![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A planned economy |
Have a lot of government interference - they decide what, when, how and who will produce all all g/s. They also decide the price and wether they will export/import Closed to outsiders and very few g/s available E.g North Korea |
|
|
A market economy |
Very little government interference Ressources are sold freely to producers who then supply whatever g/s the consumers want E.g USA |
|
|
A mixed economy |
Has both public and private g/s available. Government will regulate the market but there are lots of freedoms to encourage businesses E.G. UK, France |
|
|
Sustainability |
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs 3 main pillars: economy, environment and social. |
|
|
Demand |
A demand is a want that is backed by the ability to pay for that want |
|
|
Drawing demand curves |
Price on verticale axis and quantities demanded on horizontal axis with d or D on either end (D for lots of people d for 1) Higher prices lead to lower quantities being brought and vice versa |
|
|
Supply |
Is the quantity that a supplier is willing to provide at different prices. Typically suppliers will supply more at higher prices than lower prices as it enables producers to cover costs and make increasing profits |
|
|
Individual and market supply |

To find out the market supply curve we need to add the individual supply curves (you DONT divide by number) |
|
|
Change of price on a supply or demand curve |
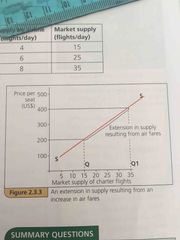
There will be an extension on the curve- shift along he curve and the whole curve will NOT shift |
|
|
What happens when Ceterus paribus is broken in a demand curve and why? |
An increase in demand will move the whole curve right. A decrease in demand will move whole demand curve left. Cause by a change in any factor apart from price of good- eg trend, change in price of substitutes and complementary goods, income, age distribution |
|
|
What is equilibrium price? |
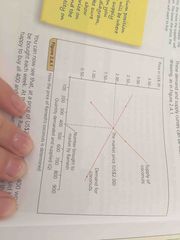
Means state of balance. Equilibrium price occurs when there is a balance between demand and supply: the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the amount that suppliers willing to provide. Marked on by Pe on price axis and Qe in quantity axis |
|
|
What is PED and how do you find it? |

PED is the price elasticity of demans and it measures the responsiveness of demand to price changes Is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded BY the percentage change in price- if answer >1 thank it is elastic, if answer=1 than it is unitary and if answer <1 than it is inelastic To find percentage change you divide the change by the original and x by 100 |
|
|
What is inelastic demand? |
Happens when good in addictive, a necessity, no substitute of small % of income so people will buy it anyway On a demand curve the line would be vertical |
|
|
Individual and market supply |
To find out the market supply curve we need to add the individual supply curves (you DONT divide by number) |
|
|
What is Price elasticity of supply and how do you can you calculate it? |
Price elasticity of supply is the extent to which supply alters in response to a change in price. It is measured by the formula |
|
|
What are the factors influencing price elasticity of supply |
The main factor influencing is time- as at a particular moment in time it may be impossible to increase supply Other factors are: the ease with which a product can be stored (if a product can be stored easily, supply will be more elastic, and if it can’t it will be more inelastic) The cost of increasing supply (the less cost it is to increase supply, the more elastic supply will be) |
|
|
What are the merits of the market system? |
-brings together buyers and sellers (this might be to trais in a traditional market or where buyers and sellers contact each other) -allocating ressources to goods in demand (the suppliers will increase supply of a good when there is lots of demand for it) -coordinating decision-making (fashion or advertisements persuade buyers and help them to decide but the decision is the buyers, sellers also make their own decisions about what to produce and sell based on what is selling) -providing plenty of choice -keeping prices down (rival businesses will seek to beat competition but providing lower prices than those offered by rivals) |
|
|
What is market failure and what are some examples of it? |
Markets are said to fail when they are inefficient. This would arise if: -they fail to produce goods that consumers want -they fail to produce the quantities of goods required -they fail to produce goods at acceptably low prices |
|
|
What is a public good? |
A good that must be provided to the whole of a community or not at all. Eg a police force. Are provided by the government who normally find them through taxes as people would be reluctant to pay for them there selves as someone could use it who hasn’t paid. |
|
|
What is a merit good? |
A merit good is one with substantial benefits for society as a whole rather than being restricted to individuals- for example inoculation against a particular disease. Must require government provision. |
|
|
What is private costs and benefits |
This is the financial advantages and disadvantages of a business |
|
|
What is externalities |
Is the result of economic activity ,such as building a factory, that is not taken into account by the individuals who make a decisions. In other words it is the external effect of a decision. |
|
|
What are social costs and benefits? |
Social benefits include the private and other posit benefits from a particular business activity or decisions. Social costs are the private costs of the company plus all other costs resulting to this. |
|
|
Change of price on a supply or demand curve |
There will be an extension on the curve- shift along he curve and the whole curve will NOT shift |
|
|
What happens when Cerberus paribus is broken in a demand curve and why? |
An increase in demand will move the whole curve right. A decrease in demand will move whole demand curve left. Cause by a change in any factor apart from price of good- eg trend, change in price of substitutes and complementary goods, income, age distribution |
|
|
What happens when ceterus paribus is broken on a supply curve and why? |
An increase in supply causes curve to shift to right. A decrease causes supply to shift to left. Can be caused by these: costs of production, changes in physical conditions (eg weather), the price of similar or related goods (if a factory makes cars and motorbikes and the price of motorbikes increases, car production will decrease), taxation and subsidies |
|
|
What is equilibrium price? |
Means state of balance. Equilibrium price occurs when there is a balance between demand and supply: the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the amount that suppliers willing to provide. Marked on by Pe on price axis and Qe in quantity axis |
|
|
What is PED and how do you find it? |
PED is the price elasticity of demans and it measures the responsiveness of demand to price changes Is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded BY the percentage change in price- if answer >1 thank it is elastic, if answer=1 than it is unitary and if answer <1 than it is inelastic To find percentage change you divide the change by the original and x by 100 |
|
|
What is inelastic demand? |
Happens when good in addictive, a necessity, no substitute of small % of income so people will buy it anyway On a completely inelastsic demand curve, the line would by verticle |
|
|
What is elastic demand? |
Is when a good it a luxury, many substitutes, large % of income or not brought often So is very price sensitive On a demand curve complete elasticity would be a horizontal line |
|
|
What is unitary demand |
When we will but the same % as the % decrease in price If % change in quantity demanded decreases by 20%/ % change of price is 20% =1 |
|
|
Total revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand |
INELASTIC GOODS: P decreases = TR decreases, P increases = TR increases ELASTIC GOODS: P decreases = TR increases, P increases = TR decreases Unitary goods: P increase of decreases = TR stays the same |
|
|
Individual and market supply |

To find out the market supply curve we need to add the individual supply curves (you DONT divide by number) |
|
|
Change of price on a supply or demand curve |
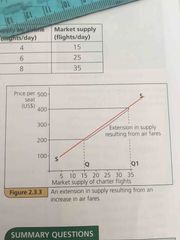
There will be an extension on the curve- shift along he curve and the whole curve will NOT shift |
|
|
What are the factors influencing price elasticity of supply |
The main factor influencing is time- as at a particular moment in time it may be impossible to increase supply Other factors are: the ease with which a product can be stored (if a product can be stored easily, supply will be more elastic, and if it can’t it will be more inelastic) The cost of increasing supply (the less cost it is to increase supply, the more elastic supply will be) |
|
|
What are the merits of the market system? |
-brings together buyers and sellers (this might be to trais in a traditional market or where buyers and sellers contact each other) -allocating ressources to goods in demand (the suppliers will increase supply of a good when there is lots of demand for it) -coordinating decision-making (fashion or advertisements persuade buyers and help them to decide but the decision is the buyers, sellers also make their own decisions about what to produce and sell based on what is selling) -providing plenty of choice -keeping prices down (rival businesses will seek to beat competition but providing lower prices than those offered by rivals) |
|
|
What is equilibrium price? |
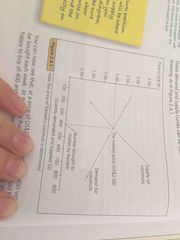
Means state of balance. Equilibrium price occurs when there is a balance between demand and supply: the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the amount that suppliers willing to provide. Marked on by Pe on price axis and Qe in quantity axis |
|
|
What is PED and how do you find it? |

PED is the price elasticity of demans and it measures the responsiveness of demand to price changes Is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded BY the percentage change in price- if answer >1 thank it is elastic, if answer=1 than it is unitary and if answer <1 than it is inelastic To find percentage change you divide the change by the original and x by 100 |
|
|
What is a merit good? |
A merit good is one with substantial benefits for society as a whole rather than being restricted to individuals- for example inoculation against a particular disease. Must require government provision. |
|
|
What is private costs and benefits |
This is the financial advantages and disadvantages of a business |
|
|
What is externalities |
Is the result of economic activity ,such as building a factory, that is not taken into account by the individuals who make a decisions. In other words it is the external effect of a decision. |
|
|
What are social costs and benefits? |
Social benefits include the private and other posit benefits from a particular business activity or decisions. Social costs are the private costs of the company plus all other costs resulting to this. |
|
|
What is Price elasticity of supply and how do you can you calculate it? |

Price elasticity of supply is the extent to which supply alters in response to a change in price. It is measured by the formula |
|
|
What happens when Cerberus paribus is broken in a demand curve and why? |
An increase in demand will move the whole curve right. A decrease in demand will move whole demand curve left. Cause by a change in any factor apart from price of good- eg trend, change in price of substitutes and complementary goods, income, age distribution |
|
|
What happens when ceterus paribus is broken on a supply curve and why? |
An increase in supply causes curve to shift to right. A decrease causes supply to shift to left. Can be caused by these: costs of production, changes in physical conditions (eg weather), the price of similar or related goods (if a factory makes cars and motorbikes and the price of motorbikes increases, car production will decrease), taxation and subsidies |
|
|
What is equilibrium price? |
Means state of balance. Equilibrium price occurs when there is a balance between demand and supply: the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the amount that suppliers willing to provide. Marked on by Pe on price axis and Qe in quantity axis |
|
|
What is PED and how do you find it? |
PED is the price elasticity of demans and it measures the responsiveness of demand to price changes Is calculated by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded BY the percentage change in price- if answer >1 thank it is elastic, if answer=1 than it is unitary and if answer <1 than it is inelastic To find percentage change you divide the change by the original and x by 100 |
|
|
What is inelastic demand? |
Happens when good in addictive, a necessity, no substitute of small % of income so people will buy it anyway On a completely inelastsic demand curve, the line would by verticle |
|
|
What is elastic demand? |
Is when a good it a luxury, many substitutes, large % of income or not brought often So is very price sensitive On a demand curve complete elasticity would be a horizontal line |
|
|
What is unitary demand |
When we will but the same % as the % decrease in price If % change in quantity demanded decreases by 20%/ % change of price is 20% =1 |
|
|
Total revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand |
INELASTIC GOODS: P decreases = TR decreases, P increases = TR increases ELASTIC GOODS: P decreases = TR increases, P increases = TR decreases Unitary goods: P increase of decreases = TR stays the same |

