![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the Solow Growth Model show?
|
How saving, population growth, and technological progress affect the level of output and growth overtime.
|
|
|
What does the Solow Growth Model assume about the production function?
|
That there is constant returns to scale.
|
|
|
Per worker terms in the Solow Growth Model are denoted by what?
|
Lowercase letters.
so, y = Y/L - output per worker k = K/L - capital per worker |
|
|
Slope of the production function in the Solow Growth Model is called what and is denoted how?
|
Marginal Product of Capital (MPK):
MPK = f(k+1) - f(k) **same as the MPL back in the early chapters** |
|
|
output per worker (y) is separated into what two portions?
|
Consumption per worker (c) and investment per worker (i).
|
|
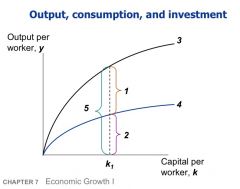
What are the labeled areas?
|
1. consumption per worker
2. investment per worker 3. Output, f(k) 4. Investment, sf(k) 5. output per worker |
|
|
Which two forces influence capital stock?
|
Investment (expenditure on new plant and equipment)
Depreciation (wearing out of old capital) |
|
|
investment per worker is expressed as
|
i = sy
where i = investment per worker s = savings per worker y = output per worker |
|
|
Why is investment expressed as sf(k)?
|
because f(k) substitutes in for y and shows that workers invest the portion of their output that they save.
|
|
|
δ represents what?
|
The certain fraction of capital stock that wears out every year.
Depreciation rate. |
|
|
How do you express the impact of investment and depreciation on capital stock?
|
Δk = i - δk, but since i = sf(k), the equation becomes:
Δk = sf(k) - δk |
|
|
δk is ____________ per ______
|
depreciation; worker
|
|
|
k* is the _____-_____ level of _______ ___ ______
|
steady-state
capital per worker |
|
|
k* is where which two things intersect?
|
The depreciation per worker function (δk) and investment per worker (sf(k)).
so the steady-state capital per worker is a state where depreciation = investment |
|
|
y = sqrt(k) is what?
|
the per worker production function
(this is where Ashley wanted to 'memorize the end of the story.') |
|
|
Steady-state k* is when investment per worker equals depreciation per worker, so how else is steady-state k* recognized?
|
when Δk = 0.
|
|
|
According to the Solow Growth Model, the ______ ____ is a key determinant of the ______-_____ _______ _____.
|
saving rate; steady-state capital stock.
|
|
|
If savings rates are high, capital stock grows. True or false.
|
True. Output also increases.
|
|
|
What is the golden rule of capital?
|
k*gold
It is the steady-state value of k that maximizes consumption. Can be found by drawing a tangent line on the steady-state output curve f(k*) |
|
|
How do you find the steady-state consumption per worker?
|
c* = f(k*) - δk*
steady-state consumption is what is left after paying steady-state depreciation on steady-state output. |
|
|
Below the Golden Rule point, what happens if steady-state capital is raised?
|
steady-state consumption increases.
|
|
|
Above the Golden Rule point, what happens if steady-sate capital is raised?
|
steady-state consumption decreases.
|
|
|
Golden Rule is expressed as k*gold but also as:
|
MPK = δ
|
|
|
When the economy begins above the Golden Rule state, does reaching the Golden Rule state produce higher consumption?
|
Yes. At all times.
|
|
|
The basic Solow Growth Model shoes that what by itself cannot explain sustained economic growth?
|
Capital Accumulation
|
|
|
What are two more sources of growth in the Solow Growth Model (outside of capital accumulation)?
|
Technology advances
Population growth |
|
|
True or False: in the Solow Growth Model, population and labor force are fixed.
|
False.
Population and Labor Growth grow at a constant rate (n) each year in the Solow Growth Model. |
|
|
What is the equation for change in capital stock per worker when one factors in population growth?
|
Δk = i - (δ + n)k.
Substitute sf(k) for i. |
|
|
How does population growth impact the steady-state of capital stock?
|
It reduces it because it shifts the depreciation/population growth (δ + n)k up without moving the per worker investment.
|

