![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the four functions of a market? |
Signal (prices provide a signal for consumers)
Incentive (prices create an incentive to alter economic behavior)
Rationing (higher prices get rid of excess demand)
Resource allocation (FoP are collected to make profitable products and services) |
How does pricing affect consumers and producers thinking |
|
|
What are two challenges to traditional economic theory about utility? |
-People don't always maximise utility (charity, acts of kindness) -People don't always act rationally - social norms |
What do people do that isn't perfectly optimising their money value for themselves |
|
|
What is bounded rationality? |
People make rational decisions but are restrained by imperfect information, limited mental processing ability and time constraint |
Uhhhhhh can I get more time |
|
|
What are some examples of nudges by government? |
Restricting choices Framing Opt out instead of Opt in Mandated choices (not letting people go for a default option) |
Arj and Owen on a mandate |
|
|
What are the three benefits of higher productivity? |
⬇️Unit Labour cost (more production from same factors)
⬆️profit = ⬆️Wages
⬇️ Production Costs = ⬇️prices, ⬆️competitiveness |
Results of lower costs |
|
|
What are the advantages to specialisation of labour? |
Specialists have higher productivity, production cheaper per good
Workers paid more if on piece rate or wages increased to reflect increased productivity |
Results of higher production |
|
|
What are the disadvantages to specialisation of labour? |
Workers may get bored and demotivated
If one part of the system breaks down, the whole production stops
Workers vulnerable to automation |
What happened to you at tesco |
|
|
How do you calculate marginal cost? |
%change in Total Cost / %change in Quantity |
Percentages |
|
|
What are some examples of economies of scale reducing costs? |
Spreading research and development costs
Reduction in the proportion of managers to workers
Bulk buying and bulk advertising
Large firms can get lower interest loans |
Don't forget the interest |
|
|
How can diseconomies of scale occur? |
Too much bureaucracy
Lack of effective communication
Demotivated workers |
Tesco hello |
|
|
What is the minimum efficient scale and what does it look like? |
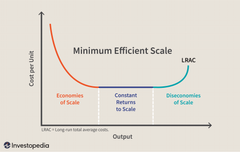
It shows the most efficient production method, where the optimum output curve is the lowest possible LRAC |
Big curve |
|
|
What are some examples of barriers to entry? |
High setup costs High sunk costs Economies of scale creating a significant advantage Predatory pricing |
Grrrr what am I |
|
|
What is allocative efficiency? |
When the production costs of a good equal the benefit (price paid) a customer receives from it |
Value for money |
|
|
What are the benefits and drawbacks of a monopoly? |
Large monopolies can benefit from economies of scale
However a large monopoly can choose to provide an inferior service creating a loss in consumer surplus |
What do big boys do when they get big |
|
|
What does the kinked demand curve look like? Why is it shaped like that? |
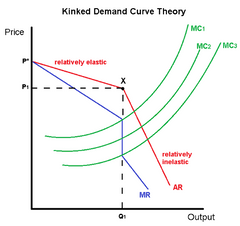
The change in demand when lowering price is inelastic, the change in demand when raising the price is elastic.
|
Fixed price |
|
|
What factors affect the competitiveness of an oligopoly? |
Barriers to entry
Size of the market : Bigger markets attract more attention from regulatory firms
Product differentiation : Low product differentiation makes collusion easier |
|
|
|
What is price discrimination? |
When firms charge different prices for an identical product. |
|
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of price discrimination? |
Advantages - Higher profits can cross subsidise less profitable ventures
Increases allocative efficiency
Disadvantages - Loss in consumer surplus Administration costs Can fund predatory pricing elsewhere |
How can firms use higher profits |
|
|
What are the benefits of a contestable market? |
Forces firms to be allocatively and productively efficient. |
|
|
|
How can markets be made more contestable? |
Privatisation Deregulation |
|
|
|
What is the principal agent problem? |
When shareholders have different objectives to company directors. |
Upper management |
|
|
What causes a shift in the curve of demand for labour from firms? |
- Improved productivity - Increased product price - Increased profit per product |
What would make it more profitable to increase production and as a result hire more people? |
|
|
The supply of labour is shifted by |
- A fall or rise in income (inverse effect on supply) - Change in population size - Change in workers expectation of the future |
Factors affecting labour and their willingness to work |
|
|
What is a monopsony? |
When there is a single buyer in a market but multiple sellers. |
Opposite of a monopoly |
|
|
What does a monopsonist market look like as a graph? |
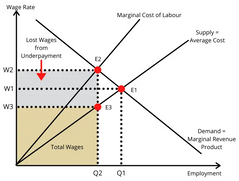
|
It's about labour markets |
|
|
How does a rise in the wages affect employment in monopsonist and perfectly competitive markets? |
Monopsonist- Raises employment as the number of workers applying increases
Perfectly Competitive - Leads to a fall in employment as it creates disequilibrium. |
Night and Day difference |
|
|
What factors affect the distribution of income? |
-Ownership of factors of production -Income from sources that aren't employment(interest, investments) -Wage/Salary differentials (salary gap size) -Globalisation - unskilled poorer, rich richer |
Don't forget Globalisation |
|
|
What factors affect the distribution of wealth? |
-Capital gains (investments appreciating) -Inheritance -Wealth taxes (wealth is usually taxed less strictly than income) |
How do the rich stay rich |
|
|
What is the gini coefficient and what does it mean? |
It shows income inequality
LOWER VALUE = LOWER INEQUALITY (the area in the distance from a straight line, straight line is full equality) |
Don't forget about what the number correlates to |
|
|
What are the negative effects of poverty? |
-Children stuck in a cycle of poverty -Worse health means they are worse at school and work -Children grow up in bad communities keeping them stuck |
Symptoms of a lack of social mobility |
|
|
What is fiscal drag? |
When high inflation pushes people up tax brackets |
Inflation affecting poor people |
|
|
What is the unemployment trap? |
Welfare pays more than employment so there is a disincentive to work. |
Damn immigrants |
|
|
What is the earnings trap? |
If you increase your income by working longer hours, you move up brackets and end up earning less overall. |
Already in a job |
|
|
What are the negative side effects of government cracking down on wealth and income inequalities? |
High taxes reduce incentives for hard work Can create earnings and unemployment trap if mismanaged |
|
|
|
What is market failure? |
Missing markets Over/Under consumption and production of a good |
Two types |
|
|
What is excludability? |
You can stop people from consuming a good |
Get out |
|
|
What is rivalry in consumption? |
By consuming a good, you can stop others from consuming it |
TriHard |
|
|
What is a quasi-public good? |
A good that exhibits some, but not all, of the characteristics of a public good |
|
|
|
What are three policies that the government can take to counter market failure from private businesses? |
Regulation (normal externality diagram) Price floors Price ceilings |
|

