land) Immigration (Labour) Training programs (Labour) |
|
|
|
What could be possible reasons for an inward shift in the PPF? (To the left) (6 possible) |
Strict Labour Laws Epidemic Natural Disaster War Soil Erosion Emigration/Brain Drain |
|
|
|
When does a market exist? |
When there are buyers and sellers of a good. |
|
|
|
What is assumed in neoclassical economics in relation to market functions? |
It is assumed that consumers, firms and the government make rational decisions to try and maximise utility, maximise profits and maximise social welfare respectively. |
|
|
|
What are the four major functions of money? |
Medium of Exchange (avoid bartering life is more efficient) Unit of Account (comparing the value of things) Means of deferred payment (taking out loans) Store of a value (you can save it) |
|
|
|
Define Demand |
Demand is the quantity of goods or services that will be bought at any given price over a period of time |
|
|
|
What is the law of demand? What three things is it dependent on? |
Law of demand is the inverse relationship between quantity demanded and price. i.e. demand curve is downsloping Exist due to: 1. The Substitution Effect (rising price of a good causes consumers to buy cheaper alternative) 2. The Income Effect (rising price of a good means that consumers won’t be able to afford it) 3. DDiminishing Marginal Utility |
|
|
|
What are movements along demand/supply curves referred to as? |
Contractions (when output is decreasing) Expansions (when output is increasing)! |
|
|
|
When do contractions and extensions take place? |
Only when price changes. Other factors cause a shift left or right. |
|
|
|
What causes a shift in the demand curve? |
Population Advertising Substitute Goods (Their Price) Income (except for inferior goods) Fashion Trends Interest Rates Complimentary Goods (Their Price) |
PASIFIC |
|
|
Define Diminishing Marginal Utility |
as more units are consumed, the product provides less satisfaction) |
|
|
|
Define Consumer Surplus |

The difference between between how much buyers are prepared to pay for a good and what they actually pay |
Demand Curve and Y-Axis (C is near D in the alphabet) |
|
|
How does the signalling function shown to be at work on graph? |
Supply Shifts Out or In as Producers enter or exit the market due to a higher or lower price respectively. Demand shifts out or in as consumers leave or enter the market due to higher or lower prices respective. Eventually causes price to decrease. |
|
|
|
How do prices change with excess supply and excess demand? |
Prices are reduced with excess supply but rise with excess demand |
|
|
|
Define Producer Surplus |
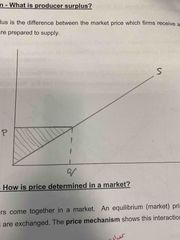
The difference between the market price which firms receive and the price at which they are prepared to supply |
Made with the supply curve and the y-axis. (P is near S in the alphabet) |
|
|
Define the Price Mechanism |

Price mechanism allocates resources in a free market. Price is determined by how demand and supply interact with each other. |
|
|
|
Define Supply |
The quantity of goods that sellers are prepared to sell at any given price over a period of time. |
|
|
|
What causes a shift in the supply curve? |
Policies and Regulations Indirect Taxes Number of Firms Technology Subsidies Weather Costs of Production |
PINTS WC |
|
|
Define Producer Surplus |
The difference between the market price which firms receive and the price at which they are prepared to supply |
Made with the supply curve and the y-axis. (P is near S in the alphabet) |
|
|
Define the Price Mechanism |
Price mechanism allocates resources in a free market. Price is determined by how demand and supply interact with each other. |
|
|
|
What are the two ways that the Price mechanism adjusts to change in the short term? |
Incentives and Rationing |
|
|
|
How does the signalling function shown to be at work on graph? |

Supply Shifts Out or In as Producers enter or exit the market due to a higher or lower price respectively. Demand shifts out or in as consumers leave or enter the market due to higher or lower prices respective. Eventually causes price to decrease. |
|
|
|
What is the metaphor used to describe how the price mechanism is able to set price? Who came up with it? |
Adam Smith described the ‘invisible hand’ of the market, |
|
|
|
How does an increase in demand affect consumer and producer surplus? |

Increases both of them |
|
|
|
How does a decrease in supply affect consumer and producer surplus? |

It decreases both of them |
|
|
|
Explain what “Incentives” means in regards to the effect of a price change. Give an example |
Changes in price incentivise existing producers to act different. E.g. higher oil prices encourage existing producers to increase output. (Expansion along supply curve) |
|
|
|
Explain how rationing works. Use an example |
When there is insufficient supply to meet demand a change in price will ration the resource by consumers’ willingness to pay. E.g. Rare football stickers can be auctioned on eBay |
|

